Introduction
Functional foods are consumed as part of a regular diet and in addition to their nutritional efficiency, they have beneficial physiological effects or reduce the risk of chronic diseases (Adefegha, 2018; Ovando et al., 2018). Microalgae are one of the most interesting sources of functional foods (Benelhadj et al., 2016; Priyadarshani and Rath, 2012). Arthrospira (Spirulina platensis) are microscopic filamentous prokaryotes (Vaz et al., 2016). Until a few years ago, fish oil was the only major source of polyunsaturated fatty acids. But now S. platensis oil, which contains significant amounts of polyunsaturated fatty acids, is also one of the main sources of these fatty acids. Algae can produce polyunsaturated fatty acids, such as docosahexaenoic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid, arachidonic acid, and gamma-linoleic acid. Numerous studies have confirmed that Spirulina is cholesterol-free and rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids (especially gamma-linolenic acid) and this makes Spirulina suitable for the treatment and prevention of atherosclerosis, obesity and high blood pressure. Due to the direct effects of gamma-linolenic acid on the immune system and use in the treatment of many diseases, there has been a great interest in producing high concentrations of gamma-linoleic acid (Andrade, 2018). Numerous studies have been done on the enrichment of quail feed with the use of S. platensis (Boiago et al., 2019), lycopene (Sahin et al., 2008), fish oil (Kamely et al., 2016), vegetation such as liquor ice (Doğan et al., 2018), and rice bran (Gopinger et al., 2016), to enrich its eggs (Wang et al., 2007). One of the side effects of using antibiotics is the formation of antibiotic resistance. This has created a crisis in human health treatment and highlighted the need for a new generation of antibiotics. The use of foods and supplements that naturally contain antimicrobial compounds has reduced the use of antibiotics by animals and their negative impact on consumers. Phytobiotics are a viable alternative and S. platensis supplements have given good results in aquaculture, poultry feeding, and agriculture (Belay et al., 1996).
Quail eggs are a good source of nutrients for human health, with marked advantages over chicken eggs (Jeke et al., 2018). Human body can not synthesize essential fatty acids and they must be received through the diet, Accordingly, the aim of this study was to investigate the effect of the addition of fortified S. platensis on the amount of essential fatty acids, especially omega 3, in quail eggs as this could provide, a functional and practical food for the diet of today’s societies.
Materials and Methods
S. platensis was enriched with iron and zinc by growing in a medium with added minerals. Samples were taken during the first (M1=at the beginning of the maximum progressive growth phase, after 7 days of initial cultivation, minerals 5 h before harvest added to S. platensis algae) and the second phases (M2=The cultivate algae after entering the logarithmic phase. In both methods EDTA-FeNa·3H2O, ferric citrate, ZnSO4·7H2O, and CuSO4·5H2O were added at the rates of 13 mg/L, 0.0396 mg/L, 0.5994 mg/L, and 0.1998 mg/L respectively (Shahtoori, 2015).
To evaluate the iron and zinc absorption in algal samples, the ICP-OES simultaneous Arcos EOP model was used. First, each treatment was digested and prepared separately (Sinaei et al., 2018). For this purpose, 1 g of the sample was digested with nitric acid and oxygenated water in the microwave for two 10 min steps at 200°C and 800 W power and the sample was finally injected into the device. To improve the accuracy of the test, the blank sample (containing nitric acid and oxygenated water without the original sample) was also injected into the device and finally, the concentration of heavy metals and elements was calculated using the following equation:
Where M is the final concentration of the elements and heavy metals of the sample in μg/g, C is the concentration obtained from the device in μg/L, V is the final sample volume in l (0.025), W the primary sample weight for acid digestion in (g) (modified Saeid et al., 2013a).
Crude S. platensis and S. platensis enriched by biosorption were each added to the base feed (2.5%, 5%, and 5.7%) and fed to 126 female Japanese quails. There were three replicates of each of the seven treatments, with six chicks per experimental unit. All chicks were eared on the same environmental conditions (Abouelezz, 2017). Experimental diets based on corn and soybean meal were adjusted for growth period and laying period (Table 1) (Hajati and Zaghari, 2019). During the experiment, the quails had free access to water and food and the rations were flour. Lighting was 24 h until 35 d, this was then reduced to 22 h with 2 h of darkness and 1 h was then added every night until it reached 8 h darkness and 16 h lighting. Laying ails started from 47 d. The eggs were collected during the 3 periods of 15 d.
Egg samples were collected at the end of the last period for analysis of fatty acids. Extraction of yolk oil: The quail egg yolk was stored at –20°C and then dried in a Christ-freezing dryer model at –80°C for 24 h at 0.0026 m bar. Hexane was added and it was kept in the refrigerator for 24 h. Samples were centrifuged at around 5,000×g at 4°C and then filtered through filter paper under vacuum condition, then the extracted oil was methylated. Fatty acid methyl ester preparation: To methylate the samples, toluene and 0.5 M sodium methoxide were added to the extracted oil. It was put in a water bath at 50°C for half an hour. Glacial acetic acid and distilled water were used to neutralize the alkali, then hexane was added to the test tube and the contents of the tube were mixed by vortexing. The tube was kept static for a few minutes and two phases formed. The lower phase contains water and the upper phase contains hexane and fatty acid methyl ester. This step was repeated. Anhydrous sodium sulfate was used for dehydration. After filtration with a Whatman 41 filter paper, the samples were placed under the hood in a water bath at 70°C to reach a volume of 1–2 mL. Samples were injected into a gas chromatography device (GC), model Shimadzu (Wang et al., 2000). During this experiment, the type of column was WAX with FID detector, injection and detector temperature was 240°C, Oven program temperature started on 60°C for 2 min and increased to 200°C at 10°C/min. It was kept at this temperature for 1 min and then the temperature was increased until 230°C at 5°C/min and kept there for 15 min (Jafari et al., 2014).
Egg samples were collected randomly for evaluation of qualitative parameters during the 3 periods of 15 d.
Egg weight parameters (EW), shape index (SI), egg volume (EV), eggshell surface (SSA), albumen index (AI), hough unit (HU), internal quality unit (IQU) and yolk index (YI) were measured on the short and long axies of the eggs using a digital caliper. Yolk and albumen diameters were measured after breaking the eggs on a smooth glass surface using a digital caliper. Yolk and albumen elevation were also measured using a standing caliper.
-
The SI was calculated as SI=d/D×100 with d and D representing the short axis and the long axis, respectively.
-
The EV was calculated as EV=4/3×π×(D/2)×(d/2)2 in which D=long egg axis, d=short egg axis and π=3.14159.
-
SSA was calculated as SSA=4.835×EW0.662 the equation below where EW=egg weight.
-
The AI was calculated as AI=h/(0.5×(D+d)) with h=height of concentrated albumen at the junction with yolk, D and d, are the long and short diameters of albumen, respectively.
-
HU was calculated as HU=100×log(h+7·57−1·7×EW0·37) with h=height of concentrated albumen at the junction with yolk and EW was=egg weight.
-
The internal quality of the egg (IQU) was calculated as IQU=100×log(h+4·18−0·89897×EW0·6674) with h=height of concentrated albumen at the junction with yolk and EW=egg weight.
-
Yolk quality was calculated by the YI as YI=h/D with h=yolk height and D=yolk diameter (Zita et al., 2013).
Eggshell strength parameters (ESS) and eggshell thickness (EST) were determined using egg multi tester model EMT-5200. For this purpose, Device Egg Shell Force Gauge Model-2 was used to measure the strength and Echo meter, 1061 (D-56 Wuppertal 1) was used to measure thickness (Abdanan Mehdizadeh et al., 2014).
In order to evaluate the yolk color (YC) and to ensure the accuracy of the test, assessments were made in all periods using the Roche color fan (0–15 degrees) (Ludke et al., 2018). In addition for eggs from the final 15-d period an assessment was made by Hunter Lab using Ultra scan VIS model (Carson et al., 1994).
For this purpose, samples were collected in each of the three periods to measure the pH, the yolk was first separated from albumen, homogenized and measured with the pH meter of the NACI model (Doğan et al., 2018).
Egg samples from each of the three periods were weighed before and after the oven drying at 60°C for 72 h and moisture content of the samples was calculated (Gopinger et al., 2016).
Iron and zinc contents were analyzed in eggs from the final period and in algal samples.
A two-way analysis of variance was carried out using SPSS software version 22. The differences between the means of different treatments and time periods were considered significant at the 5% probability level. The data were normalized, before being tested statistically. Excel was used to draw charts.
Results and Discussion
The amount of iron and zinc in the algae enriched in two ways, during the logarithmic phase (M2) and the maximum stationary phases (M1) shows in Fig. 1.
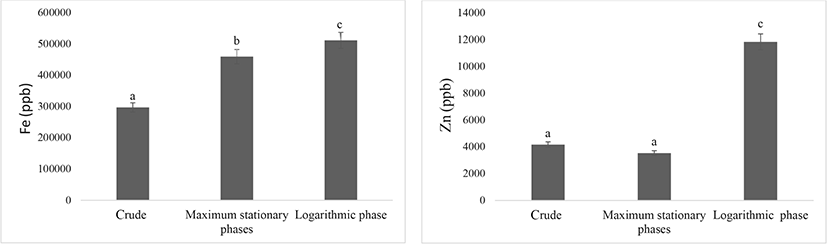
The amount of iron and zinc in the three groups differed significantly (p<0.05). These results indicate that the most suitable method for increasing iron and zinc contents in S. platensis algae is biosorption (method M2), with the increases being particularly large for zinc according to the results of Saeid et al. (2013a), the best method for enriching S. platensis is bioremediation, which is consistent with the results of this study.
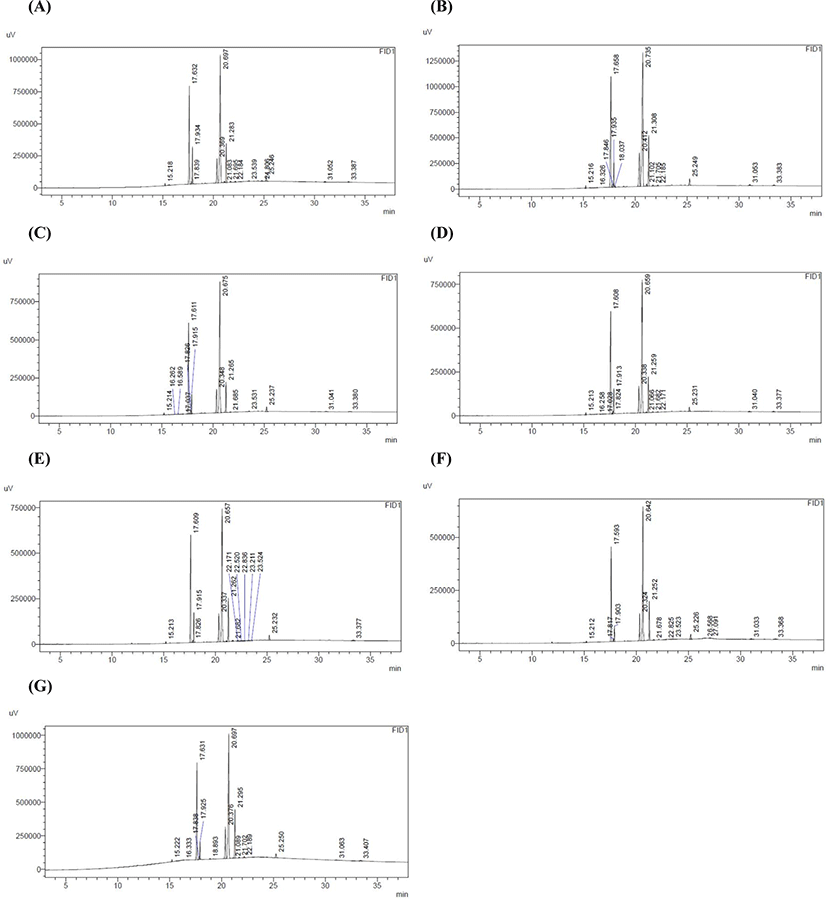
The peak of fatty acids from gas chromatography of quail eggs fed with enriched, raw, and controlled algae shows in Fig. 2. Statistical results showed a significant difference (p<0.05) in saturated fatty acids (palmitic acid and stearic acid) and unsaturated fatty acids (oleic acid and linolenic acid) between treatments compared to the control group. In general consumption of crude and enriched S. platensis (M2) showed a significant difference (p<0.05) in the amount of saturated fatty acids (palmitic and stearic acid) and polyunsaturated fatty acids (oleic and linolenic acid) relative to the control group. According to these results both crude and enriched S. platensis were effective in reducing the saturated fatty acids of palmitic acid and stearic acid. The treatments 7.5 enrich, 2.5 enrich and 7.5 crude had the largest reduction compared to the control group for palmitic acid. However, the treatments crude 2.5 and enrich 5 did not show a significant decrease in palmitic acid compared to the control group, indicating a decrease in palmitic acid in more than 66% of the enrich and 33% of crude treatments, respectively. The results showed that stearic acid showed a significant decrease in all treatments, especially enriched treatments. The effect of feeding crude and enriched S. platensis (M2) on unsaturated fatty acids of oleic acid and linolenic acid was also significant, although 66% of treatments showed no increase in oleic acid content compared to control group, the amount of oleic acid in the enriched treatments 7.5 and 2.5 showed a significant increase compared to the control group. Also, linolenic acid showed the highest increase only in the crude treatment 5 compared to the control group. Due to reduced palmitic and stearic fatty acids and increased, oleic and linolenic fatty acids when S. platensis, especially in the enriched form, one would expect reductions in lower-density lipoprotein (LDL) and the risk of cardiovascular disease and stroke. According to the results, consumption of S. platensis did not show a significant effect on the amount of linoleic acid in the treated yolk compared to the control group. Boiago et al. (2019) reported that consumption of S. platensis at levels (0%, 5%, 10%, and 15%) for 42 days (2 21-day cycles) in quail feed, reduced saturated fatty acids and increased monounsaturated fatty acids while it decreased polyunsaturated fatty acids. Abouelezz (2017) reported that consumption of S. platensis at 1% level in Japanese quail feed reduced free fatty acids, also use of S. platensis at levels [2.5%, 5%, and 7.5%] for 12 weeks in rainbow trout feed increased some acid levels (Jafari et al., 2014).
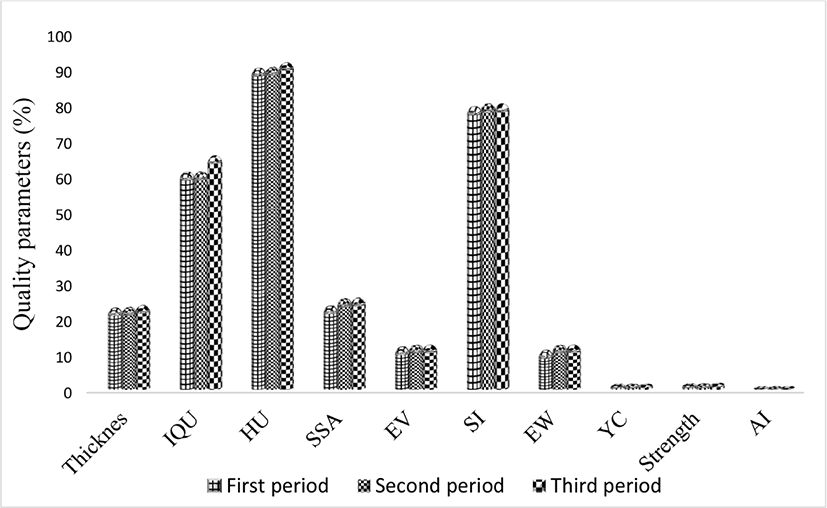
The results of Table 2 shows that S. platensis (M2) had a significant effect on egg quality parameters as assessed during the final period (EW, IQU, SI, EV, SSA, AI, and YI) (p<0.05). So that in EW, EV, and SSA parameters, 33.3% of treatments, SI of 50% of treatments (especially enrich treatments), IQU 83.3% of treatments (especially enrich treatments) and albumen and yolk indices The effects of S. platensis (M2) on egg quality parameters in samples taken in each of the three periods is shown in Fig. 3 the parameters (IQU, SSA, and EW) showed significant differences (p<0.05) between the three periods, so that all three parameters in the second period of the first period and in the third period It was longer than the first and second periods. There were significant differences (p<0.05) between periods in the HU showing decrease in albumen quality in the control group and better quality retention in egg albumen with addition of either crude or enriched S. platensis (M2) and crude compared with the control group. Dogan et al. (2016) reported that feeding 0.5%, 1%, 2% of S. platensis to quail for 8 weeks significantly increased albumen and yolk indices (p<0.05) and had a non-significant effect on HU (These results are in line with the results of this study. The present study showed that consumption of crude and enriched S. platensis had a significant effect on egg shape and weight index compared to the control group, while the results of Dogan et al. (2016) showed a significant effect (p<0.05) on egg production, but did not assess egg shape and weight index. In the present study, it was shown that consumption of crude and enriched S. platensis had a significant effect on EW, SI, and SSA in comparison to the control group, whereas Hajati and Zaghari (2019) found that consuming S. platensis at levels of 2.5, 5, 10, and 20 g/kg diet for 1 to 35 days and at levels of 1, 3, and 5 g/kg diet for up to 12 weeks gave decreases in these parameters.
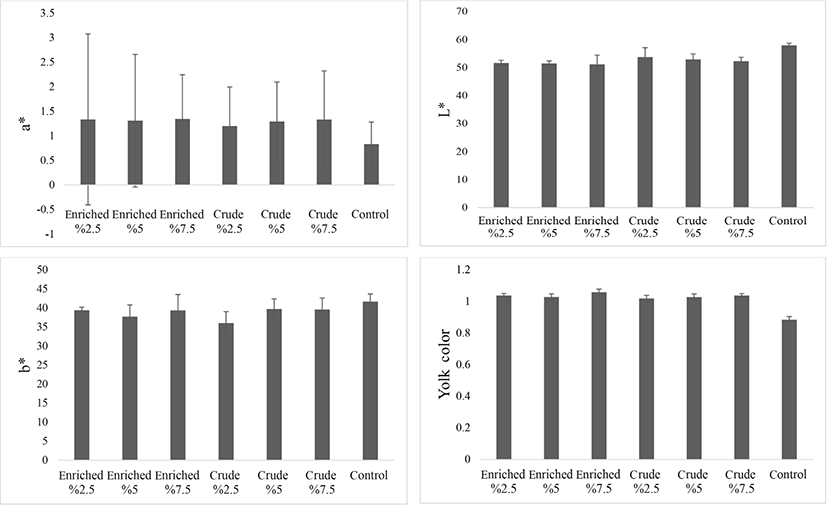
The results of the effect of S. platensis on YC evaluated by Roche color fan showed a significant difference between treatment (p<0.05; Fig. 4). All treatments, especially with enriched Spirulina, showed a significant difference from the control group. Also, the evaluation of YC by Hunter’s lab showed a significant (p<0.05) effect of enriched S. platensis on lightness index (L*) and redness index (a*). With crude Spirulina a* increased and L* decreased. The highest redness was observed in the enriched 7.5 treatment and the highest transparency in the control group. This could be due to the presence of more iron in the enriched treatments and presence of pectin in Spirulina. The yellowness index (b*) did not show a significant difference (p>0.05) among the treatments, but the control group had a numerically higher b* than the other treatments. Hajati and Zaghari (2019) indicate an increase in YC, which is consistent with the results of this study. The results of yolk colorimetry are also consistent with the reports of (Omri et al., 2019), in which S. platensis was fed at 1.5% and 2.5% to 44-week-old chickens.
The effects of S. platensis on egg moisture and albumen pH are shown in Table 3. Statistical results indicated that there were no significant differences between the three periods in egg moisture content (p>0.05). However, the moisture content for the crude 5 treatments was significantly lower than that for all other treatments (p>0.05). Evaluation of albumen pH of samples showed no significant (p>0.05) statistical differences between treatments or periods, but there was a significant interaction between treatment in three periods (p<0.05), The lowest pH was for the 2.5% enriched sample in the first period and the highest pH for the control group in the third period.
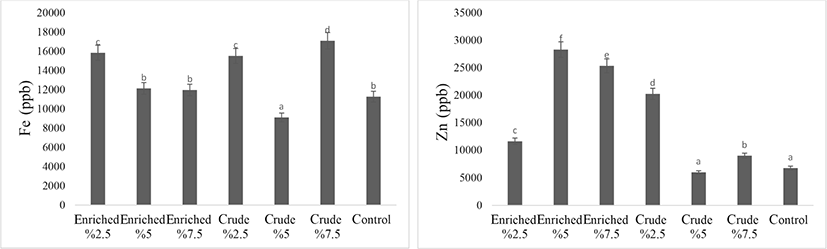
The effect of enriched and crude S. platensis on iron and zinc contents of eggs are shown in Fig. 5. Eggs of quail fed enriched or crude algae generally showed higher iron and zinc contents than those from the control group, but there were some inconsistencies in the results and further research is required. The results do, however, indicate that enriched quail eggs could be a suitable food to ameliorate iron and zinc deficiency diseases in humans. Iron depletion in the 7.5% enriched treatment and higher absorption of this element in the crude treatment could be due to the antagonistic effect of iron with copper, iron with zinc or result from using an inappropriate source of the elements (they were supplied in inorganic form) with the results of Saeid et al. (2013b) study also indicate antagonistic effects of zinc with copper, zinc with iron, or inappropriate complement form when copper-enriched Spirulina was used in pig feed, A 2.5% enriched treatment gave increases in the absorption of iron, copper, chromium, selenium, manganese, but reduction in zinc.
Conclusion
Due to the role of essential fatty acids in the improvement and prevention of cardiovascular disease and bad cholesterol (LDL), the aim in this study was to produce a product enriched with essential fatty acids, especially omega-3. By including S. platensis in the diet we succeeded in producing quail eggs with 23% more linolenic acid (omega 3) than with the control group. The content of oleic acid was increased by 7.1%, whilst contents of palmitic and stearic saturated fatty acids were decreased significantly by 6.8% and 7.2%, respectively. This indicates considerable potential for the use of Spirulina to produce quail eggs with improved quality in relation to human health.