Introduction
Velvet antler (VA) is known as the cartilaginous antler in a pre-calcified growth stage of deer species (e.g., elk and moose etc.). After surgical removal, the male deer or elk can re-produce their new antlers yearly (Li, 2012). Due to the fast rate of growth and differentiation, many components such as; amino acids, polypeptides, phospholipids and growth factors etc. are abundantly present in the antler tissue (Lai et al., 2007; Zhang et al., 2019). For over 2000 years, the VA has been used as a traditional Chinese medicine. Till now, a variety of medical, food supplement and health-enhancing products processed from the VAs with different forms (e.g., powder or extract and capsulated forms) are available on many markets (Gilbey and Perezgonzalez, 2012). Reports have shown that the VA-derived products exert a wide range of health benefits including: immune system improvement, energy and growth enhancement, anti-ageing and anti-inflammatory effects, blood pressure modulation and anti-cancer etc. (Gilbey and Perezgonzalez, 2012; Kawtikwar et al., 2010; Wu et al., 2013).
In Korea, the VA is considered as one of the most famous Korean traditional medicine in which deer (Cervus elaphus) and elk are the most commonly farmed animal species for the VA exploitation (Lee et al., 2007). However, due to the increasing demand and insufficient production in the country, a significant amount of the VAs must be imported from other countries such as Russia and New Zealand (Je et al., 2011). According to the Deer New Zealand Industry (2018), approximately 725 tons of deer VA were produced and about 200 tones were exported to health food companies in Korea. While, the Russian Velvet Antler (RVA) Industry annually produces approximately 80 tons of VA (Dalisova et al., 2019).
Flavor characteristics, rather than other attributes, are the most important sensory aspect of overall acceptability for food and beverage products (Matsuishi et al., 2004). Of which, the aroma flavor is created by a variety of volatile compounds which are formed from the precursors (e.g., amino acids [AAs], peptides, carbohydrates and lipids) present in the raw materials (e.g., meats or animal-derived materials) via the oxidation/degradation and Maillard reaction during heat processing (Macleod, 1994; Mottram, 1998). Till now, a significant number of studies have been conducted to identify the chemical constituents that contribute to the flavor characteristics of meat and meat products (Ba et al., 2013; Elmore et al., 2004; Machiels et al., 2003; Macleod, 1994; Mottram, 1998). Furthermore, researchers have found that the flavor characteristics of meat and meat products differ depending breeds (Matsuishi et al., 2004). Since, the VAs are rich in flavor precursors such as; AAs and especially lipids (Lai et al., 2007). Therefore, we hypothesized that VAs from different origins and breeds may differ in flavor precursors which subsequently affect the flavor characteristics of their final products such as extracts.
To date, some studies have been conducted to determine the antioxidant activity and chemical compositions in the New Zealand velvet antler (NZVA; Je et al., 2010) and RVA (Je et al., 2011), and bioactive compounds in Chinese VA extract (Zhang et al., 2019). However, it still remains unknown whether there are some differences existing in biological activity, chemical composition, flavor and bioactive compounds between the Korean and the imported VA products. To understand the uses of VA in its entire context, the determination of chemical composition and identification of bioactive compounds are necessary. Thus, the main objective of this study was to compare the antioxidant properties, chemical composition, flavor and bioactive compounds between the extract of Korean velvet antler (KVA) and those derived from the Russian and New Zealand VAs.
Materials and Methods
The commercial velvet antlers (VA) including: KVA and RVA both obtained from male elks (Cervus canadensis), and NZVA obtained from male red deer (Cervus elaphus) were purchased from a local supplier (Seoul, Korea) (Fig. 1). All the VA types contain upper and tip sections in the form of dry slices and each the VA type was collected from 12 animals. The average moisture content of the dry VA slices was 7.0%, 7.5%, and 8.02% for the KVA, RVA, and NZVA, respectively. Reagents used including: deionized water, acetonitrile (ACN), formic acid and methanol (mass spectrometry grade), Trolox, 2,2-diphenyl 1 picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) and 2,2’-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS) etc. were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA).
Prior to use, the VAs (n=24 per each type) were sampled for the microbiological analysis. Briefly, each sample (10 g) was taken and added with 90 mL of saline solution in sterile plastic pouches. The samples were then homogenized using a Bagmixer stomacher (Interscience, Saint Nom, France) for 1 min. Thereafter, the homogenized samples were serially diluted with the saline solution and used for total aerobic plate count (APC) and mold determination. For enumeration, 1 mL of the diluted sample was spread on the APC Petrifilm and Mold and Yeast Petrifilm (3M Healthcare, St. Paul, MN, USA) and incubated for 48 h at 37°C. Colonies appeared on the plates were enumerated and calculated as Log10 colony-forming unit per gram sample (CFU/g). Each sample was determined in triplicate.
Prior to the extraction, the VAs were ground into powder form. All the VAEs were prepared under identical conditions as follows: for each kind of VA, six extraction batches (approximately 750 g each) was extracted with 6,000 mL of distilled water at 95°C for 20 h in an electrical extractor (Gyeongseo Machinery, Seoul, Korea). When the extraction process was completed, it was filtered through a cloth strainer. The solids content in the VAEs were also determined using a digital measuring device (model: ATAGO PAL-2, Seoul, Korea). Finally, all the three VAEs contained approximately 12.51% solids (average extraction yield: around 2.1 kg per batch) were considered as the original extracts. For the analysis of flavor compounds, about 10 mL of the original VAE in each the extraction batch was taken without further treatment (to avoid the loss of compounds). The rests of the VAEs were then concentrated in a freezing-drier to a dry powder form and then used for analysis of antioxidant assays, AAs and bioactive compounds.
The DPPH test was applied to determine the antioxidant activity of the VAEs. Prior to use, the VAEs were diluted with distilled water to various concentrations (0, 2, 4, 6, 12, and 16 mg/mL). The DPPH test was carried out following the method of Zhao et al. (2010) with suitable modifications. Briefly, 1.9 mL of 0.5 mM DPPH in 95% ethanol was mixed with 0.1 mL of each diluted extract type (at different concentrations). The mixture was shaken vigorously and incubated at room temperature for 30 min in the dark. The absorbance was measured at wavelength of 517 nm using a spectrophotometer. The inhibition of DPPH radicals was calculated as follows:
Where, Ablank=Absorbance of the control (without sample) solution; Atest: Absorbance of VAE.
DPPH radicals scavenging activity of the VAEs was then calculated and expressed as the half maximum inhibitory concentration (IC50) value (mg VAE/mL).
The ABTS assay was done using the method of Re et al. (1999) with suitable modifications. Briefly, ABTS·+ cation radical was produced by the reaction between 2 mM ABTS in water and 2.45 mM potassium persulfate (1:1 ratio). The reaction mixture was kept in the dark at room temperature for 12-16 h before using. The ABTS· radical solution was then diluted with 95% ethanol to obtain an absorbance of 0.730 unit at 734 nm using a spectrophotometer. Then 0.1 mL of VAE at different concentrations (as mentioned in the DPPH assay) was mixed with 1.9 mL of ABTS· radical solution. After incubating at room temperature for 10 min in the dark, the absorbance was measured at the wavelength of 734 nm using a spectrophotometer. The inhibition of ABTS radicals was calculated as follows:
Where, Ablank=absorbance of the control (without sample) solution; Atest: absorbance of VAE. The ABTS radicals scavenging activity of the VAEs was then calculated and expressed as the half maximum inhibitory concentration (IC50) value (mg VAE/mL).
For the determination of minerals, crude fat and protein contents, the VAs were pulverized into an 80 mesh size in an herbal medicine manufacturing grinder (Hwajin Biotech, Korea). The mineral contents were determined according the method of Matilainen and Tummavuori (1996) with suitable modifications. Briefly, VAE (1 g each) with 7 mL nitric acid in Teflon vessel was kept for 12 h at room temperature. The sample solution was heated at 180°C for 50 min and then cooled at room temperature. The minerals were analyzed using an atomic emission spectrophotometer ICP-OES (iCAP 7400 Duo, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). For the detection, different wavelengths such as Na at 588.9 nm, Fe at 248.3 nm, Mn at 279.5 nm, Zn at 213.9 nm etc. were set for each the mineral. For qualification, mineral standards at different concentrations were used and run under the same conditions, and the final concentration of each mineral in the VAs was calculated using its standard calibration curve.
For the crude fat and protein contents, which were determined following the procedures as described by Jeon et al. (2010) and the results were expressed as mg/100 g of VA.
The AA content in the VAEs was determined using the procedure of Qu et al. (2002). Briefly, each sample (2.5 g, in powder form) was homogenized in 5 mL distilled water. After filtering through a 0.45 μm filter membrane (Merk Millipore, Carrigtwohill, Cork, Ireland), the filtrates were used for analysis of AAs. The AAs were determined using an ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC, Waters, Milford, USA) connected to an Intrada AA column: 2 ×50 mm, 3μm (Imtaka, Uphur St, Suite A, Portland). The chromatographic separation was carried out using solvent A (ACN: 100 mM ammonium formate, 20:80 v/v) and B (ACN: tetrahydrofuran: ammonium formate: formic acid, 9:75:16:0.3 v/v). The separation conditions set were: 100% B for 3 min, 83% B for 3.5 min, and with 100% A for 3.5 min then maintain 100% B for 7 min and re-equilibrated before the next sample injections. The AAs were identified based on the retention time of the standard AA mixture, and individual AA values were expressed as μmol/g sample.
The extraction of flavor compounds in the VAEs was carried out using a solid phase micro-extraction (SPME) technique according to the methods of Ba et al. (2010) and Murat et al. (2012). Thereafter, the volatiles were determined using a gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) system under conditions as described by Ba et al. (2010). Briefly, 1.0 mL of original VAE was placed into a 20-mL headspace vial and 1.0 μL of internal standard (2-methyl-3-heptanone, 816 mg /mL in methanol) was also added. The vial was then tightly capped with PTFE-faced silicone septum for extraction. The extraction, absorption and desorption of the flavor compounds were carried out by using a SPME sample preparation instrument equipped with a carboxen–polydimethylsiloxane (75 μm) fiber (Supelco, Bellefonte, PA, USA) connected to Gas Chromatography (Model: 7890B GC) with Mass Spectrophotometry (Model: 5977B MSD, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The extraction was carried out at 60°C for 60 min and the fiber containing volatiles were then desorbed at 250°C at the injection port for 5 min with a split flow of 10 mL/min. The separation of volatiles was carried out on a capillary column (30 m×0.25 mm i.d.×0.25 μm film thickness) at a constant flow rate of 1 mL/min. The oven temperature held at 40°C for 5 min, then increased at rate of 8°C/min to 250°C and held at this temperature for further 5 min. The flavor compounds were identified by either comparing their mass spectra with those already present in the mass spectral libraries (Agilent Technologies) or by comparing their retention times with those of external standards. The identified compounds were quantified by comparison of their peak areas with that of the internal standard.
Prior to use, all the VAEs (1 g each) were dissolved in distilled water and then filtered through the 0.45 μm filter membrane (Merck Millipore). An ultra-performance liquid chromatography- tandem mass spectroscopy (UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS, Xevo TQ-5, Waters, Milford, MA, USA) was used and the conditions for separation and detection of the bioactive compounds in the VAEs were followed the protocol of Zhang et al. (2019) with suitable modifications. The chromatographic separation was carried out on an ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 column (100 mm×2.1 mm, 1.8 μm, Waters) at temperature of 40°C and a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min after injecting 5 μL of each the VAE. The mobile phase consisted of solvent A (distilled water+0.1% formic acid) and solvent B (ACN+0.1% formic acid). The elution ingredient was set as 97% phase A for 0–5 min; 3%–100% liner gradient phase B for 5–16 min; 100% phase B for 16–17 min; 100%–3% phase B for 17–19 min; 97% phase A for 19–25 min. The compounds eluted from the column were detected by a high-resolution tandem mass spectrometer SYNAPT G2 Si HDMS QTOF (Waters) in positive and negative ion modes. For positive ion mode, the capillary voltage and the cone voltage were set at 2 kV and 40 V, respectively. While 1 kV and 40 V, respectively were set for negative ion model. Centroid MS mode was used to collect the mass spectrometry data. The primary scan ranged from 50 to 1,200 Da and the scanning time was 0.2 s. All the parent ions were fragmented using 20–40 eV. The information of all fragments was collected and the scan time was 0.2 s. In the data acquisition process, the LE signal was gained every 3 s for real-time quality correction. For accurate mass acquisition, leucine encephalin at a flow rate of 10 μL/ min was used as a lock mass by a lock spray interface to monitor the positive ([M + H]+ = 556.2771) and the negative ([M − H]− = 554.2615) ion modes. Data acquisition and analysis were controlled by UNIFI V1.71 software (Waters) and the peaks were then identified by screening against the propriety scientific library of UNIFI V1.71.
Data was analyzed using one-way ANOVA procedure of the Statistic Analysis System (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA, 2007). Means and standard errors were calculated for the variables. The origin of VAs was considered as the main effect in the model. Means were compared using Duncan’s multiple range test. The significance was defined at p<0.05.
Results and discussion
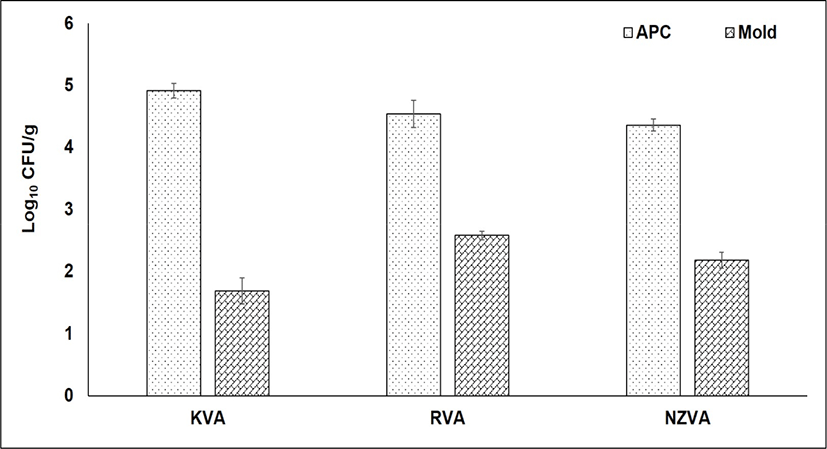
The bacterial and mold counts of three VA types are presented in Fig. 2. The APC, also known as the total of bacteria, indicates bacterial populations that can grow in aerobic condition at moderate temperature. In the present study, no statistical differences in the APC were found among the VA types (p>0.05). The APC was found at 4.91, 4.54, and 4.36 Log10 CFU/g in the KVA, RVA, and NZVA, respectively. Similarly, no differences in the mold number occurred among the VA types (p>0.05). In general, the mold was found at a relatively low number (1.69–2.58 Log10 CFU/g) in all the VA samples. Till now, there is no published research reporting the mold level in the dry VA samples. However, compared to mold level (3–4.87 Log10 CFU/g) reported by Pérez-Chabela and Rodriguez-Serrano (1999) for various meat types (e.g., beef, chicken, horse and sheep) under retail sale, the VA samples from all origins in the present study had a lower number. These contrasting results could be attributed to the moisture content differences among the sample types studied because a high moisture or water activity is the favorable environment for the mold growth (Rico-Munoz et al., 2019). Molds cause not only food spoilage but also food safety issue due to production of toxins and allergens (Rico-Munoz et al., 2019). Additionally, the growth of molds on animal-derived products may result in off-flavor and unpleasant appearance (Delgado et al., 2016). In food industry, the level of APC and mold is considered as the useful information on the general quality and shelf-life of foods. According to the Microbiological Guideline for Food (Centre for Food Safety, 2014), the maximum limit of APC in raw foods should be below 108 CFU/g. Based on this guideline, therefore, it may be said that all types of VAs were guaranteed in term of microbiological quality.
Antioxidant activity that protects cells against the destructive effects by free radicals is one of the most important beneficial effects of antioxidants present in natural materials. The antioxidant activity of the VAEs may not be attributed to a single mechanism. In the present study, therefore, two different assays including DPPH and ABTS were used to evaluate the antioxidative capacity of the VAEs. The results of antioxidant activity of all three VAE types were expressed as IC50 value (mg VAE/mL) as shown Fig. 3. Regarding the ABTS assay, the IC50 values of KVA, NZVA, RVA extracts were 6.54, 7.52, and 17.79 mg VAE/mL, respectively. Thus, the lowest IC50 value was found in the KVA extract and this value was approximately three times lower compared to that of the RVA extract (p<0.05). These result signifies that the ABTS radicals scavenging activity was the highest in the KVA extract, followed by the NZVA and RVA extracts. The ABTS radicals scavenging activity is mainly due to the electron transfer mechanism in which the oxidants (e.g., ABTS radicals) are reduced by antioxidant compounds (Floegel et al., 2011).
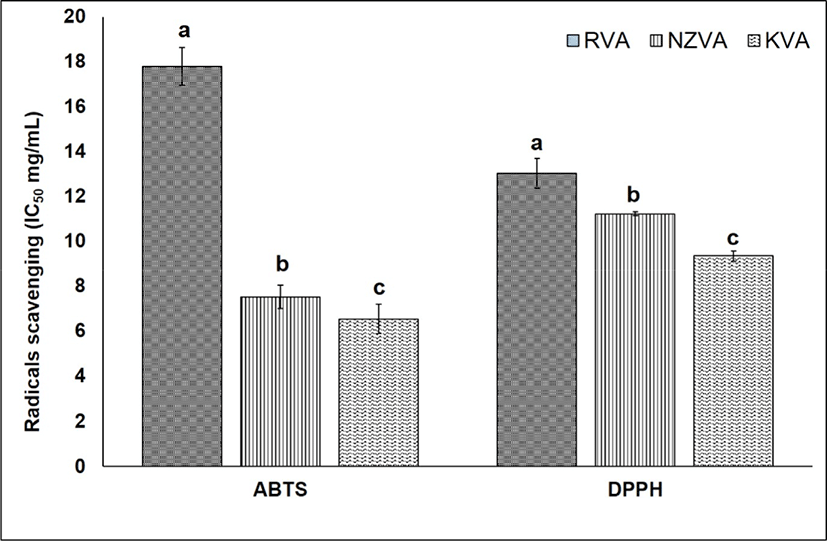
Till now, the DPPH free radicals scavenging assay has widely been used to assess the antioxidant activity in natural extracts (López-Alarcón and Denicola, 2013). Results showed that the IC50 values of KVA, NZVA, RVA extracts were 9.37, 11.25, and 13.01 mg VAE/mL, respectively. Thus, the extract of KVA again showed its significantly (p<0.05) higher radicals scavenging activity compared to those derived from the imported NZVA and RVA. The mechanism underlying the DPPH free radicals scavenging has been proposed as the ability of antioxidants to donate a hydrogen atom to the DPPH free radicals (Shimada et al., 1992). Researchers have found that AAs, nucleotides and peptides are the major active components responsible for the antioxidant activity of the VA extracts (Zhao et al., 2010). Likewise, in vitro studies have also reported a high antioxidant activity of protein hydrolysate from deer VA (Wu et al., 2013; Yu et al., 2011). Thus, it may be said that the KVA extract exhibited a stronger antioxidant activity, this could be due to its higher amount of antioxidants compared to the imported VAs (e.g., NZVA or RVA).
The concentrations of crude protein, fat and minerals of VA types are presented in Table 1. Minerals are considered as the important micronutrients that play a vital role in maintaining human health (Tapiero and Tew, 2003). Our results show that the concentration of Fe was significantly higher in the KVA compared to the RVA (p<0.05). While, the Mn, Zn, and Ca contents were higher in the RVA compared to the KVA or NZVA (p<0.05). No differences in the Cu and Mg contents were found among three VA types (p>0.05). Similarly, all of these minerals have also been reported by Wu et al. (2013) for Chinese deer VA.
The protein and fat concentrations among the VA types ranged from 9.21 to 13.90 g/100 g and 0.22 to 0.80 g/100 g, respectively. Interestingly, the KVA showed significantly higher amounts of fat and protein contents compared to the imported VA types (p<0.05). The results indicating the mineral, fat and protein contents difference may be linked to the breed and feeding diet differences among the three VA types studied.
The concentrations of AAs in the KVA, RVA, and NZVA extracts are presented Table 2. It is well recognized that AAs are the important components for development of tastes (e.g., sweetness and umami) and flavor characteristics of animal-derived products (Macleod, 1994; Mottram, 1998; Kato et al., 1989). Furthermore, hydrophobic AAs (e.g., glycine, leucine, phenylalanine and alanine etc.) are responsible for the biological activities (antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capacities) in VAE (Zhao et al., 2016). The outcome of our analysis showed that a total of twenty AAs was detected in all three VAE types. However, only six AAs (glycine, alanine, proline, lysine, methionine and tyrosine) were affected by the VA origin. Particularly, the concentrations of glycine, alanine, methionine and tyrosine were significantly higher in the KVA extract compared to the RVA or NZVA extract (p<0.05). While, the concentrations of lysine and proline were higher in the NZVA extract compared to those in the RVA extract (p<0.05). We also observed that glycine, alanine, leucine and valine were the most predominant AAs in all three VAE types. Similar to the current findings, Jeon et al. (2010) also found that glycine, alanine, leucine and valine contents were the predominant AAs in Korean elk VA at all growth period, and VA sections.
Odor, a part of flavor, is a very important component affecting the sensorial quality as well as the purchasing decision by consumers for foods and beverage products (Charalambous, 1978; Macleod, 1994). Till now, a wide variety of commercial health-enhancing or functional food and supplement products originated from the deer and elk VAs is available on the markets in Korea, China, Japan and Canada (Wu et al., 2013). In fact, however, there have been no published researches reporting the volatile odor components in these VA products. The volatile compounds identified in the three VAEs are presented in Table 3. By using the SPME/GC-MS technique, a total of 32 compounds including esters (12), alcohols (3), aldehyde (1), ketones (6) and hydrocarbons (10), pyrazines (5), sulfur-containing compounds (7), and furans (2), were identified for the first time in the VAEs. Amongst, ester was the most predominant class of aroma compounds. Interestingly, all of the esters (12 compounds) were found in the KVA whereas, 8 esters (e.g., methyl acetate, methyl propionate, ethyl butanoate, ethyl hexanoate, 2-isobutoxyethyl propionate, chrysanthenyl propionate, isobutyl pentyl carbonate and methyl octanoate) were not detectable in the imported RVA or NZVA derived-extracts. However, the statistical analysis showed that only two esters (1-methoxy-2-propyl acetate and ethyl octanoate) were significantly different among the three VAE types, with higher amounts in the KVA compared with those in the RVA and NZVA (p<0.05). Esters are known as the major lipid-derived products which are usually formed from esterification of alcohols and acids (Macleod et al., 1988; Mottram, 1998). Thus, the mechanism behind the formed esters may be understood as follows: the oxidation/degradation of lipids during the extraction process resulted in formation of alcohols and acids which then reacted with each other to form the esters. Amongst, some compounds such as; ethyl acetate or ethyl butanoate and ethyl octanoate have also been detected in acerola fruit extract (Vendramini and Trugo, 2000) or strawberry juice (Lambert et al., 1999) and pear juice (Chung et al., 1993; Riu-Aumatell et al., 2004). Additionally, some esters such as; ethyl hexanoate, methyl acetate and methyl octanoate have been reported in cooked lamb (Bueno et al., 2011) and beef (Schindler et al., 2010), respectively. The ethyl butanoate has been reported to confer floral, sweet-apricot, ether-fruit and sour-cheese odors of fruit juices (Lambert et al., 1999), and methyl octanoate and ethyl hexanoate are associated with citrus-like and strawberry-butter odors in cooked beef and lamb meat (Bueno et al., 2011; Schindler et al., 2010). However, further study is needed to characterize the odor characteristics of each the detected ester and its odor detection threshold in the VAEs.
Regarding the alcohol class, all three compounds named eucalyptol, 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol and 2-furanmethanol were found in the KVA extract while, the 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol was found in both the RVA and NZVA extracts. However, no significant differences in their amounts were found among the VAE types (p>0.05). The 2-furanmethanol is known as the product formed from the Mallard reaction between AAs and reducing sugar (Ba et al., 2013). This compound frequently appears in cooked meats at a low concentration (Ba et al., 2010; Elmore et al., 2004).
Only one aldehyde (3-methylbutanal) was found at a relatively low amount in the RVA (0.001 μg/mL) and NZVA (0.001 μg/mL) extracts. This aldehyde has been reported to possess chocolate and caramel odors in cooked beef, and is mainly formed from the Strecker degradation of leucine (Machiels et al., 2003).
Regarding the ketone class, only 2,4-dimethyl-3-hexanone showed a significant difference among three VAE types in which the KVA extract had higher amount (0.15 μg/mL) compared to the RVA and NZVA extracts (p<0.05). Ketones are known as the lipids-derived products which are produced during heating/cooking process (Mottram, 1998). Out of them, 2-heptanone was only found in the KVA extract while, 2,5-dimethyl-3-hexanone was not found in the RVA extract. The 2-heptanone is produced from the oxidation of C18:2n-6 (Ba et al., 2013), and it has been reported to confer fruity, spicy, gas and gravy odors in cooked beef (Calkins and Hodgen, 2007; Machiels et al., 2003). In the present study, hydrocarbons were the second most predominant class of volatile compounds after esters. Hydrocarbons are usually formed from the lipids oxidation/degradation or Maillard reaction in meat and meat products during heating/cooking process (Macleod, 1994; Mottram, 1998). Our results showed that all the hydrocarbons were found in the KVA extract, however, only 2,2,6-trimethyl-octane which was found in all three VAE types.
In general, most of the volatile compounds identified were originated from the lipid oxidation/degradation during drying and extracting process while, only few were formed from the Mallard reaction between AAs with reducing sugars. Noticeably, compared with the RVA and NZVA-derived extracts, the extract of KVA was more diverse in the quality and quantity of volatile odor compounds. These obtained results could be related to differences in animal breeds and rearing systems etc. which might affect the flavor precursors (e.g., lipid composition) in the VAs (Lee et al., 2007; Ward et al., 2014).
The outcome of UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS analysis displayed a high diversity of bioactive substances, with over six hundred compounds. With such a large number of identified compounds, there was some difficulty in presentation of the results in detail, therefore, the metabolic profiles in the VAE types were simply summarized in Fig. 4A. There were 412 compounds which all were commonly found in all the VAEs from three countries (as shown in the overlap area of circles). Interestingly, 109, 107, and 84 marker compounds were only found in the KVA, NZVA, and RVA extracts, respectively. It was also noted that some compounds were also found in two different VAE types for instance; 13, 13 and 11 compounds were found in both the KVA and RVA; KVA and NZVA; and RVA and NZVA extracts, respectively. Although the quantifications of the identified compounds were not done, there might be some differences existing in their levels among the three VAE types as shown in Fig. 4B. It shows a high variation in relative intensities of peaks (area percent) among the VAE types. Aligning with the present findings, Zhang et al. (2019) also reported 84 bioactive compounds in VAE of Chinese deer.
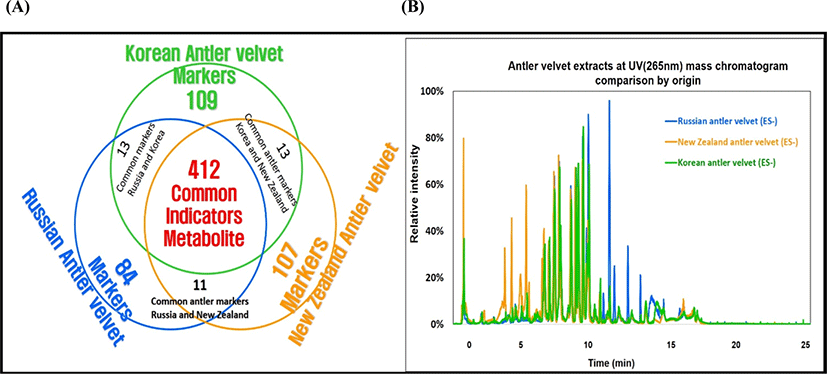
Otherwise, we found that the identified compounds may come from various chemical classes such as steroids, alkaloids, esters, AA, peptides and phospholipids (data not shown). Amongst, some representative compounds such as; iriomoteolide 1a (accepted ID: CSID17627054), hovenidulcioside A2 (accepted ID: HMDB41029) and ginsenoside F3 (accepted ID: HMDB39556) in the KVA extract; Notoginsenoside I (accepted ID: HMDB31371), ganoderic acid H (accepted ID: HMDB35987) and mibefradil (accepted ID: CSID54673) in the RVA extract; Papulacandin A (accepted ID: CHEBI:72611), 2-palmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (accepted ID: CSID21403165) and tetra-(3E)-3-hexen-1-yl methylenebis (phosphonate) (accepted ID: CSID4524297) in the NZVA extract, all of them have also been reported to exert the important biological functionalities (e.g., immune activity and disease healing and anti-cancer etc.) in literatures (Elkhatee et al., 2018; Ghosh and Yuan, 2009; Zhang and Wang, 2006). This study, for the first time, identified and compared the bioactive substances in the VAEs from different countries, and it may be said that all the VAEs studied are rich in the bioactive substances. However, it is also noted that the variations in the bioactive substances may result in different pharmaceutical and medical properties among the VAE types. Additionally, the bioactive compounds identified (the compounds only found in each country) in this study may confer their potential applications as candidate biomarkers to discriminate the VAs quality from different country of origins. Further profound study is needed to quantify these candidate biomarkers in the VAEs.
Conclusion
This study for the first time determined and compared the microbiological quality, antioxidant activity, minerals and flavor and bioactive compounds between the Korean and imported VAs-derived extracts. Generally, all the VA types presented a relatively low level of APC and mold. The KVAs had higher Fe content while, the RVA had higher Mn, Zn, and Ca contents compared to the other remaining VA types. In both the DPPH and ABTS assays, the KVA extract exhibited higher free radicals scavenging activities, suggesting their stronger antioxidative capacity compared with the imported VAs-derived extracts. Compared to the imported VAs-derived extracts, the KVA extract showed significantly higher amounts of some essential AAs such as glycine, alanine and methionine. A total of 32 volatile odor compounds were identified in the VAEs. The KVA extract exhibited a higher diversity (both in quality and quantity) of volatile odor compounds compared to the RVA and NZVA extracts. This implies that the extract of KVA may exhibits a stronger odor intensity compared to those derived from the imported VAs. The results of aroma analysis, therefore, could be the important basis for adjustment of the VA content in its products according to consumer’s preference. Over six hundred metabolite compounds were identified; 412 compounds were commonly found in all three VAE types while, 109, 107, and 84 candidate marker compounds were only found in the KVA, NZVA, and RVA extracts, respectively. Based on the results obtained in the present study, it may be concluded that the country of origin partly affected the antioxidant activity, chemical composition, flavor and bioactive compounds of the VAEs.













