Introduction
Sheep milk is an important source of food for human consumption. The high demand for milk due to the increasing human population raises various concerns regarding food quality and safety (Sun et al., 2015). Feed is the most important and variable element in milk production (Wang et al., 2020), and its quality has significant effects on animal health, production performance, and milk quality (Qi et al., 2018). Therefore, rations need to be adjusted via systemic manipulations (Angeles-Hernandez et al., 2020). It is necessary to reduce food production costs to promote global food safety and environmental nutrition sustainability, which may have beneficial effects on global food production (FAO, 2018). The problem of meeting food demands due to the increasing population results in malnutrition and a lack of micronutrients in the population (Georganas et al., 2020). Losses of nutrients during the production, postharvest, and processing stages of the food supply chain are known as “food waste” (Gustavsson et al., 2011). Food byproducts have good nutritional value and provide high-quality nutrients for human consumption (Lipinski et al., 2013; Westendorf, 2000). Pistachio shell (PIS), pomegranate hull (POM), and olive pulp (OP) are unique among food byproducts due to the bioactive substances they contain. Food byproduct can replace some of the feed sources used in animal nutrition (Ominski et al., 2021). Therefore, the utilization of these valuable plant parts, which are treated as agricultural byproduct, as feed contributes to the development of biofunctioning of sheep milk in addition to economic contribution (Georganas et al., 2020).
Pistachio, pomegranate and olive are widely produced in the Southeast region of Turkey (TÜİK, 2020). Therefore, there are many production facilities where these fruits are processed and a high amount of byproducts is produced. These fruit byproducts constitute important environmental problems for the production enterprises (Sagar et al., 2018). On the other hand, due to reasons such as climate change and environmental pollution, there is a low yield in grain harvests, which are widely used in animal husbandry (Nardone et al., 2010). This situation causes significant problems in accessing roughage resources in countries. For this reason, it is necessary to investigate alternative feed sources for animal feeding and to reveal their effects on animal products.
To date, most studies have focused on management strategies for improving dairy nutrition. Although these studies were employed to improve milk production and quality, the relevant physiological and metabolic mechanisms remain unclear. Sheep milk contains high contents of proteins, fats, and lactose. The composition of sheep milk differs from that of other dairy animal milk (Bittante et al., 2022; Ospanov and Toxanbayeva, 2020). Low molecular weight amino acids in milk and dairy products are the end products of gene expression in various metabolic pathways affecting the mechanism of lactation (Sun et al., 2020). It is useful to measure the levels of these compounds for determining the metabolic properties of milk (Murgia et al., 2016; Sundekilde et al., 2014; Wu et al., 2021). However, limited studies have been conducted on changes in milk composition in different ration applications. Chromatographic methods based on mass spectrometry have been applied to various studies on the metabolite profiles of different milk types (Caboni et al., 2016; Mung and Li, 2018). Most studies have focused on cow milk, and there are few studies on sheep milk and its products. In this study, it was aimed to determine the effects of different rations and food byproducts, which are rich in terms of bioactive compounds (PIS, POM, and OP), on the bioactive composition of sheep milk through milk amino acid and fatty acid parameters.
Materials and Methods
The research was conducted in the Farm Animals Unit of Harran University’s Animal Experiments Application and Research Center. The necessary permissions for the applications to be conducted related to the study were granted by Harran University’s Animal Experiments Local Ethics Committee (2022-001/10). In the study, 40 Awassi sheep (body weight: 64.04±1.04 kg; days in milk: 75.25±1.06; daily milk yield: 1,191.45±48.02 g) were used as animal material. PIS, POM, and OP were dried and added to the ration in powder form. During the study, the sheep in the groups were fed with four different rations. The rations given to sheep during the study included (1) a control diet without additional byproducts (CON), (2) PIS, (3) POM, and (4) OP. The rate of byproducts to be included in the ration was 5 percent. The contents and nutritional compositions of the rations used in the study are shown in Table 1. The raw nutrient contents of POM, PIS, and OP used in this study are presented in Table 2, amino acids, and fatty acids contents are presented in Table 3 and Table 4, respectively.
Milk samples collected during the morning milking on the 45th day of the research were used to determine amino acid and fatty acid profiles. Pre–post dipping was performed before and after milk samples were collected to ensure milking hygiene. Samples were kept at −80°C until they were analyzed.
Milk samples were separated from proteins and other macromolecules by the 3 KDa Amicon filter method. The resulting filtrate was analyzed via liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), and the amino acids present in the sample were determined. The samples were prepared according to the commercial kit protocol. For this purpose, a 50-μL sample was transferred to a sample bottle, 700-μL reagent-1 was mixed with the internal standard mixture labeled with a 50-μL stable isotope, and the mixture was vortexed for 5 s. It was injected into the LC-MS/MS (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) system according to the device’s instructions (mass detector parameters; gas temperature: 150°C, gas flow: 10 L/min, nebulizer pressure: 40 psi, and capillary voltage: +2,000 V). The specified amino acid concentration was determined in μmol/L (Oz et al., 2022).
For fatty acid analysis, 5-mL hexane was added to 5-mL milk and vortexed for 5 min. The resulting mixture was centrifuged at 2,500×g for 15 min and kept in a dark environment at +4°C for 24 h. Then, the supernate was mixed with 2-mL 1 M KOH-methanol, and 5 mL of 14% boron trifluoride was added. The sample was methylated for 60 min at 100°C and then extracted using 10-mL hexane. Fatty acid methyl esters were read on the gas chromatography-flame ionization detection (GC-FID) device (GC-FID: Nexis GC 2030, Shimadzu; Colon: TR-882192 Capillary Column TR-CN100, Teknokroma, Barcelona, Spain). Helium was used as the carrier gas. The column temperature was initially at 50°C and was increased by 10°C/min to 190°C. It took 130 min for the fatty acid methyl esters to be read on the device. The temperature of the injector was 270°C, and the temperature of the detector was 300°C (Razzaghi et al., 2015).
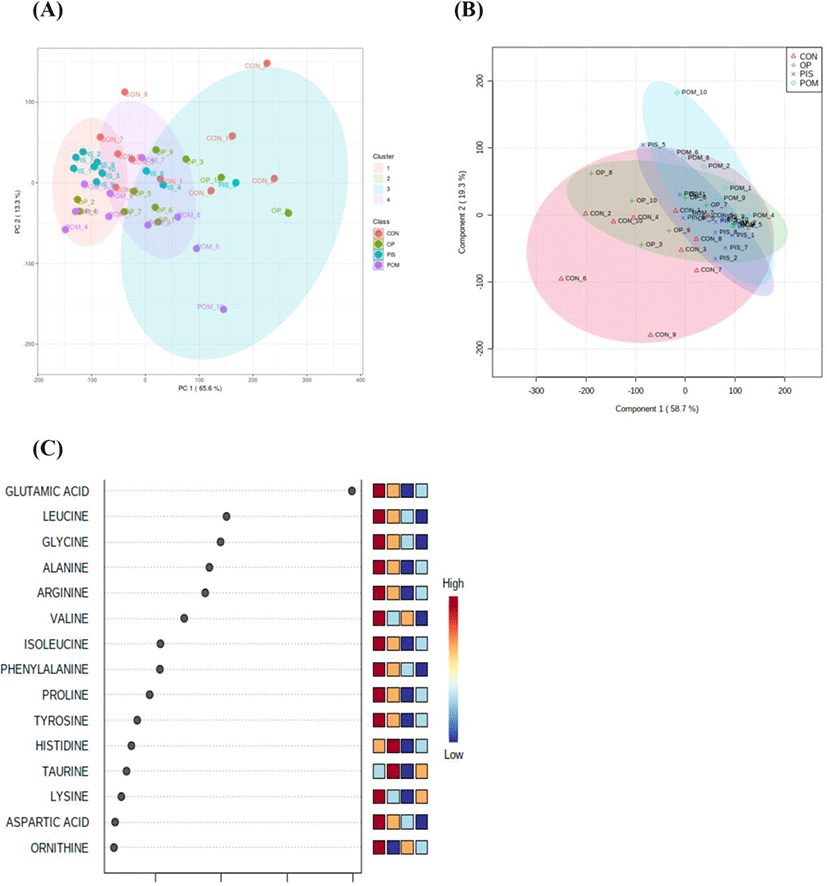
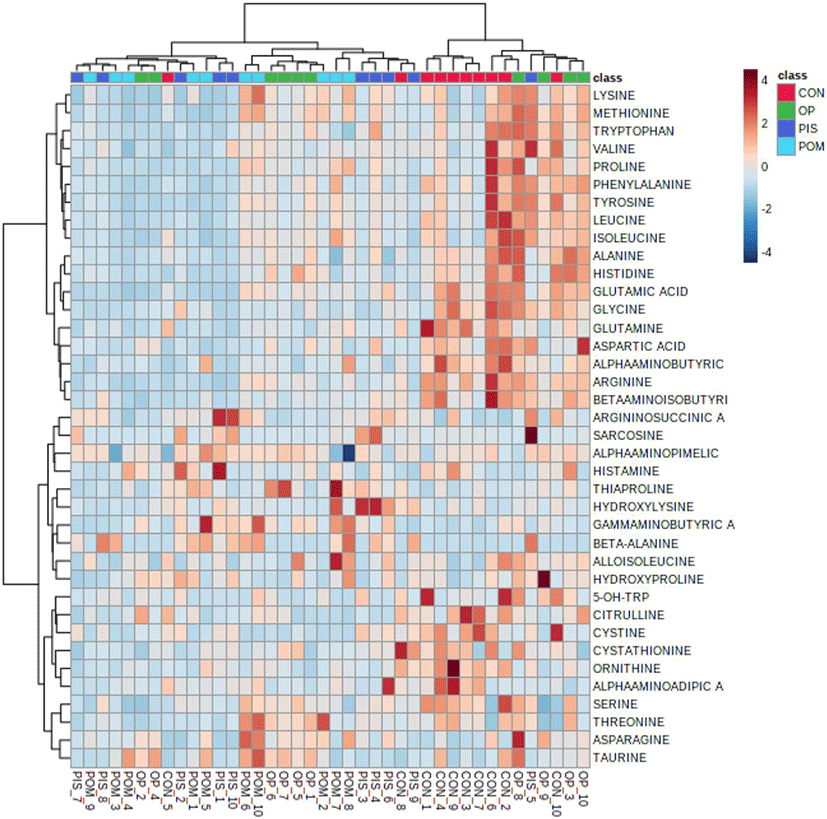
The assumptions of equality and normality of variances in the data were made using the Levene and Shapiro–Wilk tests (p>0.05). Amino acid and fatty acid data in the groups were compared using a general linear model and the Tukey honestly significant difference multiple comparison test. Amino acid data obtained from LC-MS/MS analysis was uploaded on the metaboAnalyst 5.0 (https://www.metaboanalyst.ca/) server. Principal component analysis (PCA) was first performed to detect the segregation and clustering of amino acids detected in the CON, PIS, POM, and OP groups. Then, partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) was applied to maximize segregation and clustering. The variable importance in projection (VIP) scores of amino acids contributing to the discrimination of the groups was calculated. A hierarchical clustering heat map was created to visualize the differentiating amino acids in the CON, PIS, POM, and OP groups. The data were presented as X±SE (mean±SE). The statistical significance level was evaluated as p<0.05 for all tests.
Results
The LC–MS/MS analysis of the sheep milk samples revealed the presence of 38 amino acids (Table 5). In the research groups, there were dramatic reductions in alanine, citrulline, glutamine, glutamic acid, glycine, leucine, ornithine, and alpha-aminoadipic acid. Significant increases in amino acids were detected in the following groups: argininosuccinic acid, gamma-aminobutyric acid, beta-alanine, and sarcosine in the PIS group; Asparagine, gamma-aminobutyric acid, beta-alanine, and taurine in the POM group; alanine, histidine, gamma-aminobutyric acid, and taurine in the OP group. PCA and PLS-DA analyses to visualize the sample distribution determined in the groups are presented in Figs. 1A and B. PCA was performed to provide an overview of the difference in 38 amino acid profiles between groups that were fed different diets containing pistachio, pomegranate and olive byproducts. The findings of the analyses revealed that there was no clear separation and clustering among the groups. PLS-DA was performed to maximize the differences between the groups. Although it provided better segregation and aggregation compared to PCA, the groups did not differ significantly. The VIP graph of the amino acids distributed in the CON, PIS, POM, and OP groups is shown in Fig. 1C. Glutamic acid, leucine, and glycine (Fig. 1C) are the amino acids with the highest scores (Fig. 2A). Other amino acids that contributed to the discrimination in the groups are shown in Fig. 2. The applications of 5% PIS, POM, and OP in the study had no statistically significant effects on the short-, medium-, and long-chain fatty acid concentrations of milk (Table 6; p>0.05).
Discussion
Amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, play a vital role in various processes, such as the synthesis of proteins, hormones, and neurotransmitters in the human body (Khadka, 2021). Amino acids, like vitamins and minerals, aid in our overall health and well-being. They also perform several genetic functions, such as body functioning, growth, and health maintenance, by optimizing the concentration of micronutrients (Mariotti and Gardner, 2019). Amino acid supplementation has various benefits, including increasing the performance and the secretion of anabolic hormones, shifting energy use during exercise, preventing the negative effects of excessive exercise, and preventing mental fatigue (Molinero and Márquez, 2009). Due to these properties, increasing the levels of amino acids with biological function in foods for human consumption increases the nutritional value of sheep milk. In the current study, the amino acid profiles of sheep milk were determined and the effects of PIS, POM, and OP added to sheep rations on amino acids and fatty acid profiles of milk were compared.
Most of the biofunctionality of dairy products is attributed to peptides released during the gastrointestinal absorption process or the enzymatic degradation of milk proteins via fermentation (Abd El-Salam and El-Shibiny, 2013). In this study, high levels of arginine, glutamic acid, lysine, and valine were detected in sheep milk. Milk amino acid concentrations differ in other livestock species for milk production purposes (Caboni et al., 2019; Xu et al., 2020). This difference can be considered a marker to separate milk from different species (Murgia et al., 2016). Valine, one of the main branched amino acids identified in our study, plays a role in the metabolic pathways for the production of branched-chain fatty acids (Li et al., 2020a) and contributes to the flavor of dairy products (Chilliard et al., 2003). As a result of this property, valine can be effective in the aroma formation of sheep milk. Glutamic acid exerts multifunctional effects on intestinal health and energy metabolism (Smilowitz et al., 2013). De novo serine synthesis is critical for the development and function of the central nervous system. Serine, as a nonessential amino acid, has many metabolic functions during different stages of development, such as nucleotide synthesis, protein synthesis, amino acids, and neurotransmitter synthesis, and provides precursors for serine-derived lipids (Tabatabaie et al., 2010). Arginine plays an important role in transcriptional regulations, such as protein–DNA, protein–RNA, and protein–protein interactions (Li et al., 2020b). This study found a dramatic reduction in amino acids, such as alanine, citrulline, and glutamine, in the POM, PIS, and OP groups. Some of the amino acids required for milk protein synthesis are provided via diet (Wang et al., 2019). These amino acids should be in digestible and absorbable forms in the gastrointestinal tract. The ratio of amino acids, such as histidine and glutamine, affects the absorption of other amino acids and creates a restrictive effect in terms of protein yield (Bequette et al., 2000; Meijer et al., 1993). This may lead to different milk amino acid concentrations in research groups.
PISs, POMs, and OP are rich in phenolic compounds (Aliyari et al., 2020). Although phenolics do not have any direct effect on the rumen, they slow down the physical and microbial degradation of the consumed feed by creating a flexible covalent bond with hemicellulose and cellulose (Waghorn and McNabb, 2003). The different phenolic contents and amounts of the feed additives used in the research may change the digestive kinetics of the feeds used and increase the concentrations of the amino acids in the POM, PIS, and OP groups. Previous studies have reported that PISs are rich in asparagine, citrulline, ornithine, tyrosine, beta-alanine, and arginosuccinic acid amino acids (Koyuncu et al., 2018; Koyuncu et al., 2021). Among these amino acids, beta-alanine and arginosuccinic acids were found to be higher in milk from sheep fed with PISs than in milk from other groups. Beta-alanine combines with histidine to form a molecule within the cell called carnosine (Varanoske et al., 2019). Carnosine buffers the acidic environment created by intense exercise, allowing for better durability and performance (Shbib et al., 2021). Gamma-aminobutyric acid, which is detected in large quantities in the POM and OP groups, is a neurotransmitter that blocks the stimulation of nerve cells in the brain. It creates a calming and protective effect on the body and brain (Sharma and Bist, 2019). Free forms of amino acids can be utilized faster in intestinal absorption (Murgia et al., 2016). The differences in the amino acids among the research groups could be due to the differences in the amino acid content of the PIS, POM, and OP used as feed additives. The high concentrations of amino acids in milk, which are also found in high concentrations in the products used as feed additives, may contribute to the change in the biofunctional structure of milk. Most studies in which PIS, POM, and OP are used in animal nutrition focus on milk yield and milk quality. In these studies, it was emphasized that byproducts used as feed additives had a similar effect on milk yield and milk quality (Kahraman et al., 2022). The presented study gained importance in terms of revealing the effect of PIS, POM, and OP on milk amino acid profile.
The different dietary programs applied in the study did not affect the concentrations of short-, medium-, and long-chain fatty acids in milk. Our results are partially similar to the change in short- and medium-chain saturated fatty acid concentrations reported by Razzaghi et al. (2015) in a study using pistachio peel and tomato pulp in goats. It has been reported that tomato pulp and OP added to the ration of Awassi sheep raised in Syria caused similar results in terms of fatty acid change (Abbeddou et al., 2015). In studies where olive byproducts were added to sheep rations, it was stated that the olive tree leaves changed cis-9 and trans-11 conjugated linoleic acid values (Tsiplakou and Zervas, 2008). The increase in fatty acids with fewer than 16 carbon chains is either due to excess secretion of long-chain fatty acids from the blood or due to higher de novo synthesis of short-chain fatty acids in the mammary gland (Dorea and Armentano, 2017). Fatty acid profile changes in sheep milk are due to ration (Chiofalo et al., 2004) and genotypic (Payandeh et al., 2016) differences as well as ration and breed interactions (Tsiplakou and Zervas, 2008).
Agricultural byproduct and byproducts are rich in bioactive components that show antimicrobial and antioxidant activity and have several positive effects on health. Fruit and vegetable industry byproducts containing a high content of antioxidant components, such as carotenoids, tocopherols, flavonoids, and ascorbic acid, are used as substitutes for synthetic antioxidants in food, cosmetic, and pharmaceutical industries (Duda-Chodak and Tarko, 2007). Under normal conditions, biologically active compounds found in plants are not easily accessible and these natural compounds need to be subjected to an extraction process (Ribeiro et al., 2015). The high levels of some amino acids in sheep milk, which exist in food byproducts (PIS, POM, and OP) and are rich in terms of bioactive compounds, reveal the use of animals as converters in making these amino acids suitable for human consumption. The findings we obtained from the study increase the amount of amino acids with biological functions such as beta-alanine, argino succinic acid and gammaminobutyric acid, increasing the nutraceutical and therapeutic effect of sheep milk. However, significant reductions in amino acid concentrations of alanine, citrulline, glutamine, glutamic acid, glycine, leucine were observed. Therefore, the benefit-harm relationship should be considered in this change in the milk amino acid profile. This study has shown promising results on the use of agricultural byproducts with biofunctional properties in animal feed and the transfer of these properties to animal products. In addition, the inclusion of PIS, POM, and OP in rations contributes to the potential health benefits as well as the reduction of food byproduct.
Conclusion
In the presented study; it was determined that PIS, POM, and OP added to sheep rations at a rate of 5% caused significant changes in milk amino acid profiles without affecting the milk fatty acid profile. It is recommended to continue in vivo and in vitro studies, in which food byproducts known to have health effects are mixed into the rations at different rates, in order to improve the bioactive properties of sheep milk.













