Introduction
Honey has been consumed for the nutraceutical values and various health benefits, including anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, and anti-bacterial properties, in addition to wound-healing ability (Alvarez-Suarez et al., 2013). With regard to biological functions, honey is an interesting natural source for medicinal uses (Mandal and Mandal, 2011). Among the different categories of honey, Manuka honey (MH) has predominantly attracted attention owing to its biological functions including anti-bacterial activity (Alvarez-Suarez et al., 2013). MH is derived from the Manuka tree (Leptospermum scoparium) growing throughout New Zealand and eastern Australia and has long been used for treating infections, including those associated with abscesses, surgical wounds, traumatic wounds, and burns (Kato et al., 2012; Patel and Cichello, 2013).
E. coli O157:H7 is a serotype of E. coli producing Shiga toxins 1 and 2 as important virulence factors and causes significant disorders such as hemorrhagic colitis and bloody diarrhea (Mohawk et al., 2010). This pathogen is able to attach, colonize, and form biofilm, which is more than 100 times resistant than planktonic cells, on abiotic surfaces (e.g., steel, plastic, and glass) and biotic surfaces (e.g., fruits, vegetables, and meat) (Jefferson, 2004; Uhlich et al., 2006). Consequently, biofilms have become problematic in various food industries, including breweries, dairy, poultry, and meat processing, because bacteria readily form biofilms on the surface of food and food-related facilities (Srey et al., 2013). Hence, this study demonstrates the anti-biofilm property of MH against E. coli O157:H7.
Materials and Methods
E. coli O157:H7 ATCC 35150 was obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA) and cultured in Luria-Bertani (LB) medium (LPS solution, Daejeon, Korea) at 37°C. For the experiments, E. coli O157:H7 was cultured at 37°C for 8 h and was diluted to 1×108 colony forming unit (CFU) per mL corresponding to 0.2 at 600 nm of optical density (OD) in fresh LB broth. MH with Unique Manuka Factor (UMF) 5+ (Comvita, Paengaroa, New Zealand) was purchased from a local shop in Seoul, Korea, and was diluted in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), filtered through a 0.2-μm filter.
Biofilm formation assay was performed as described previously (Kim et al., 2019). Briefly, E. coli O157:H7 (100 μL; 1×108 CFU/mL) was cultured with or without MH (0, 0.1, and 0.2 g/mL) in a microtiter plate for 24 h at 37°C. After washing the microtiter plate with PBS, biofilm was stained 0.1% crystal violet for 30 min. For quantification of biofilm, 0.1% acetic acid and 95% ethanol were added to dissolve the bacterial cells bound crystal violet and the absorbance was measured at a wavelength of 595 nm to determine biofilm formation. Additionally, at 24-h incubation, E. coli O157:H7 biofilm cells were serially diluted and CFU of E. coli O157:H7 were determined by plating on LB agar. For the effect of pre- or post-treatment with MH on the biofilm of E. coli O157:H7, MH (0, 0.1, and 0.2 g/mL) was treated to a microtiter plate for 24 h. The bacterial suspension was then added and further incubated at 37°C for 24 h. Conversely, the bacterial suspension was treated to a microtiter plate at 37°C for 24 h followed by the addition of MH (0, 0.1, and 0.2 g/mL) and further incubation at 37°C for 24 h. E. coli O157:H7 biofilm was then assessed as described above.
To examine the viability of cells in E. coli O157:H7 biofilm, reduction assay was performed using XTT (2,3-Bis [2-methoxy-4-nitro-5-sulfophenyl]-2H-tetrazolium-5-carboxanilide) (Biotium, Fremont, CA, USA). In brief, after the formation biofilm of E. coli O157:H7 with or without MH in a microtiter plate for 24 h, planktonic E. coli O157:H7 cells were removed by washing with PBS. Subsequently, PBS (200 μL) and XTT solution (100 μL) were added to the microtiter plate and incubated at 37°C for 2 h. The absorbance of developed color was measured at a wavelength of 492 nm, while the absorbance of background was detected at a wavelength of 630 nm. Normalization for the consequential absorbance was obtained by the subtraction of the background absorbance values.
To examine adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production in biofilm cells, E. coli O157:H7 was formed biofilm with or without MH for 24 h. Thereafter, ATP production was assessed using BacTitier-Glo microbial cell viability assay kit (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). Bioluminescence was determined at 560 nm using VICTOR X4 multi-label plate reader (Perkin Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA).
The inhibitory effect of MH on the growth of E. coli O157:H7 planktonic cells was determined. Briefly, E. coli O157:H7 was incubated with or without MH (0.1 and 0.2 g/mL) for 1, 3, 6, 12, and 24 h. Following incubation, the bacterial growth was measured at a wavelength of 595 nm.
Results are expressed as mean SD of triplicate samples obtained from independent three experiments. Statistically significant difference was determined in comparison with controls by conducting an unpaired two-tailed t-test and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) using GraphPad Prism 5 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA) and IBM SPSS Statistics 23 software (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA), respectively.
Results and Discussion
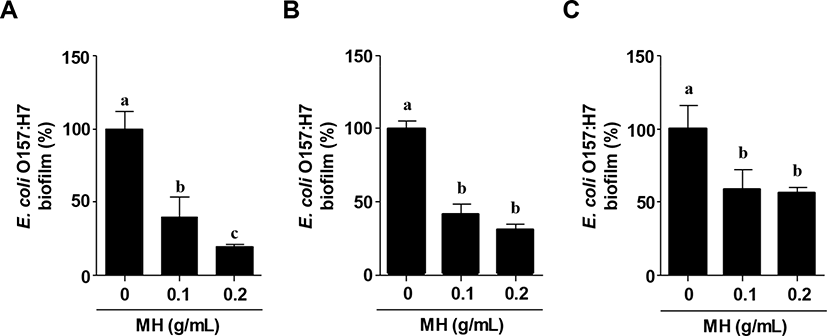
MH significantly inhibited biofilm formation by E. coli O157:H7 (Fig. 1A). Further, to examine the preventive effect of MH on biofilm formation, MH was added 24 h prior to the inoculation of E. coli O157:H7. Fig. 1B showed that MH markedly reduced the biofilm formation by E. coli O157:H7. Moreover, MH effectively disrupted E. coli O157:H7 biofilm (Fig. 1C); however, the inhibitory effect was not dose-dependent similar to that related to pre-treatment with MH. Although honey has been used as a traditional medication for microbial infections, the anti-bacterial properties of honey, including MH, have been mostly focused against clinical isolates in chronic wounds. Ulmo honey and MH exhibited optimal anti-bacterial activities against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates as well as E. coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa according to agar diffusion assay analysis (Sherlock et al., 2010). Another study also showed similar results that MH eradicated methicillin-resistant S. aureus in a synergistic manner with antibiotics (Jenkins and Cooper, 2012). More recently, it was demonstrated that a multispecies biofilm consortium of wound pathogens, including S. aureus, Streptococcus agalactiae, P. aeruginosa, and Enterococcus faecalis, was attenuated by MH and honeydew honey (Sojka et al., 2016). Although these previous studies about honey including MH revealed effective anti-bacterial agents, this study showed for the first time that MH significantly reduced the biofilm formation as well as the disruption of E. coli O157:H7 biofilm.
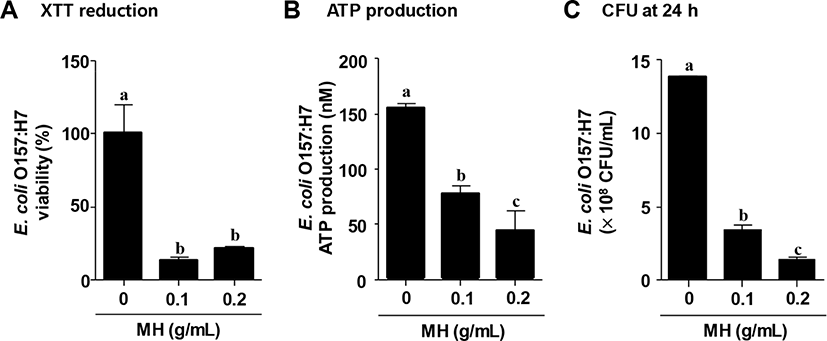
Metabolically active cells are able to enhance XTT reduction, reflecting an increase of viability of biofilm mass (Nett et al., 2011; Sivaranjani et al., 2016). As shown in Fig. 2A, XTT reduction assay indicated that the viability of E. coli O157:H7 biofilm cells was significantly reduced by approximately 80% when treated with 0.1 g/mL MH, and treatment with 0.2 g/mL MH also significantly decreased viability (>70% reduction). Various anti-microbial agents prevented the biofilm formation of foodborne pathogens by decreasing the cellular metabolic activity of biofilm cells (Khan et al., 2017; Luís et al., 2014; Sivaranjani et al., 2016). Gallic acid, caffeic acid and chlorogenic acid significantly inhibited the XTT reduction of S. aureus, consequently preventing the biofilm formation (Luís et al., 2014). Furthermore, ATP production was measured in E. coli O157:H7 biofilm cells treated with or without MH. As expected, MH dose-dependently inhibited ATP production in E. coli O157:H7 biofilm (Fig. 2B). Therefore, these results indicate that MH suppressed the E. coli O157:H7 biofilm by decreasing the cellular metabolic activities such as XTT reduction and ATP production. Additionally, the viability of E. coli O157:H7 biofilm cells with or without MH was evaluated by counting CFU after 24-h incubation. Treatment with 0.1 g/mL MH was highly effective against E. coli O157:H7 viability, facilitating significant removal of bacteria (>70% reduction); furthermore, 0.2 g/mL MH demonstrated approximately 90% reduction in the viability of E. coli O157:H7 (Fig. 2C).
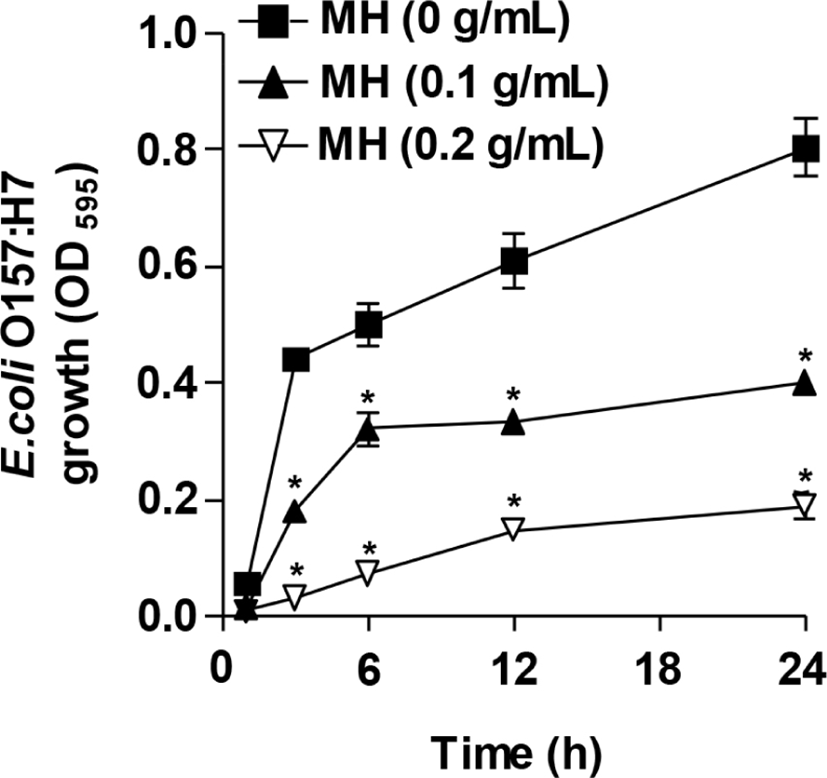
As can be seen in Fig. 3, the presence of 0.1 g/mL MH significantly inhibited the growth of E. coli O157:H7 planktonic cells even after 1-h incubation. A significant extent of inhibition was observed for another 24 h as opposed to the control culture of E. coli O157:H7. Similarly, a higher inhibitory effect on the growth of E. coli O157:H7 planktonic cells was exerted by 0.2 g/mL MH throughout the incubation time (1–24 h), suggesting that MH is effective against the growth of E. coli O157:H7 planktonic cells. Similar results were given in previous reports that cell-free supernatants of Pediococcus acidilactici HW01 suppressed the growth of Candida albicans as well as the biofilm formation (Kim and Kang, 2019). In addition, bacteriocin of Lactobacillus brevis DF01 inhibited the growth of E. coli, resulting in the reduction of biofilm formation (Kim et al., 2019). In accordance with the previous studies, this study also demonstrated that MH effectively inhibited the biofilm formation by decreasing the growth and viability of E. coli O157:H7. However, ginseng extract significantly prevented the biofilm formation by P. aeruginosa, whereas it did not reduce the growth of P. aeruginosa planktonic cells (Wu et al., 2011). Therefore, it can be speculated that the anti-biofilm ability against pathogenic bacteria may be differently regulated by decreasing the growth and viability of pathogenic bacteria, which result in the obstruction of biofilm formation at the initial stage, or by disrupting the established biofilm.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this study noticeably demonstrated that MH suppressed the biofilm formation of E. coli O157:H7 by decreasing bacterial growth and viability. Several studies have shown that MH has anti-bacterial activity against foodborne pathogens. This study, however, demonstrated that MH exerts anti-biofilm activity against E. coli O157:H7. Although extensive studies would be needed to establish the precise mechanism(s) of inhibitory action, results from this study suggest that MH may be promising a natural anti-bacterial agent for controlling E. coli O157:H7.













