Introduction
Fermented ham is a traditional meat produced mainly in Europe and North America, South America, Asia, Oceania and Africa. Traditional fermentation procedure of fermented ham involves the application of mixture of salt and nitrite, and the addition of spices like pepper, all spice and coriander for enhancing flavor and curing or ripening procedure during several weeks or months (Campbell-Platt and Cook, 1995).
Starter cultures having various functional properties are used to reduce ripening time, add functionality and enhance flavor or safety of fermented meat products. In the previous studies, Vural (1998) who studied on the effects of three different starter cultures in Turkish semidry fermented sausages, and reported that the combination of Pediococcus acidilactici, Staphylococcus xylosus (SX) and P. pentosaceus (PP), and the combination of S. carnosus (SC) and Lactobacillus pentosus (LP) in fermented sausages significantly reduced the pH, increased the lactic acid content and improved the characteristics of sausage, such as color, appearance, flavor and general acceptability as compared to control (no starter culture). Park et al. (1997) studied the physicochemical properties of fermented sausages manufactured with starter cultures of SC plus LP, SC plus PP, and SX plus PP had higher L values, hardness and sensory scores than those of sausages prepared with SC plus LP.
The antimicrobial activities of various starter cultures has been studied in fermented meat products. Among them, Sameshima et al. (1998) reported that L. rhamnosus, L. paracasei and L. sake isolated from the intestinal tracts inhibited the growth of Staphylococcus aureus in fermented sausage. The antibacterial activity of L. sake had antimicrobial activity for Listeria monocytogenes has been documented (Papamanoli et al., 2003). Kaban and Kaya (2006) reported that mixed starter cultures (Pediococcus acidilactici + Lactobacillus curvatus + Staphylococcus xylosus and Lactobacillus sakei + Staphylococcus carnosus) in Turkish dry-fermented sausage had significant inhibition effects on the growth of S. aureus.
Starter cultures are used to improve the sensory quality or flavor profile of fermented meat products. Enzymatic and chemical reactions, such as proteolysis and lipolysis that developed during curing or ripening time have been attributed to the generation of flavor precursors, starter cultures and endogenous are important in these reaction (Martin et al., 2006; Toldra, 1998).
Garriga et al. (1996) conducted sensory evaluation of fermented sausages manufactured with various Lactobacillus strains as starter cultures and reported that L. plantarum CTC305 had the highest acidic taste that was unacceptable by the panelists, whereas L. curvatus CTC 371 could improve odor intensity, aged flavor and atypical flavor as compared to control. Martin et al. (2006) reported that fungi such as Penicillium chrysogenum and Debaryomyces hansenii have a positive impact on the volatile compounds of ripened pork loins, being they were responsible for higher levels of long chain aliphatic and branched hydrocarbons, furanones and long chain carboxylic acids.
These starter cultures mentioned above are mainly lactic acid bacteria (LAB), which are isolated from various sources that included the intestinal tracts, feces, fermented products. Since the interest in isolation of starter cultures has greatly increased, many researchers tried to investigate various sources having potentiality to be used as starter cultures. Among those, kimchi is Korean traditional foods prepared by fermented with LAB originating from raw materials including cabbage, radish, garlic, onion and ginger. LAB is present in properly fermented kimchi at 107-109 colony forming unit (CFU)/g, which depends on temperature and humidity of fermentation (Lee et al., 1992; Lee et al., 2006). Thus, the objective of this study was to investigate the effects of combined starter culture isolated from kimchi on physicochemical properties, functionality and flavor profile of fermented ham, as compared to those with commercial starter culture.
Materials and methods
Domestic pork loins from the same origin of animals slaughtered the previous day were purchased from a wholesale meat market, and the excess fat was trimmed. As a commercial starter culture, LK-30 plus (Lactobacillus sake + Staphylococcus carnosus + Micrococcus varians) of Gewuerzmüeller Inc., German) was used for comparison with a novel mixed starter culture isolated from kimchi. It was compared of lactic acid bacteria isolated from kimch, including Lactobacillus plantarum L155 having cholesterol assimilation activity, Lactobacillus plantarum L167 producing angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibition peptides and Pediococcus damnosus L12 producing bacteriocin, was used as a novel mixed starter culture (LLP) as previously reported by Han et al. (2006). The formulation of curing solution is summarized in Table 1.
| Ingredients | Weights (g) |
|---|---|
| Water | 1,000 |
| Salt | 150 |
| Sugar | 70 |
| NaNO2 | 0.4 |
| NaNO3 | 0.7 |
| White pepper | 3.0 |
Two experiments, 1 and 2, were designed. The first experiment (1) was carried out to compare physicochemical and textural properties between commercial starter culture (LK-30 plus) and a novel starter culture (LLP). Experiment 2 compared physicochemical and textural properties between no starter culture and LLP, in fermented ham. After loins were cut into approximately 250-300 g of strips, each strip was stuffed into a net casing. In experiment 1, the loin strips were divided into two batches (A and B). Batched containing LK-30 plus and LLP of approximately 106 cells/g were divided into batch A and B, respectively. After the inoculated strips were cured into brine solution (Table 1) at 8±1℃ for 7 d, then were dried at 8±1℃ for 1 d. Then they were cold-smoked on smoke chamber (NU-vu, ES-13, Food System, Canton, MA, USA), and were held at 15℃ and a relative humidity of 85% on Temperature & Humidity chamber (Myung Technology, Korea) for about 3 wk.
pH values were measured five times using solid pH meter (Mettler Toledo, MP120, Switzerland), which was calibrated with a buffer (pH 4 and 7). Moisture, crude fat and crude protein contents were determined according to AOAC (1995), using the dry-oven (102℃, 16 h) method, soxhlet fat extraction and BUCHI protein analyzer (Kjeltec Auto System, B-322, Switzerland), respectively.
Hunter L (lightness), a (redness) and b (yellowness) values were measured five times using Chroma meter (CR-10, Minolta Corp. Ramsey, Japan). Saltiness of samples was measured five times using salt manager (SATO SK-10S, Japan).
Allo-kramer shear forces (kgf/g) were measured using Instron Universal Testing Machine (Model 3344, USA). Fermented ham samples were measured using a 10-blade Allo-kramer shear probe with a 200 mm/min cross speed (Lee and Chin, 2011).
Weight loss (WL, %) of samples was calculated as follows: WL (%) = (A − B) × 100 / A (A = initial sample weight; B = sample weight during ripening).
Total plate count, deMan, Rogosa and Sharpe (MRS) and violet red bile (VRB) agar were used to determine total bacteria counts, lactic acid bacteria (LAB) and Enterobacteriaceae, respectively. In brief, homogenized samples (10 g) were mixed with 90 mL of sterile distilled water (DW) and after shaking well, serial dilutions were prepared. Aliquots (0.1 mL) of each dilution was spread on plate count, MRS and VRB agar. They were incubated at 37℃ for 2 d, counted and expressed as Log CFU/g.
Cholesterol content of samples was measured according to the method of Searcy and Bergquist (1960). After a 4 mL-aliquots of fat extract were dried under nitrogen in a 60℃ water bath, fat residues were saponified with 10 mL of 15% ethanolic KOH. Then, 5 mL of double distilled water was added and allowed to cool down to the room temperatures, as previously reported by Kim et al. (2014).
Volatile compounds of samples were extracted using solid-phase microextraction (SPME) technic. Homogenized samples (10 g) and internal standard (1 mL, 200 ppm chlorobenzene in methanol, Supelco, USA) were transferred into a 40 mL amber screw top vial with hole cap PTFE/silicone septa (Supelco, USA). Before extraction of volatile compounds, fiber (75 mm, Carboxen-polydimethylsiloxane, Supelco, USA) was conditioned by heating in a gas chromatograph injection port equipped flame ionization detector (GC-FID) at 250℃ for 1 h. Vials including samples were preheated for equilibration at 50℃ for 30 min, and SPME fiber for extraction of volatile compounds was exposed to the headspace above the sample at 50℃ for 30 min. After injection SPME fiber in GC-FID injection port, volatile compounds extracted from sample were isolated from SPME fiber at 250℃ for 5 min. Qualitative analysis of volatile compounds was performed by GC-MS (mass spectrometry). The operation conditions of GC-FID and GC-MS were listed in Table 2. Quantitative analysis of volatile compounds was calculated as follows:
Concentrations (mg/kg) = each peak area × 20 / peak area of internal standard
Three-week ripened hams were sliced and evaluated by seven panelists using 8-point hedonic scale (1, worst; 8, best). Panelist evaluated sensory parameters such as flavor, texture, juiciness, color, saltiness and overall acceptability.
The experiment was replicated three times. Data were analyzed using two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) in SPSS 12.0 software for Windows, as factors for starter cultures and curing (0, 3, and 7 d) or ripening time (0, 7, 14, and 21 d). Means were separated by the Duncan's multiple range test (p<0.05).
Results and Discussion
Since interactions between starter cultures and processing time (curing or ripening time) were not observed in all parameters, the data were pooled with the results presented in Tables 3-7. As shown in Table 3, moisture, fat and protein contents (%) were affected by processing time due to the evaporation of moisture during processing time. As a result, moisture content was decreased, while fat and protein contents were increased with increased processing time (p<0.05). These results might be partially due to the release of moisture in fermented loin hams due to relatively lower humidity and air circulation during ripening time. However, proximate compositions were not affected by starter cultures (A vs B) (p>0.05). This result was supported by Cenci-Goga et al. (2012) in which the control and selected dairy-origin starter (SDS) added fermented sausages were changed in the physicochemical characteristics during fermentation or ripening time. Cagno et al. (2008) reported that the three Italian sausages had 41-47% moisture, 18-25% fat and 25-37% protein with pH of 5.99-6.62, which was higher than our results. The two type of the Italian fermented sausages were similar moisture content to our products with higher fat content. However, the protein contents of our fermented ham were higher than those of the Italian fermented sausages.
| Batches1 | Curing and ripening time (d) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||
| A | B | Curing 0 | Ripening 0 | Ripening 21 | |
| Water | 61.97 | 61.72 | 73.09a | 70.46a | 41.98b |
| Fat | 2.94 | 3.48 | 2.73b | 1.64b | 5.26a |
| Protein | 26.64 | 26.07 | 18.37b | 20.32b | 40.37a |
a-cMeans with same row with same superscripts are not different (p>0.05).
1Batches: A=fermented ham with commercial starter culture (LK-30 plus); B=fermented ham with probiotic starter culture (Lactobacillus plantarum L155 + Lactobacillus plantarum L167 + Pediococcus damnosus L12).
a,bMeans with same row with same superscripts are not different (p>0.05).
1Batches are same as Table 3.
cTPC: Total plate count.
dMRS: Lactobacilli de Man, Rogosa, Sharpe Agar.
eVRB: Violet Red Bile Agar.
a-cMeans with same row with same superscripts are not different (p>0.05).
1Bathces are same as Table 3.
dTPC: Total Plate Count.
eMRS: Lactobacilli de Man, Rogosa, Sharpe Agar.
fVRB: Viole red Bile Agar.
a,bMeans with a same superscript within a row are not different (p>0.05)
1Batches are same as Table 3.
a,bMeans with a same superscript within a row are not different (p>0.05).
1Batches are same as Table 3.
2t: trace, not detected.
The results of physicochemical, microbial and functional properties as affected by starter cultures and curing time in fermented hams are shown in Table 4. Starter cultures didn’t affect pH, microbial properties and cholesterol contents during curing time (p>0.05), however, saltiness were increased, but Hunter color values (L, a, and b) were decreased with increased curing time (p<0.05). These results indicated that brine solution permeated into the fermented hams, resulting in these parameter during curing time. However, pH values were ranged from 5.50 to 5.56, which didn’t a marked change during curing time. This result is in agreement with the results of Krockel (1995) who reported that pH values of fermented hams were not remarkably reduced during curing procedure. Thus, curing process of fermented ham for 7 d affected the saltiness and color values of fermented ham (p>0.05).
Table 5 shows physicochemical, microbial and functional properties as affected by starter cultures and ripening time of fermented loin hams. No differences as affected by starter cultures were observed in all parameters (p>0.05), except for increased total bacterial counts (TPC) and lactic acid bacteria (LAB), in which both TPC and LAB was more detected in fermented hams inoculated probiotic starter culture (batch B) than counterparts (batch A). pH value of batch B (5.38) was lower than one of batch A (5.42) (p<0.05). This result might be partially due to higher level of LAB during ripening. Shear value was increased during ripening due to drying of moisture form the fermented ham (p<0.05), however, no differences were observed between two batches (p>0.05). Li et al. (2013) reported that dry fermented sausage containing ground deordorized yellow mustard, the potential antioxidant, had lower shear value than the control, and increased the shear value with increased ripening for 28 d. Popp et al. (2013) reported that turkey fermented sausages with dark, normal, and pale muscle had similar shear values and concluded that turkey meat could be used to manufacture the fermented sausages without quality defects. Cholesterol contents of batch A and B were 70.16 and 67.95 mg/100 g, respectively, and were similar to each other. Muguerza et al. (2001) reported that the cholesterol level was reduced about 12-13% in Spanish fermented sausages with 20-25% replacing level, and up to 22% in sausages with 30% replacing with pre-emulsified olive oil. The cholesterol level of fermented ham was similar to those of 30% replacing with the olive oil due to the low-fat content in the fermented ham. However, saltiness, Hunter a and b values, weight loss, shear force and cholesterol contents were increased with increased ripening time (p<0.05). These results may be due to moisture loss of fermented hams developed in ripening chamber. Olivares et al. (2010) evaluated the fat reduction and ripening time on the sensory characteristics of fermented sausages, and concluded that fat reduction affected texture and other parameters, and ripening time also significant affected the quality differences. They also suggested that the rate of processing time was depended on the fat content, and that slow fermentation process was beneficial to produce low-fat fermented sausages without detrimental to the textural appearance.
Total eight volatile compounds were identified from fermented hams during curing process (Table 6). These were not affected by starter cultures and curing time, except for trans-caryophyllene. Among volatile compounds identified, ethanol was the most abundant compounds (more than 90%), followed by 1-hydroxy-2-butanone and hydrazine. These results were similar to the previous report of Rivas-Cañedo et al. (2009) who reported that the alcohol, aldehyde and alkanes were the higher level in volatile compounds identified from Spanish dry-fermented sausage ‘salchichon’.
Total fifty-eight volatile compounds were identified from fermented hams during ripening process (Table 7). Among identified compounds, alcohols, esters and furans were the main volatile compounds extracted from fermented hams. Martin et al. (2006) studied effects of selected fungal to the volatile compounds on fermented ham and reported that alcohols were the most representative compounds in final products, especially, ethanol. These results are in accordance with our results. Of the 58 compounds, two compounds, (3-methyl-oxiran-2-yl)-methanol and ethyl propanoate, were affected by starter cultures (p<0.05). Among them, the concentrations of ethanol, ethyl acetate and 2-furfural in fermented hams inoculated LK-30 plus were 1397, 459 and 311 mg/kg, those in loin hams inoculated probiotic starter culture were 1579, 538 and 302 mg/kg, respectively. The ratios of these three compounds in batch A and B were approximately 76.2 and 77.8% in total concentration of the identified compounds, respectively. These results suggested that probiotic starter culture (LLP) isolated from kimchi developed in this study could be used as starter culture due to the similar volatile compounds except for few cases. Rivas-Cañedo et al. (2009) conducted the evaluation of volatile compounds in pressure-treated Spanish fermented sausages and reported high levels of alcohol, aldehyde, and alkanes, as compared with the control samples. Olivares et al. (2011) also reported that a total of 95 volatile compounds were identified using SPME, GC, and mass spectrophotometry and the volatile compounds of hexanal, 2-nonenal, and 2, 4-nonadienal, ethyl butanoate and 1-octen-3-ol highly affected the consumer preference of aroma in overall quality.
Concentrations and type of identified volatile compounds during ripening time were more than those of identified volatile compounds during curing time. These differences may be due to the smoking procedure that was performed prior to ripening. The main volatile compounds derived from smoking were furans and phenols. In the initial ripening time (0 d), compounds such as 2-furfural (1053 mg/kg), ethanol (886 mg/kg), 5-methyl-2-furfural (108 mg/kg), 2-methoxy-phenol (77.9 mg/kg) and 2-(hydroxymethyl)-furan (70.4 mg/kg) were the most representative volatile compounds, and were derived from smoking procedure, except for ethanol. However, since most compounds derived from smoking were markedly decreased with increased ripening time, these compounds might not affect the flavor profiles of final products. Ethanol, which was significantly increased with increased ripening time, might affect the flavor profiles of final products. Ethyl acetate, hexanal and hydrazine were produced 702, 124 and 102 mg/kg in 21 d of ripening time, respectively, and were the most representative volatile compounds in the final products. Although ethyl acetate was not detected during the initial ripening time, it showed the greatest increase during ripening. Ester compounds having fruity smell characteristics were mainly produced by esterification of carboxylic acids and alcohols (Sabio et al., 1998). Therefore, fruity smell characteristics of fermented hams manufactured in this study might have been derived from ethyl acetate. Hexanal is an aldehyde that has a “grassy” odor and formed during the oxidation of linoleic acid vis 13-hydroperooxide. Increasing hexanal content indicated that fermented hams were oxidized during ripening time. Because aldehyde compounds like hexanal have lower threshold values, they contribute to flavor profiles of fermented hams (Sabio et al., 1998). Also, significant increases were observed in acetic acid, 3-methoxy-1,2-propanediol, methyl pentanoate, 1-(2-furanyl)-ethanone, 3-methyl-2-cyclopenten-1-one, 2-hydroxy-3-methyl-2-cyclopenten-1-one, 2,2,4,6,6-pentamethyl-heptane, 2,4,6-trimethyl-octane, 2,3-dimethyl-2-cyclopenten-1-one, 3,6-dimethyl-undecane, 4,8-dimethyl- undecane and 1-cyclohexen-1-al (p<0.05). Volatile compounds such as oxo-acetic acid, 3-furfural, 2-furfural, 2-(hydroxy methyl)-furan, 1-(acetyloxy)-2-propanon, 5-hexanedione, 2,5-dimethyl-2,4-hexadiene, 5-methyl-(5H)-furan-2-one, 1-methoxy-1,3-cyclohexadiene, 5-methyl-2-furfural, 1-methoxy-1,3-cyclohex adiene, 2-methyl-phenol, 2,6-dimethyl-4H-pyran-4-one were decreased with increased ripening time (p<0.05). Cagno et al. (2008) reported that total of 52 volatile compounds were observed in three Italian fermented sausages and the main components of these volatile compound were alcohol, aldehyde and terpenes.
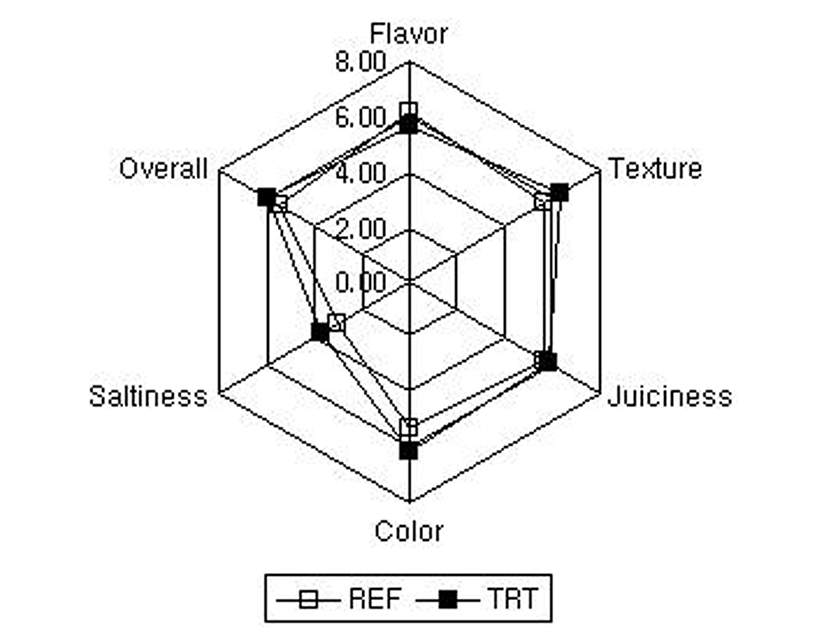
As shown in Fig. 1, fermented hams (batch B, TRT) manufactured with probiotic starter culture (LPP) had higher sensory score in texture, color and overall acceptability than counterparts (batch A, REF), while the opposite trend was observed in flavor. These results indicated that mixed probiotic lactic acid bacteria, Lactobacillus plantarum L155, Lactobacillus plantarum L167 and Pediococcus damnous L12, could be possibility to be used as starter culture in fermented meat products. Cenci-Goga et al. (2012) reported that fermented sausages made with selected dairy starter cultures were slightly saltier, juicier and in general more acceptable in consumer sensory evaluation. Olivares et al. (2010) reported that the sensory data from consumer sensory of fermented sausages were mainly affected by mostly fat content, indicating that the ripening time should be controlled depending on the fat content.
Conclusions
Fermented hams with commercial starter culture (A, LK-30 plus) and mixed starter culture developed in this study (B) were evaluated the product quality during processing time. Curing process increased saltiness, however, decreased hunter color values (L, a, and b values). Ripening process increased most parameters due to the drying process. The mixed starter culture had higher lactic acid bacteria than the commercial one. While 8 volatile compounds were identified from fermented hams during curing process, total 58 volatile compounds were identified from fermented hams during ripening process. The main volatile compounds were alcohols, esters and furans. However, no differences in volatile compounds were observed between two batches. Fermented hams containing mixed probiotic starter culture had higher sensory score in texture, color and overall acceptability than counterparts. In conclusion, mixed probiotic starter culture isolated from kimchi in this study could be used as a starter culture for the manufacture of fermented ham to replace with the commercial starter culture.













