Introduction
Diabetes mellitus is defined as a group of metabolic diseases characterized by high blood glucose levels resulting from either failure of insulin secretion or insulin resistance (American Diabetes Association, 2004). Insulin, a hormone responsible for maintaining normal blood glucose levels, is produced by pancreatic beta-cells. In 2019, diabetes contributed to 1.5 million deaths among people worldwide. It was reported that 422 million adults were living with diabetes in 2014 (World Health Organization, 2021). In Indonesia, diabetes was responsible for 6% of all deaths in 2016, and overweight was the dominant diabetes-related risk factor (24.4%), followed by physical inactivity (22.8%) and obesity (5.7%; World Health Organization, 2021).
Diabetes occurs when glucose metabolism is inappropriately regulated by insulin, leading to increased blood glucose levels and resulting health complications. Prolonged high blood glucose levels in patients with diabetes mellitus increase the formation of reactive oxygen species, which trigger oxidative stress and deteriorate pancreatic beta-cells, thereby disturbing insulin production.
Apart from genetic inheritance, insulin resistance mechanisms, and physical inactivity, unhealthy diets featuring high levels of carbohydrate consumption represent the main cause of diabetes (Lyssenko et al., 2008). The composition of gastrointestinal microbiota in relation to the diet is also considered important in the development of insulin resistance (Zhang and Zhang, 2013). Previous clinical studies observed an increased ratio of Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes in obese people with insulin resistance (Ley et al., 2006; Tilg and Kaser, 2011; Tremaroli and Bäckhed, 2012). Differences of the microbial composition between normal-weight and obese people with insulin resistance suggest that the intestinal microbiota affects energy, metabolic homeostasis (Cani et al., 2007; Turnbaugh et al., 2006), mucosal immunity, and systemic inflammation (Bäckhed et al., 2004; Gravitz, 2012). The administration of probiotics containing beneficial microbes has previously been reported to modify the intestinal microbiota and subsequently prevent or delay the onset of diabetes (Cani et al., 2007; Cani et al., 2008).
Probiotics are known as “living microorganisms which when administered in adequate amounts confer a health benefit on the host” (FAO and WHO, 2002). The antihyperglycemic effects of probiotics have already been reported (Honda et al., 2012; Yun et al., 2009; Zhang et al., 2014). A previous study found that Lactobacillus casei AP reduced blood glucose and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels and increased high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels in diabetic rats (Widodo et al., 2019). Meanwhile, Moon et al. (2014) reported the ability of the probiotics Pediococcus acidilactici strain M76 and P. acidilactici DSM 20284 to reduce cholesterol levels in vivo. To function as probiotics and guarantee safety for daily human consumption, bacterial strains must be nonpathogenic, and they must ideally originate from humans (Dunne et al., 1999; Dunne et al., 2001). P. acidilactici strain BE is a probiotic strain isolated from the feces of an infant who consumed breast milk (Widodo et al., 2012), whereas Pediococcus pentosaceus strain M103 was isolated from Etawah crossbred goat milk (Widodo et al., 2016). Previous studies found that P. acidilactici strain BE and P. pentosaceus strain M103 can acidify milk with good physicochemical and microbiological qualities (Widodo et al., 2016; Widodo et al., 2017). These two probiotics may have potential effects on blood glucose levels in diabetic rats. However, to the best of our knowledge, little research has been conducted on these effects.
This study aimed to identify the potential effects of milk fermented with P. acidilactici strain BE or P. pentosaceus strain M103 on blood glucose levels and pancreatic beta-cell indicators in diabetic rats.
Materials and Methods
P. acidilactici strain BE originating from the feces of an Indonesian infant younger than 1 month (Widodo et al., 2012) and P. pentosaceus strain M103 isolated from Etawah crossbred goat milk (Widodo et al., 2016) were used as bacterial cultures. Bacterial cells were purified via plating on De Man–Rogosa–Sharpe agar (MRSA, Merck, Jakarta, Indonesia) supplemented with 0.5 g/L L-cysteine (Sigma-Aldrich, Panjang Rd, Singapore) and incubated at 37°C for 24 h.
P. acidilactici strain BE and P. pentosaceus strain M103 were grown on MRS broth and harvested at logarithmic phase. The bacterial cultures (5% v/v) were separately inoculated in sterilized skim milk (18% w/v) and incubated at 37°C for 10 h. Bacterial cultures at this growth stage were used as starters for fermentation. Fresh milk obtained from local farms was added to skim milk powder (Mirota KSM, Yogyakarta, Indonesia) to obtain an 18% total solid (w/v) and then pasteurized at 80°C for 10 min. After cooling, 500 mL of heat-treated milk were separately inoculated with 1) a 2% (v/v) culture of P. acidilactici strain BE and 2) a 2% (v/v) culture of P. pentosaceus strain M103. Fermentation was conducted at 37°C for 10 h, and the fermented products were stored at 4°C until further analysis.
The pH value of the fermented milk products was measured using a pH meter (Hanna Instruments, Nuşfalău, Romania). Protein levels were analyzed using the Micro–Kjeldahl method (AOAC, 2005), fat analysis was conducted using the Babcock method (AOAC, 2005), and lactose analysis was performed using the titration method (AOAC, 2005). Antioxidant activity was analyzed using the 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl radical-scavenging method developed by Brand-Williams et al. (1995). HPLC was used to measure short chain fatty acids (SCFA) according to the procedure described by Bevilacqua and Califano (1989). HPLC was run using a reverse-phase C8 column at room temperature, a mobile phase of 0.5% w/v buffer [(NH4)2HPO4 with a of pH 2.24 with H3PO4]-0.4% (v/v) acetonitrile and 1.2 mL/min flow rate with UV detection at 214 nm. Viscosity measurements were performed as described by Tunçtürk (2009) using a model DV III digital rheometer (Brookfield Engineering Laboratories, Middleborough, MA, USA). All viscosity measurements were expressed in cP, performed in triplicate, and averaged. Viable cells were counted using the total plate count method. A 1-mL aliquot of fermented milk was diluted 7-fold in a sterile solution of 0.85% (w/v) NaCl, plated onto MRS agar, and incubated at 37°C for 24–48 h. The colonies were then counted, and total bacterial numbers per sample were estimated.
Animal experiments were conducted at the animal research facilities of Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM, Yogyakarta, Indonesia) and approved by the ethical commission of the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine UGM (Ethical Clearance number 00076/EC-FKH/Ex./2021). In total, 25 white Wistar rats (male, 8 weeks old, average body weight of 267.11±20.66) were used in the experiments. All rats were housed in a temperature-controlled (25±2°C) animal cage (40×50×30 cm3) under a 12-h/12-h light/dark cycle and 70±10% humidity. Feed was provided at 20 g/rat/day, and water was provided ad libitum in the cage. The provided feeds included normal feed (ADII feed; Japfa Comfeed, Surabaya, Indonesia) and high-fat feed. The nutritional contents of the normal and high-fat feed are provided in Table 1.
| Normal feed | High-fat feed1) | |
|---|---|---|
| Crude fat (%) | 3–7 | 36.72±0.08 |
| Crude protein (%) | Minimum 15 | 15.01±0.03 |
| Ash concentration (%) | Maximum 7 | 4.98±0.14 |
Rats were acclimatized for 7 days before treatment and then randomly divided into five treatment groups. Group 1 included nondiabetic rats fed normal feed (P1). Group 2 included diabetic untreated rats fed high-fat feed and treated with streptozotocin (STZ, N-methyl nitroso-carbomyl; Sigma-Aldrich, Jakarta, Indonesia) starting at 40 mg/kg on day 25 (P2). Group 3 included diabetic rats fed high-fat feed, treated with STZ starting on day 25, and fed 2 mL of milk fermented with P. acidilactici strain BE (1×108 CFU/mL) for 15 days starting on day 29 (P3). Group 4 included diabetic rats fed high-fat feed, treated with STZ starting on day 25, and fed 2 mL of milk fermented with P. pentosaceus strain M103 (1×108 CFU/mL) for 15 days starting on day 29 (P4). Group 5 included diabetic rats fed high-fat feed, treated with STZ starting on day 25, and then treated with metformin (45 mg/kg) for 15 days starting on day 29 (P5). Throughout the experimental period, rats’ weight was monitored every 7 days.
Blood samples from each animal were collected into tubes before and after treatment through the retroorbital vein to determine blood glucose levels. Blood was incubated at room temperature for 15 min, and serum was separated by centrifugation at 4,000×g for 10 min. Blood glucose was measured by an enzymatic colorimetric test based on glucose oxidase (DiaSys Diagnostic Systems Gmbh, Proline, Jakarta, Indonesia) following the manufacturer’s instruction. Triglyceride levels were measured using an enzymatic colorimetric test (Cayman Chemical Company, Ann Arbor, MI, USA), and the results were measured by spectrophotometry at a wavelength of 546 nm. HDL and LDL levels were measured using the precipitation method with a specific reagent and read by spectrophotometry at a wavelength of 546 nm.
Fecal samples were collected before and after treatment to count total lactic acid bacteria (LAB). Fecal sample collection was conducted in the morning, and samples were immediately transferred into sterile tubes and stored at 5°C. Total LAB counts were performed on MRS agar and incubated at 37°C for 48 h under microaerobic conditions with the addition of Ox Bile (Oxoid, Jakarta, Indonesia).
This experiment was performed after measuring blood glucose levels before and after treatment. As P4 treatment did not affect blood glucose levels in diabetic rats, samples from this group were excluded and represented by samples from P2. At the end of the experiment (day 43), representative rats from the P1, P2, P3, and P5 groups were euthanized using ketamine and xylazine. The pancreas of each animal was harvested, cleaned, and fixed in 10% formalin for 72 h. The tissue samples were dehydrated using a series of increasing alcohol concentrations (70%, 80%, 90%, and 95%) and embedded in paraffin wax. A microtome was used to obtain 8-μm sections, which were placed onto glass slides for hematoxylin and eosin staining. The 8-μm-thick paraffin sections were mounted on positively charged slides and subjected to IHC staining using an avidin–biotin detection system (Ventana, Tucson, AZ, USA), following the manufacturer’s instructions. Sections were incubated with polyclonal guinea pig anti-insulin antibody (1:100, N1542, Dako, Carpinteria, CA, USA) for 10 min at room temperature. The IHC procedure was performed using an automatic immunostainer (BenchMark XT, Ventana). The reaction was visualized using 3,3-diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride (DAB Substrate Kit, Thermo Fischer Scientific, Rockford, IL, USA). Sections were counterstained with Harris hematoxylin. Slides were examined and photographed using a light microscope (BX51, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). Histomorphometric scoring of the immunoreactive section of the pancreatic beta-cells was performed by calculating the immunoreactive score (IRS) according to Fedchenko and Reifenrath (2014).
Results and Discussion
P. acidilactici strain BE and P. pentosaceus strain M103 were used to ferment fresh milk to generate fermented products for further experiments. Milk fermentation was conducted for 10 h, and the quality of the fermented products was evaluated (Table 2). Table 2 revealed that milk fermented with P. acidilactici strain BE and P. pentosaceus strain M103 had no physicochemical differences in terms of total LAB counts and fat, protein, and lactose levels.
The lactose and fat contents of the fermented products were lower than those of fresh milk (data not shown), indicating that bacterial starters degraded these macromolecules during fermentation. Lactose was fermented to produce ATP as energy, whereas fat might have been degraded by lipase to produce fatty acids, which are further used for cellular anabolism. The viscosity of milk fermented with P. acidilactici strain BE was relatively higher (2,092.22±63.80 cP) than that of milk fermented with P. pentosaceus strain M103 (1,938.78±43.13 cP, Table 2). The viscosity of fermented milk is strongly influenced by the formation of curd during fermentation. In addition, viscosity is also affected by the production of high-molecular-weight exopolysaccharides (Tiwari et al., 2021). As a comparison, the viscosity of yogurt is 100–2.825 cP, that of condensed milk is 2,600 cP, and that of milk whey sugar is approximately 800–1,500 cP (Denin-Ɖurđević et al., 2002).
Higher antioxidant activity was observed after fermentation (8.49±0.25% and 6.34±0.50% for milk fermented with P. acidilactici BE and P. pentosaceus M103, respectively) compared to unfermented freh milk. Pasteurized milk has antioxidant activity of 1.85±0.08% (data not shown). Albera and Kankofer (2009) reported a number of components that contribute to antioxidant activity in milk, including antioxidative enzymes (i.e., glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutase) and nonenzymatic antioxidants (i.e., lactoperoxidase, lactoferrin, ceruloplasmin). Milk fermented with P. acidilactici BE also produced higher butyrate (850±50.00 mg/kg) than the milk fermented with the P. pentosaceous strain M103 (700±1.00 mg/kg, Table 2). Meanwhile, a higher amount of acetate was produced in the milk fermented with the P. pentosaceous strain M103 (627.24±6.35 mg/kg) than that in the milk fermented with P. acidilactici BE (263.78±0.78 mg/kg, Table 2).
Diabetes was induced in rats by a combination of high-fat feeding and STZ treatment on day 25. Throughout the experiments, body weight and blood glucose levels were measured on days 0, 7, 14, 21, and 29. Day 29 was the first day of blood glucose measurements after STZ induction and the day on which treatment began. Fig. 1 illustrates that blood glucose levels were significantly elevated (p<0.05) on day 29 (4 days after STZ induction).
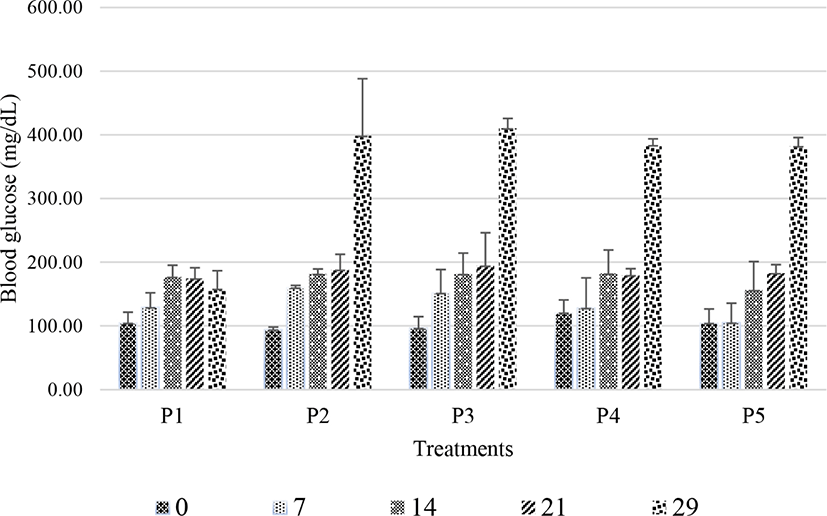
Fig. 1 indicates that rats displayed increased blood glucose levels on day 29. Rats fed normal feed without STZ induction (P1) had the lowest blood glucose levels (158.18±28.36 mg/dL). Meanwhile, rats in groups P2–P5 all had glucose levels exceeding 250 mg/dL. On day 29, the average blood glucose levels of rats in groups P2, P3, P4, and P5 were 398.40±89.66, 410.27±15.54, 383.70±10.08, and 382.30±13.39 mg/dL, respectively. These data suggest that the combination of high-fat feeding and STZ induction at 45 mg/kg for 4 days effectively induced diabetes in rats. Elias et al. (1994) previously observed symptoms of diabetes in rats within 2–4 days after STZ injection at 60 mg/kg. STZ is a cytotoxic chemical that damages pancreatic beta-cells of the islets of Langerhans (Akbarzadeh et al., 2007; Szkudelski, 2001) and causes the degeneration of beta-cells (Ikebukuro et al., 2002). As beta-cells produce insulin, the degeneration of beta-cells in the islets of Langerhans affects insulin production, resulting in uncontrolled blood glucose levels (Akbarzadeh et al., 2007).
Blood samples from rats before (day 29) and after treatment (day 43) were collected and assayed (Table 3). Table 3 illustrates that rats fed normal feed (P1) had the lowest blood glucose level on day 43 (206.98±8.74 mg/dL), whereas untreated diabetic rats (P2) had the highest blood glucose level (352.07±50.67 mg/dL). In addition, a significant reduction of blood glucose levels was observed in rats fed milk fermented using P. acidilactici strain BE (P3, from 410.27±15.54 to 304.07±9.88 mg/dL) or treated with metformin (P5, from 382.30±13.39 to 253.33±40.66 mg/dL) on day 43, suggesting the that P. acidilactici strain BE and metformin can decrease blood glucose levels. Metformin, which had the strongest effect, decreases blood glucose levels by suppressing hepatic gluconeogenesis and improving insulin signaling (An and He, 2016) through both AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)-dependent and AMPK-independent mechanisms (inhibition of mitochondrial respiration and mitochondrial glycerophosphate dehydrogenase) as well as a mechanism involving the lysosome (Rena et al., 2017). In animal studies, metformin reduced hepatic glucose production by more than 60% in a euglycemic clamp study (Takashima et al., 2010) and suppressed endogenous glucose production in high-fat diet-fed rats by 50% (Song et al., 2001).
| Before | After | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 158.18±28.36 | 206.98±8.74 | 0.02* |
| P2 | 398.4±89.66 | 352.07±50.67 | NS |
| P3 | 410.27±15.54 | 304.07±9.88 | 0.04* |
| P4 | 383.70±10.08 | 349.80±10.08 | NS |
| P5 | 382.30±13.39 | 253.33±40.66 | 0.02* |
After 15 days of the consumption of milk fermented with P. acidilactici strain BE, decreased blood glucose levels were observed. These findings indicated that milk fermented with P. acidilactici strain BE potentially reduced high blood glucose levels in diabetic rats. This finding was in line with previous findings that the administration of milk containing L. casei AP for 15 days significantly reduced blood glucose levels in Sprague–Dawley rats fed a high-fat, high-fructose diet (Widodo et al., 2019). Another previous study reported similar findings using the probiotic strains L. casei Q14 and Lactobacillus rhamnosus NCDC17 (Singh et al., 2017). The antihyperglycemic ability of P. acidilactici strain BE in this study is likely attributable to its ability to synthesize butyrate (Table 2). Widodo et al. (2012) previously reported the ability of P. acidilactici strain BE to metabolize and produce acetate, butyrate, and propionate. Butyrate, a component of SCFAs, is known to alleviate hyperglycemia by increasing insulin sensitivity and energy expenditure (Gao et al., 2009). Conversely, diabetic rats fed milk fermented with P. pentosaceus strain M103 exhibited numerically, but not significantly, lower blood glucose levels after treatment (Table 3).
This study obtained evidence that probiotics can lower blood glucose levels in diabetic rats. The mechanism by which probiotics reduce glucose levels involves several processes, including increases of SCFA levels, inhibition of immune responses and oxidative stress, elevation of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and insulinotropic polypeptide secretion, and increases of glucose transporter 4 activity. The decrement of blood glucose levels may also be related to the inhibition of alpha-glucosidase by probiotics. Alpha-glucosidase participates in the hydrolysis of carbohydrates into glucose. Panwar et al. (2014) reported that probiotics can induce the production of alpha-glucosidase, which suppresses postprandial hyperglycemia, delays carbohydrate digestion, and prevents excessive glucose absorption.
Probiotics reduce blood glucose levels by activating pancreatic beta-cells; therefore, they have a significant role in maintaining blood glucose homeostasis for insulin production (Hirahatake et al., 2014). Yogurt supplemented with honey can be used as an antihyperglycemic agent that suppresses glucose absorption and glucose production through the action of α-glucosidase along with activating antioxidants that restore the function of pancreatic beta-cells (Hirahatake et al., 2014). Probiotics have been reported to exert antidiabetic effects on insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus by increasing the number of natural killer T-cells and significantly reducing fasting blood glucose levels (Zhang et al., 2016).
Turnbaugh et al. (2009) reported that switching from a low-fat to high-fat diet shift the metabolic pathways in the microbiome and altered microbiome gene expression in gnotobiotic mice. A similar study by McNulty et al. (2011) reported that introducing fermented milk product containing a consortium of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis, two strains of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus, Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris, and Streptococcus thermophilus into gnotobiotic mice resulted in significant changes in expression of microbiome-encoded enzymes involved in carbohydrate metabolism. These findings suggest that microbiome-associated gene expression and its metabolic pathways was mostly affected by the incorporation of probiotic-containing diet, thereby regulating key metabolic functions and this may responsible to the host clinical conditions. In this study, the decrement of blood glucose levels after the consumption of milk fermented with P. acidilactici strain BE might be influenced by the microbiome gene expression and its related metabolic functions. Therefore, a metagonomic study following the consumption of milk fermented with P. acidilactici strain BE need to be conducted.
Total cholesterol, triglyceride, LDL, and HDL levels were measured in all groups (Table 4). STZ injection increased triglyceride, cholesterol, and LDL levels in diabetic rats (P2–P5). However, treatments with milk fermented with P. acidilactici BE or P. pentosaceus M103 or metformin did not induce significant changes of cholesterol, triglyceride, LDL, and HDL levels in diabetic rats (Table 4).
A previous study identified that fermented milk containing the probiotics Bifidobacterium and L. acidophilus can reduce total cholesterol, LDL, and very-low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels and increase HDL levels (Kang et al., 2010). Probiotics assimilate cholesterol and deconjugate bile salts by producing bile salt hydrolase (BSH) and reducing blood cholesterol levels (Kang et al., 2010). The administration of BSH-active L. acidophilus CHO-220 combined with the prebiotic inulin significantly reduced plasma total cholesterol and LDL-C levels in prior research (Jones et al., 2013). However, in our study, administration of the probiotics P. acidilactici BE and P. pentosaceus M103 did not change the lipid profiles of diabetic rats.
Stool was collected from nondiabetic and diabetic rats before and after treatment with fermented milk or metformin, followed by total LAB measurements (Table 5).
| Before | After | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 7.34±0.09 | 7.35±0.06 | NS |
| P2 | 6.64±0.78 | 6.96±0.04 | NS |
| P3 | 6.36±0.08 | 7.88±0.10 | 0.01* |
| P4 | 6.23±0.03 | 7.90±0.07 | 0.01* |
| P5 | 7.08±0.02 | 7.08±0.11 | NS |
A significant increase in the total LAB count was observed in groups P3 and P4 (both p<0.05). Treatment with milk fermented using P. acidilactici BE or P. pentosaceus M103 increased the total LAB counts by 23.99% and 28.25%, respectively. Meanwhile, total LAB counts were not significantly changed in groups P1, P2, and P5. These findings were consistent with the results of Palani Kumar et al. (2021), who observed increased counts of Lactobacillus spp. in the feces of diabetic rats treated with Lactobacillus fermentum MCC2760. The researchers determined that the probiotic reduced pathogen counts in feces; suppressed the expression of inflammatory markers (TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-12); increased IL-10 expression in adipose tissues; and improved the expression of GLP-1, ZO-1, and CB2 in the intestine.
Immunohistochemistry is a staining technique used to identify tissue or cell components through the interaction between antigens and antibodies. Antibody binding sites are identified by direct antibody labeling or the use of secondary labeling methods (Kabiraj et al., 2015). IHC staining is suitable for observing insulin based on its ability to monitor the distribution of specific enzymes in normal cell structures and detect cell components and biomacromolecules. The appearance of a brown color in the area of the cell with specific antigen–antibody bonds indicates a positive IHC reaction (Szkudelski, 2001). Fig. 2 presents the histopathological findings of pancreatic beta-cells in rats subjected to IHC staining with anti-insulin antibody.
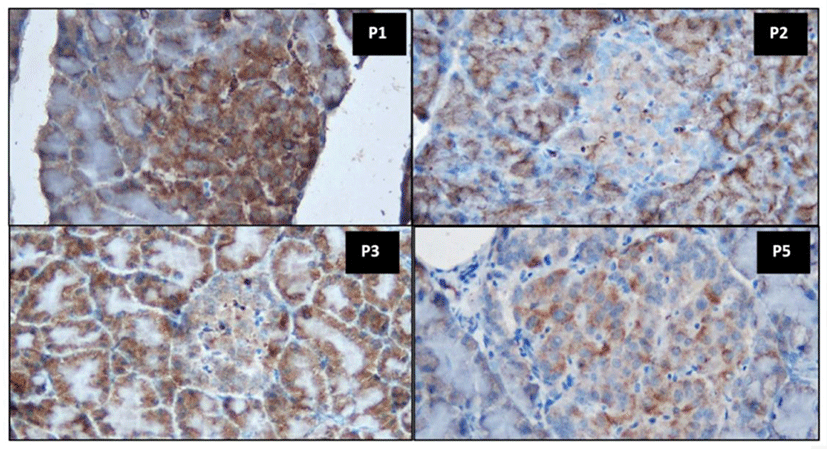
In nondiabetic rats, the insulin-secreting beta-cells represented the main cell population in the islets. Positive insulin production, as a marker of immunoreactive pancreatic beta-cells, was characterized by dark brown granules present in the cytoplasm of beta-cells (P1). Immunostaining in diabetic untreated rats (P2) revealed a decreased number of beta-cells similarly as observed in diabetic rats treated with metformin (P5). Decreased insulin production in pancreatic beta-cells positively stained with anti-insulin antibody indicated reduced insulin synthesis by these cells. This confirmed the damaging effects of STZ on pancreatic beta-cells.
An apparent increase in insulin production was observed in diabetic rats treated with milk fermented using P. acidilactici BE (P3, Fig. 2). This suggested that the administration of milk fermented using P. acidilactici strain BE both reduced blood glucose levels (Table 3) and improved the function of pancreatic beta-cells (Fig. 2) in experimental animals. The improvement of pancreatic beta-cell counts may be related to antioxidants and other bioactive compounds synthesized by P. acidilactici BE in fermented milk products. Yadav et al. (2008) reported that probiotic cultures of L. acidophilus NCDC14 and L. casei NCDC19 had antioxidant activity, allowing them to inhibit lipid peroxidation and reduce oxidative damage in pancreatic beta-cells in rats. Fig. 2 illustrates the stronger immunoreactivity of pancreatic beta-cells in diabetic rats treated with milk fermented with P. acidilactici BE compared to the findings in diabetic rats treated with metformin. This finding strongly suggests that the administration of fermented milk containing the probiotic P. acidilactici strain BE more strongly improves beta-cell counts than metformin.
Immunohistochemistry was performed to observe pancreatic cells capable of producing insulin. Insulin production by pancreatic beta-cells was assessed using IRS (Table 6). In this experiment, group P4 was excluded because blood glucose levels were not reduced by treatment.
Conclusion
The administration of milk fermented using P. acidilactici strain BE resulted in reduced blood glucose levels and increased insulin production in pancreatic beta-cells in diabetic rats. Our findings demonstrated that milk fermented with P. acidilactici BE had similar effects on blood glucose levels and the structure of insulin-producing pancreatic cells as metformin.













