Introduction
Intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) with intact tight junctions (TJs) form a barrier between the external environment and the mammalian host (Yu et al., 2018). Normal functioning of the intestinal epithelial barrier is critical for maintaining health (Citi, 2018; Odenwald and Turner, 2017; Turner, 2009). Disruption of TJs and paracellular permeability can promote the entry of molecules and activate the immune system, leading to continuous tissue destruction (Lee, 2015). Hence, maintaining the integrity of the intestinal epithelial barrier is critical for inhibiting the development of gastrointestinal diseases and inflammation (Tlaskalová-Hogenová et al., 2004).
Indole, an interspecies and interkingdom signaling molecule, plays essential roles in bacterial pathogenesis and eukaryotic immunity (Lee et al., 2015). The human intestinal tract is rich in a diverse range of about 1014 commensal bacteria, some of which are crucial for nutrient assimilation and benefit the immune system (Tlaskalová-Hogenová et al., 2004). A metabolomic study demonstrated that the production of indoxyl sulfate and the antioxidant indole-3-propionic acid in animal blood depended entirely on enteric bacteria (Wikoff et al., 2009). In addition, indole and its derivatives may influence human diseases, such as bacterial infections, intestinal inflammation, neurological diseases, diabetes, and cancers (Lee et al., 2015).
Multiple protein complexes, which are crucial components of TJs, are located in IECs (Tsukita et al., 2001) and include occludin, claudins, and zonula occludens (ZO). These protein complexes are vital for the maintenance of TJs and permit cytoskeletal regulation of the intestinal barrier integrity (Van Itallie and Anderson, 2006). Pathogens damage the intestinal epithelial barrier, increase intestinal permeability, and induce the development of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC; Guo et al., 2015). IBD includes two chronic idiopathic inflammatory diseases, ulcerative colitis, and Crohn’s disease (Arrieta et al., 2009). Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is a harmful antigen that can trigger inflammatory responses in the intestinal tissue and can be detected in the serum of patients with NEC and IBD (Han et al., 2020). Recent studies have identified the association between clinically relevant concentrations (1–10 ng/mL) of LPS and intestinal barrier dysfunction under in vivo and in vitro conditions (Guo et al., 2013). In our previous study, Latilactobacillus curvatus BYB3 decreased the disease activity score of dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in a mouse model (Wang et al., 2022). Supplementation with indole or using Lactobacillus reuteri with high aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) ligand production can improve some metabolic symptoms (Swimm et al., 2018). Therefore, we hypothesized that L. curvatus BYB3 has a similar function. The supernatants of L. curvatus BYB3 and the metabolites of L. curvatus BYB3+indole ameliorated LPS-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction by upregulating the levels of TJ proteins in Caco-2 cells. These findings illustrated the mechanism underlying the destructive effect of clinically relevant concentrations of LPS on the intestinal epithelial barrier, providing evidence for the clinical application of metabolites of L. curvatus BYB3+indole in the treatment of LPS-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction.
The AhR is a ligand-dependent transcription factor that is widely expressed in vertebrates and is involved in numerous biological processes, such as cell proliferation (Xie et al., 2012), apoptosis (Marlowe et al., 2008), differentiation (Xie et al., 2012), and inflammatory response (Neavin et al., 2018). The AhR separates from its molecular chaperone complex and forms a heterodimer with the aryl hydrocarbon nuclear translocator (ARNT) in the nucleus. This AhR-ARNT dimer then binds to the upstream regulatory region of its target genes, such as the cytochrome P450 family 1 genes (CYP1A1 and CYP1B1; Esser and Rannug, 2015). Indoles may have utility as an intervention to limit the decline of barrier integrity and the resulting systemic inflammation that occurs with aging (Powell et al., 2020). Indoles and indole-metabolites secreted by the commensal bacteria have been shown to extend the healthspan of diverse organisms, including Caenorhabditis elegans, Drosophila melanogaster, and mice. The effects of indole and metabolites on animal heatlthspan were found to be AhR-mediated (Sonowal et al., 2017).
This study was conducted to research the effect of L. curvatus BYB3 on the intestinal epithelial barrier of the Caco-2 cells. Furthermore, we investigated the differences in mRNA expression levels of CYP1A1 and AhR in response to the metabolites of L. curvatus BYB3 and indole.
Materials and Methods
LPS derived from Escherichia coli O111:B4 was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Burlington, MA, USA) and dissolved in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) to prepare the stock solutions with concentrations of 1 mg/mL. DL-indole-3-lactic acid (ILA), 3-indoleacetic acid (IAA), indole-3-acetamide (IAM), and indole were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, and trifluoroacetic acid was procured from Daejung Chemicals and Metals (Siheung, Korea). All reagents were stored as specified by the manufacturer. The following antibodies were used in the study: Zona occludens 1 (ZO-1) antibody (Cat No.21772-1-AP, Proteintech, Chicago, IL, USA), claudin-1 antibody (Cat No. ab211737, Abcam, Cambridge, UK), nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) antibody (sc-372, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA), p-NF-κB p65 (Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA), β-actin C4 antibody (sc-4778, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA), secondary R-antibody (Cat. No. A11036, Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA), and Westar Supernova (Code.XLS3,0100, Cyanagen, Srl, Bologna, Italy).
Twenty-one probiotic candidates (Table 1) were cultivated in MRS medium (DifcoTM Lactobacilli MRS broth, BD Diagnostics, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) for 24 h at 37°C. Before use, the overnight LABs were diluted to a cell density of 107 CFU/mL in MRS broth prior to use. Indole was added at a final concentration of 58.5 mg/mL, and the cells were incubated at 37°C for 24 h. Then samples were centrifuged at 2,719.5×g for 15 min at room temperature. A total of 1 mL of the supernatant was collected and mixed immediately with 0.4 mL of Kovac’s reagent to determine the extracellular indole concentration. After the Kovac’s reagent was added, the mixture was vortexed to separate the phases. The top phase was collected, and the absorbance was measured at 540 nm.
| No. | Strains | Abbreviation | Source | Renamed genus (Zheng et al., 2020) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | L. curvatus BYB1 | BYB1 | Kimchi | Latilactobacillus curvatus |
| 2 | L. curvatus BYB2 | BYB2 | Kimchi | Latilactobacillus curvatus |
| 3 | L. curvatus BYB3 | BYB3 | Kimchi | Latilactobacillus curvatus |
| 4 | L. curvatus BYB4 | BYB4 | Kimchi | Latilactobacillus curvatus |
| 5 | L. curvatus BYB7 | BYB7 | Kimchi | Latilactobacillus curvatus |
| 6 | L. brevis OB1 | OB1 | Kimchi | Levilactobacillus brevis |
| 7 | L. brevis OB4 | OB4 | Kimchi | Levilactobacillus brevis |
| 8 | L. brevis OB3 | OB3 | Kimchi | Levilactobacillus brevis |
| 9 | L. sakei OB8 | OB8 | Kimchi | Latilactobacillus sakei |
| 10 | L. casei MYA5 | MYA5 | Kimchi | Lacticaseibacillus casei |
| 11 | L. sakei JNU533 | JNU533 | Kimchi | Latilactobacillus sakei |
| 12 | L. sakei MYA6 | MYA6 | Kimchi | Latilactobacillus sakei |
| 13 | L. fermentum NS4 | NS4 | Kimchi | Limosilactobacillus fermentum |
| 14 | L. amylovorus CH6 | KCNU | Swine intestine | Unchanged |
| 15 | L. acidophilus GP1B | GP1B | Swine intestine | Unchanged |
| 16 | L. plantarum L67 | L67 | Infant feces | Lactiplantibacillus plantarum |
| 17 | L. plantarum OY1 | OY1 | Kimchi | Lactiplantibacillus plantarum |
| 18 | L. plantarum OY2 | OY2 | Kimchi | Lactiplantibacillus plantarum |
| 19 | L. fermentum JNU532 | JNU532 | Kimchi | Limosilactobacillus fermentum |
| 20 | L. fermentum JNU534 | JNU534 | Kimchi | Limosilactobacillus fermentum |
| 21 | L. rhamnosus GG | LGG | Human intestine | Latilactobacillus rhamnosus |
L. curvatus BYB3 cells were isolated from traditional homemade kimchi in Gwangju and Jeollanam-do, and maintained in MRS broth. Cells were incubated in the MRS broth at 37°C and centrifuged at 1,500×g for 15 min at room temperature to obtain cell pellets. The pellets were stored in 10% glycerol or skim milk at –80°C until further use. The supernatant was filtered using a 0.2 μm syringe (Sartorius AG, Gottingen, Germany). The cells in the indole group were treated with 58.5 mg/mL indole, those in the BYB3 group were incubated with L. curvatus BYB3, and those in the BYB3+indole group were treated with both L. curvatus BYB3 and 58.5 mg/mL indole. The three groups were incubated in the MRS medium for 24 h at 37°C. The cell pellets were discarded, and the CFSs were used to treat the Caco-2 cells.
The Caco-2 cells used in the study were obtained from the Korean Cell Line Bank (No.30037.1, Seoul, Korea). Caco-2 cells were cultured in Modified Eagles Medium (MEM), high glucose (HyClone Laboratories, Logan, UT, USA), supplemented with 20% fetal bovine serum (GibcoTM, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), 1% MEM non-essential amino acids solution (100×; GibcoTM, Thermo Fisher Scientific), and 1% antibiotic-antimycotic solution (GibcoTM, Thermo Fisher Scientific) at 37°C in an atmosphere containing 5% CO2. The medium was replaced every two or three days. The Caco-2 cells (1×106 cells) were seeded in a 20×90 mm dish and treated with 10 ng/mL of LPS. They were then treated with 1 mL of indole, 1 mL of L. curvatus BYB3, and 1 mL of the BYB3+ indole metabolites supernatants.
Caco-2 cells (1×103 cells/cm2) were seeded in a Corning®, Costar®, Transwell® chamber with 0.4 μm pores (Corning, New York, NY, USA) that had been placed in a 24-well plate. Another Transwell® plate was kept blank. After reaching confluence, the cells were differentiated and polarized for 7–10 days in the culture medium. Subsequently, the Caco-2 cells were treated with 10 ng/mL of LPS and later with 100 μL of indole supernatant, 100 μL of L. curvatus BYB3 supernatant, and 100 μL of BYB3+ indole supernatants. The TEER assay was used to measure cell monolayer integrity before and after all treatments. The TEER was measured using an epithelial volt-ohm-meter equipped with a chopstick electrode [Millicell® ERS-2 (Electrical Resistance System), EMD Millipore, Burlington, MA, USA]. The electrode was immersed at a 90° angle, with one tip in the basolateral chamber and the other in the apical chamber. Care was taken to prevent contact of the electrode with the monolayer. Measurements were performed in triplicate for each monolayer. An insert without Caco-2 cells was used as a blank; the mean resistance of the blank was subtracted from all samples. The unit area resistance was calculated by dividing the resistance values by the effective membrane area (0.33 cm2).
Caco-2 cells (1×106 cells) seeded in a 20×90 mm dish were treated with 10 ng/mL of LPS followed by treatment with 1 mL of indole supernatant, 1 mL of strain 3, 15 and LGG supernatant, and 1 mL of indole+strain 3, 15 and LGG supernatants. After incubation for 24 h, the cells were collected for further analysis. Total RNA was isolated and converted into complementary DNA (cDNA) as described previously. Briefly, 2 μg of total RNA was used to cDNA using a Maxime RT PreMix kit (Oligo Dt primer; Cat. No. 25081, iNtRON Biotechnology, Seongnam, Korea). The following primers were used for real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR; Table 2).
| Gene | Primer sequences | References |
|---|---|---|
| CYP1A1 | F: TCGGCCACGGAGTTTCTTC | (Yang et al., 2022) |
| CYP1A1 | R: GGTCAGCATGTGCCCAATCA | |
| AhR | F: CAAATCCTTCCAAGCGGCATA | (Behfarjam and Jadali, 2018) |
| AhR | R: CGCTGACCTAAGAACTGAAAG | |
| GAPDH | F: GAAATCCCA CACCATCTTCC | |
| GAPDH | R: AAATGAGCCCCAGCCTTCT |
PCR was performed under the following conditions: Initial denaturation at 94°C for 3 min, followed by 40 cycles of the program with incubations at 94°C for 30 s, 60°C for 30 s, and 72°C for 1 min, followed by incubation at 65°C for 5 s, until the end of the program. The relative gene expression levels were determined by comparative analyses using the formula:
Caco-2 cells (1×106 cells) were seeded in a 20×90 mm dish and treated with 10 ng/mL of LPS and then 1 mL of the indole supernatant, 1 mL of BYB3 supernatant, and 1 mL of indole+BYB3 metabolites supernatant. After incubation for 24 h, the cells were collected for further analysis.
The total protein concentration in the cell lysates was determined using the PRO-PREP protein extraction solution (iNtRON Biotechnology). Briefly, 5×106 cells were immersed in 400 μL of the PRO-PREP solution and homogenized in ice for 10–20 min. The mixture was then centrifuged at 13,000×g at 4°C for 5 min, and the extracted protein was collected in the supernatant. The protein concentration was determined by the Pierce BCA Protein Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Equal amounts of protein (50 μg per lane) were separated using 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel, electroblotted (Mini-PROTEAN® II Cell Systems, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA), and transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane (Bio-Rad Laboratories). The proteins were blocked with 5% skim milk (Difco Laboratories, Detroit, MI, USA) and underwent overnight antibody incubation against E-cadherin, N-cadherin, Vimentin, and β-actin at 4°C. After incubation, the membranes were washed and incubated with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-mouse or anti-rabbit antibodies for 1 h at room temperature. After each was washed three times with PBST for 10 min, protein bands developed. The bands were detected via enhanced chemiluminescence, and the band density was determined using β-actin as the reference protein.
Caco-2 cells were seeded on a 24-well plate at a density of 1×103 cells/mL. These cells were treated with 10 ng/mL of LPS and then with 100 μL each of indole, L. curvatus BYB3, BYB3+indole metabolite supernatants. After treatment for 24 h, the cells were collected for the next step.
The cells were prepared as described in Material and Methods. Caco-2 cells were grown on glass coverslips; the slides were washed with PBS for 5 min at room temperature, fixed with 3.7% formaldehyde in PBS buffer for 20 min at 4°C, and again rinsed thrice with PBS buffer for 5 min at room temperature. The monolayers were permeabilized with 0.5% TritonTM X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich) for 20 min at room temperature and rinsed three times with PBS buffer for 2 min at room temperature. The slides were blocked with 5% skim milk in tris buffered saline with Tween® (TBST) for 1 h at room temperature without rinsing. They were then incubated with rabbit polyclonal anti-ZO-1 antibody, rabbit monoclonal anti-claudin-1 antibody, and rabbit polyclonal anti-NF-κB p65 antibody for 2 h at room temperature. The slides were rinsed thrice with TBST for 5 min at room temperature. The remaining incubations were performed in the dark. The slides were further incubated with an Alexa Fluor® 568 goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody (Abcam). Nuclei were stained using 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride (DAPI; Cat. No D1306, Invitrogen) for 15 s at room temperature. The samples were covered with a coverslip using the Vectashield® anti-fade mounting medium (Vector cat. #H-1000, Vector Laboratories, Newark, CA, USA). The edges of the coverslips were sealed by nail polishing. The slides were examined and analyzed using a fluorescence microscope (Olympus BX50, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan).
The indole derivatives in the CFSs were analyzed as previously described. Briefly, filtered samples were injected (10 mL), in triplicate, into an HPLC system (KNAUER, Wissenschaftliche Geräte GmbH, Berlin, Germany) equipped with a C-18 gravity 150×4.6 mm column, particle size: 5 μm (Macherey-Nagel GmbH & Co. KG, Düren, Germany). The flow rate was set to 1 mL/min, and the column oven temperature was maintained at 30°C. The running buffers were 0.3% trifluoroacetic acid solutions prepared in ultra-pure water (A) and acetonitrile (B). The process was initiated with an A:B ratio of 90:10; the linear gradient was applied to reach this ratio in 1 min. The steps included gradients with 55% solution A: 45% solution B for 28 min, 5% solution A: 95% solution B for 30 and 35 min, and 90% solution A: 10% solution B for 36 min. The measurements were stopped after 45 min. The detection wavelength was set at 280 nm.
All data are presented as mean±SD of triplicate experiments. Statistical significance comparing different sets of groups was determined using the Student’s t-test. In experiments comparing multiple experimental groups, statistical differences between groups were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Statistical analyses were performed using IBM® SPSS® Statistics 20 (IBM, Chicago, IL, USA), and a p<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
The probiotic candidates (Table 1 and Fig. 1) show the Lactobacillus strains’ ability to metabolize and reduce indole concentration during fermentation. Among the tested Lactobacillus strains, 3 (L. curvatus BYB3), 15 (Lactobacillus acidophilus), and 21 (Lactilacobacillus rhamnosus GG) demonstrated remarkable indole reducing abilities and were selected for subsequent analyses.
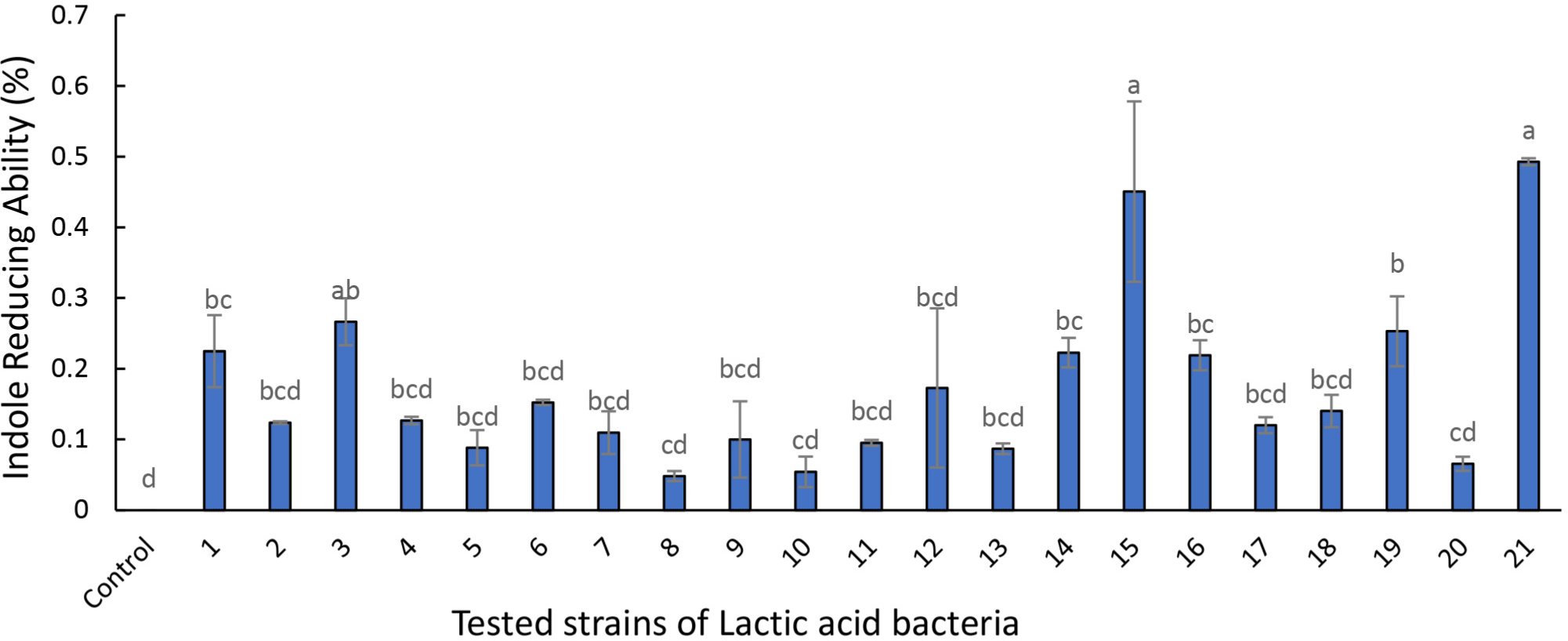
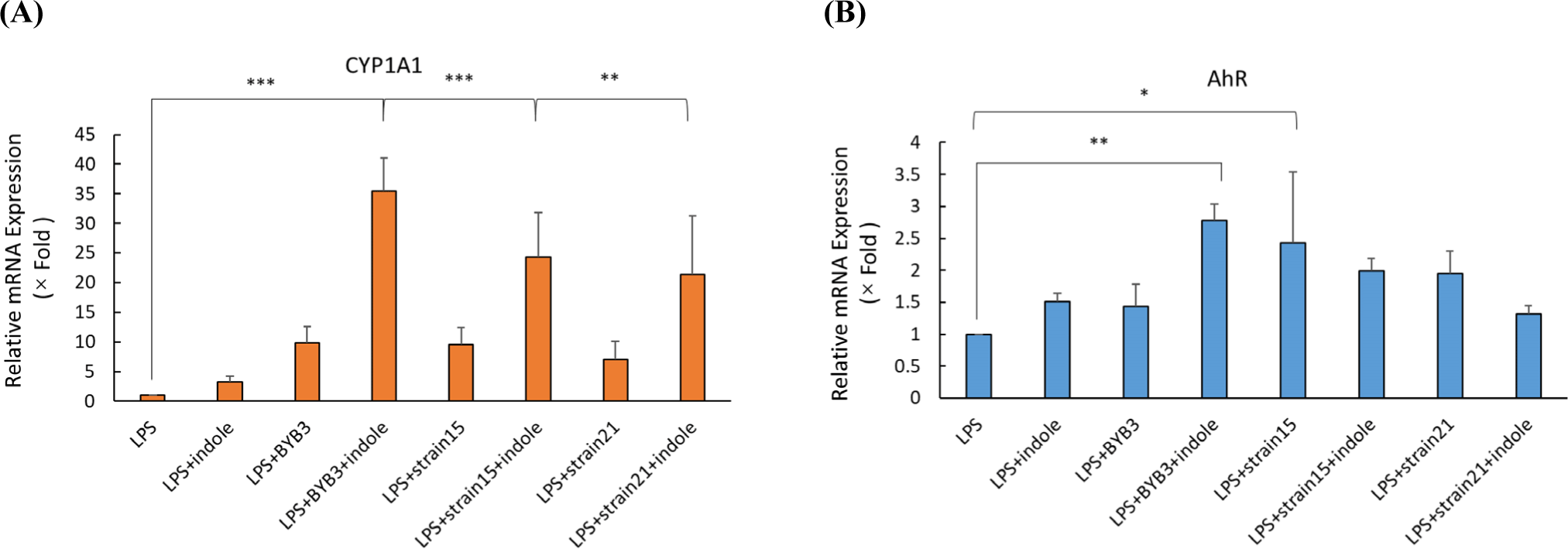
Caco-2 cells were treated with the 10% MRS as the control and 10% supernatant of the strains (3, 15, and 21) previously screened for 24 h. Treatment of the Caco-2 cells with 10 ng/ mL of LPS simulated the conditions of colitis. A previous study detected increased expression of CYP1A1, which is indicative of the AhR activation (Yu et al., 2018). To confirm the activation of the AhR by the metabolites, the mRNA expression levels of CYP1A1 and AhR were determined after treating the Caco-2 cells for 24 h with LPS alone or in combination with other supernatants. The supernatants of L. curvatus BYB3 and indole significantly increased the mRNA expression CYP1A1 and AhR by 35-fold and 3-fold, respectively (Figs. 2A and B).
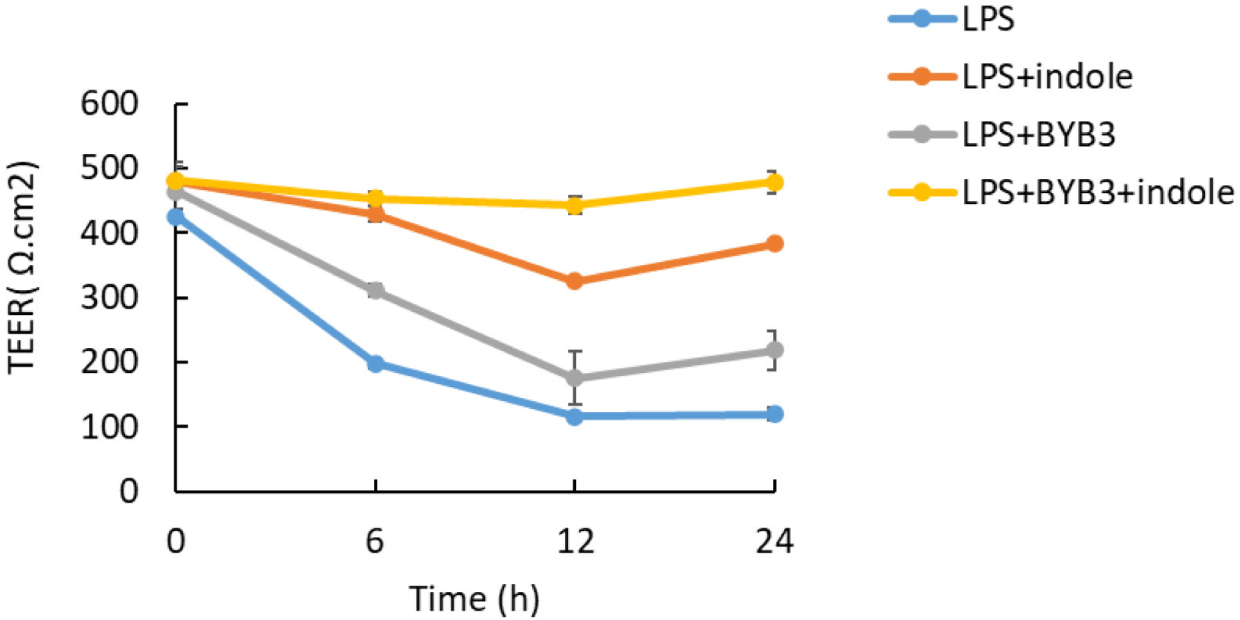
The TEER was used to measure cell monolayer integrity, which was assessed before and after all treatments. LPS increased the permeability of the intestinal epithelial barrier. However, the effects of the metabolites of L. curvatus BYB3 and indole on the LPS-mediated increase in intestinal permeability are unknown. LPS significantly decreased the TEER after 12 h; the reduction continued for 24 h after application (Fig. 3). In contrast, the metabolites of L. curvatus BYB3 and indole remarkably increased the TEER. This finding suggests that the metabolites reduced the permeability of the intestinal epithelial barrier. In addition, the supernatants of L. curvatus BYB3 and indole increased the TEER. However, co-treatment with the metabolites and LPS significantly restored the LPS-mediated increase in the permeability of the intestinal epithelial barrier in Caco-2 cells (Figs. 2 and 3). Hence, these metabolites could significantly protect against LPS-induced intestinal permeability.
LPS down-regulated the expression of the ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-1 proteins. Caco-2 cells were co-treated with 10 ng/mL of LPS, the supernatants of indole and L. curvatus BYB3, and the metabolites of BYB3+indole for 24 h to determine alterations in the expression of the TJ proteins. The Caco-2 cells treated with L. curvatus BYB3+indole showed increased expression of the ZO-1 and claudin-1 proteins compared to cells treated with LPS alone (Figs. 4A and B). Furthermore, cells treated with the metabolites of BYB3+indole showed a significant increase in the expression of ZO-1 and claudin-1.
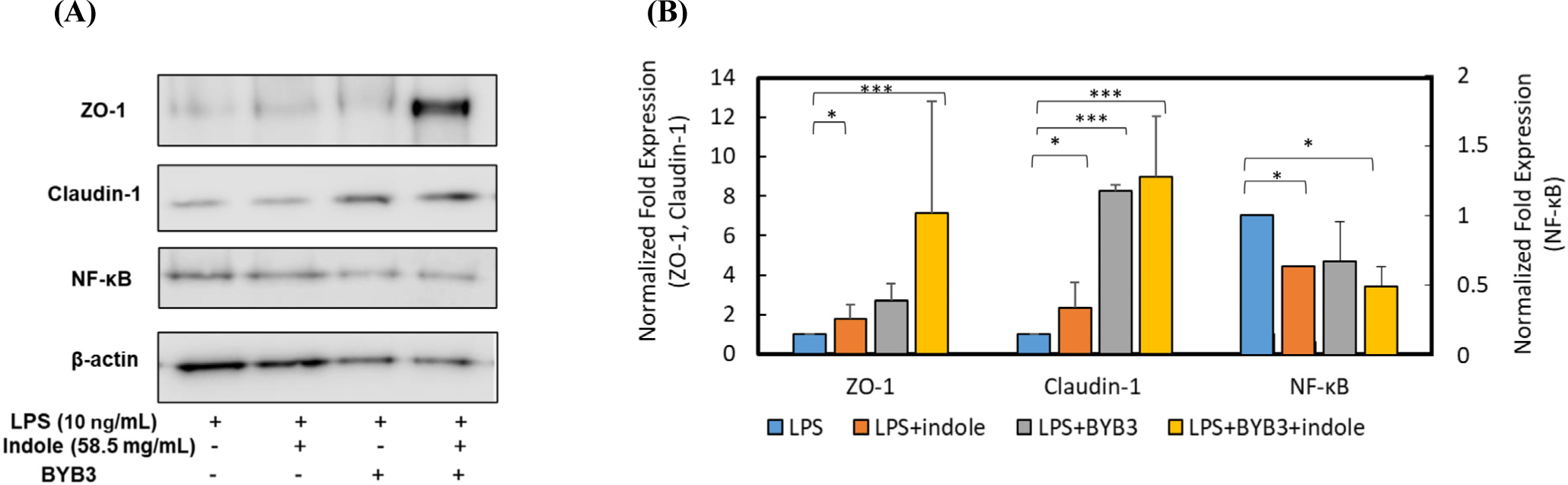
To explore the anti-inflammatory effects of the metabolites on Caco-2 cells, alterations in NF-κB, a biomarker of inflammation, were examined. NF-κB p65 and the protein levels of total and phospho-p65 were detected by Western blot analysis. Compared to the LPS-treated cells (10 ng/mL, control), the Caco-2 cells treated with the supernatants of L. curvatus BYB3, indole, and metabolites of BYB3+indole showed decreased NF-κB expression. The reduction was significant in the presence of the metabolites of L. curvatus BYB3+indole. Interestingly, co-treatment with the metabolites of L. curvatus BYB3+indole and LPS had a remarkable effect on the attenuation of LPS-induced inflammation.
Immunofluorescence was used to detect the localization and expression of TJ proteins, as these results were more intuitive. The LPS-treated group showed severe disruption in the structure of TJ proteins structure (Fig. 5). In contrast, the TJ protein ZO-1 was intact without any damage in the cells treated with LPS+BYB3+indole. LPS-induced disruption was repaired in the LPS+indole, and LPS+BYB3 treated groups. Examination of claudin-1 expression revealed a trend similar to that observed for ZO-1 (Figs. 5A and B).
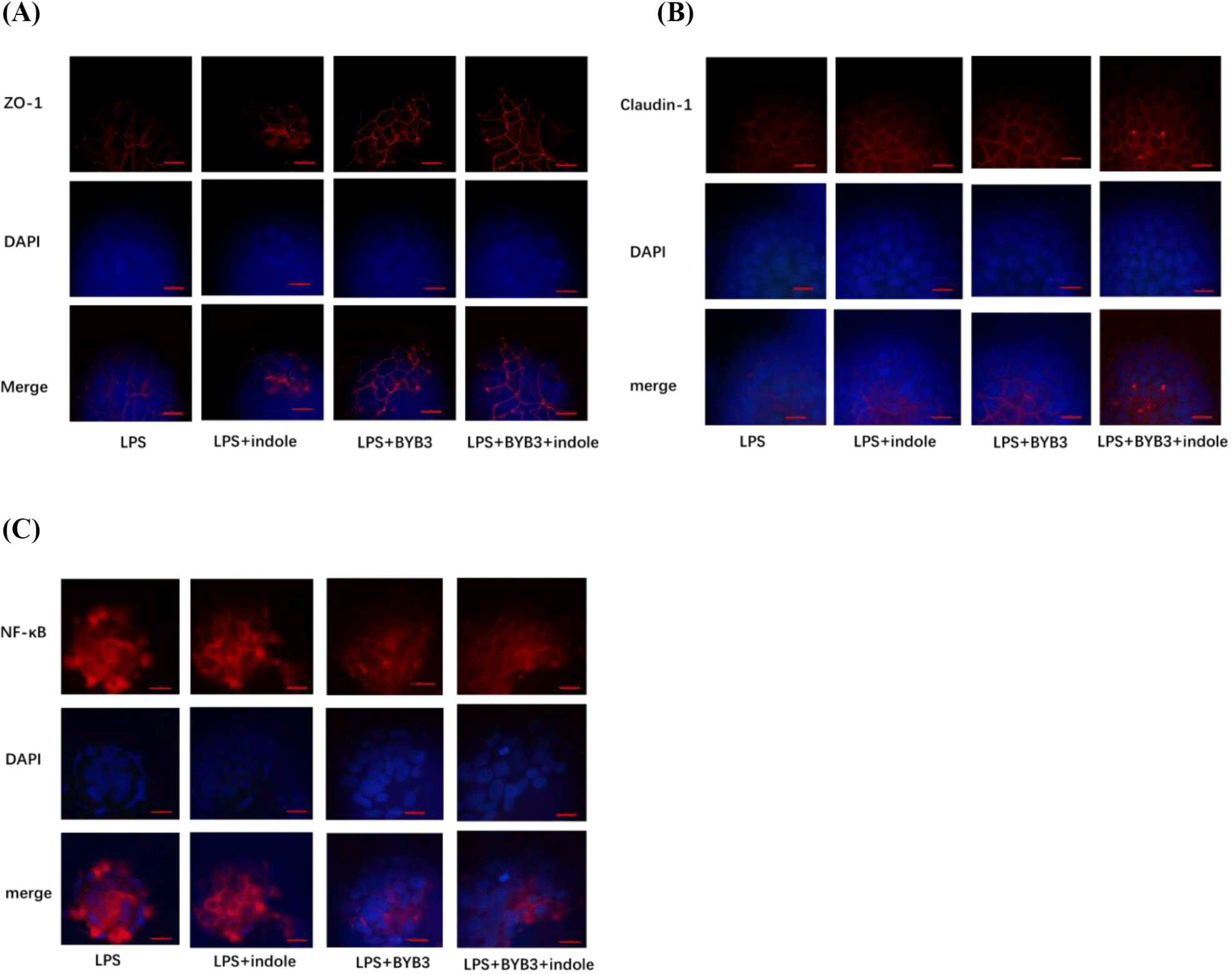
Consistent with this observation, immunofluorescence analysis of NF-κB demonstrated that p65 accumulated within the nucleus of Caco-2 cell monolayers treated with the metabolites of L. curvatus BYB3+indole. However, incubation with LPS decreased LPS-induced nuclear accumulation of NF-κB (Fig. 5C).
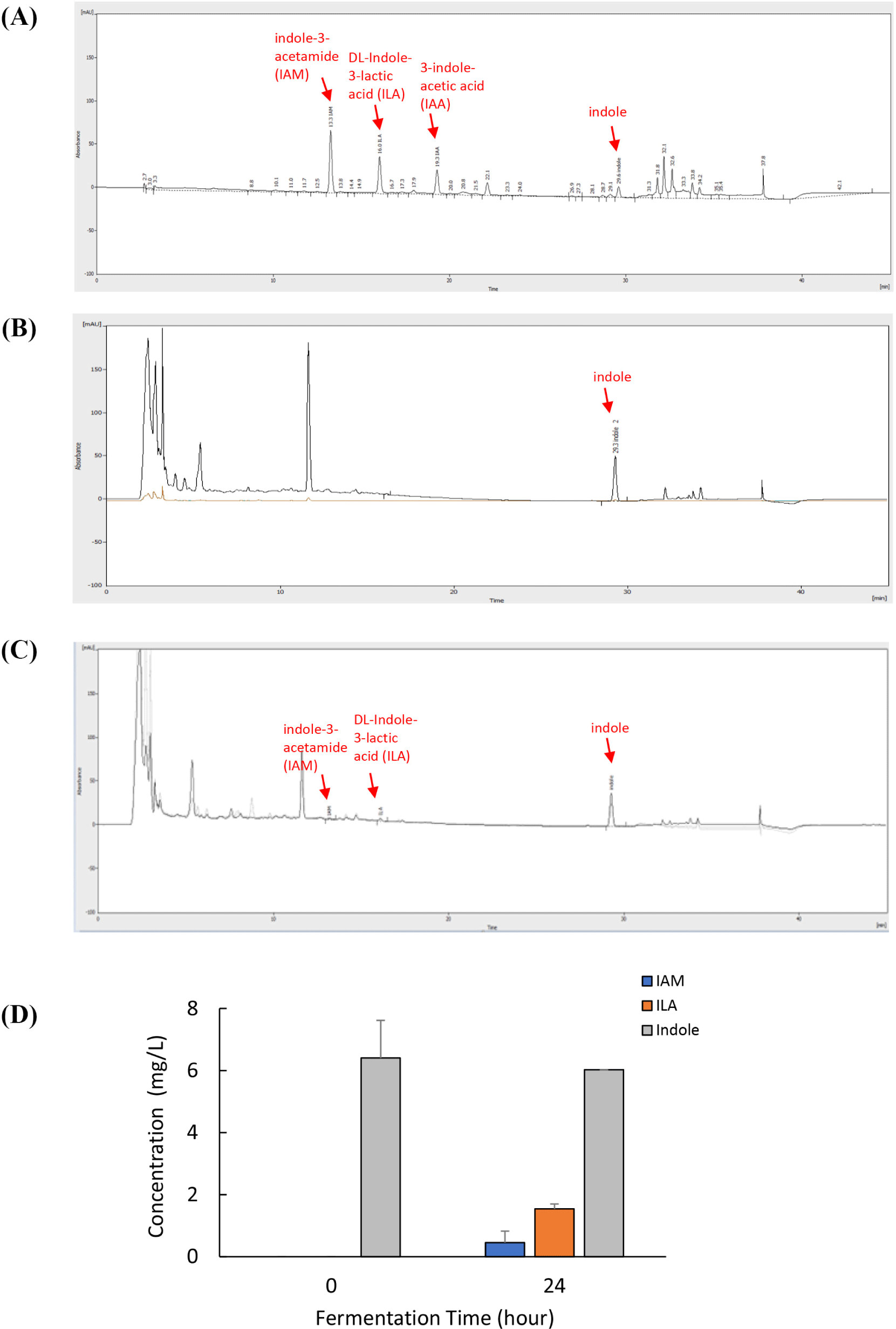
HPLC analysis was performed to precisely identify and quantify indole derivatives. Several indole derivatives (100 μM each) were separated, and their peaks were detected by HPLC using a C-18 reverse column (Fig. 6). Under optimal conditions, the retention times of IAM, ILA, IAA, and indole were 13.2, 16.1, 19.3, and 29.1 min, respectively (Fig. 6A). The peak in Fig. 6B corresponds to the main components because of the presence of indole from the supernatants of the indole-treated 0 h. The three peaks in Fig. 6C represent IAM, ILA, and indole. The main component in Fig. 6C, indicated by three peaks, including two of IAM and one of ILA, represented the supernatant of the L. curvatus BYB3 group fermented for 24 h. The indole content in the supernatants of the L. curvatus BYB3+indole group was reduced, and IAM and ILA metabolites were observed to varying degrees (Fig. 6D).
Discussion
Indole alleviates the symptoms of gastrointestinal disorders by activating the AhR (Hubbard et al., 2015). Several compounds have been proposed as putative endogenous AhR ligands, many of which are produced via pathways involved in the metabolism of tryptophan and indole, including indole-3-aldehyde, IAA, and many more (Bittinger et al., 2003; Chung and Gadupudi, 2011). In our previous study, AhR activation inhibited NF-κB expression, in vivo and in vitro (Salisbury and Sulentic, 2015). In macrophages, the activation of AhR signaling blocks NF-κB binding sites and masks NF-κB transcription activity, suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation (Huai et al., 2014). Hence, the current study aimed to identify the potential effect of metabolites of L. curvatus BYB3 and indole in mediating the recovery of TJ after LPS-induced disruption of the intestinal barrier in the colon mucosal cell layer. Our preliminary studies showed that L. curvatus BYB3 might play a role in alleviating inflammatory responses. However, the association between intestinal TJ proteins and inflammation influenced by L. curvatus BYB3 was not elucidated under in vitro conditions. The findings from this study suggest that the metabolites of L. curvatus BYB3 and indole can activate the AhR.
In previous studies, LPS-induced inflammation disrupted the integrity of IECs and increased paracellular permeability (Gao et al., 2017). The results from this study demonstrated that the supernatants of L. curvatus BYB3, indole, and metabolites of BYB3+indole inhibited LPS-induced inflammation in IECs by enhancing the expression of TJ proteins and decreasing paracellular permeability in Caco-2 cells. However, direct evidence is required to explore the association between the supernatants of cells treated with L. curvatus BYB3, indole, and the metabolites of L. curvatus BYB3+indole and intestinal permeability; such evidence was not available earlier. ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-1 are important TJ proteins that maintain permeability in the small intestine (Anderson and Van Itallie, 1995). Western blot analysis revealed that the administration of the metabolites of L. curvatus BYB3+indole significantly improved intestinal epithelial barrier function by increasing the expression of the TJ proteins ZO-1 and claudin-1. Deregulated NF-κB activation has been previously reported to contribute to the pathogenesis of various inflammatory diseases (Liu et al., 2017). In this study, the metabolites of BYB3+indole decreased NF-κB expression.
In a previous study, we determined that Lactobacillus improved the intestinal epithelial barrier function by increasing the expression of TJ proteins (Zeng et al., 2020). TEER is a commonly used indicator of intestinal epithelial membrane permeability (Srinivasan et al., 2015). An increase in the TEER and a decrease in paracellular permeability reflect the enhancement of the barrier function (Capaldo et al., 2017). The small intestine is one of the main organs of the digestive system, and the Caco-2 cell monolayer is a recognized intestinal cell line.
According to this study’s HPLC analysis, only three indole compounds were detected among the metabolites of L. curvatus BYB3+indole, namely IAM, indole, and ILA. Several Bacteroides spp. and Clostridium bartlettii have been reported to produce ILA and IAA, whereas Bifidobacterium spp. have been reported to produce ILA (Aragozzini et al., 1979; Russell et al., 2013). However, there are few reports of L. curvatus producing ILA.
Our results provide evidence that microbiota-mediated metabolism inhibits LPS-induced inflammation, increasing the expression of TJ proteins. Based on the primary research results of this study, key metabolic molecules that improve intestinal should be investigated in further studies. We demonstrated that the metabolites of L. curvatus BYB3 and indole inhibited LPS-induced inflammation in IECs by enhancing TJs, which, in turn, reduced paracellular permeability. HPLC results confirmed that various concentrations of indole and indole derivatives (ILA and IAM) enhance TJ protein expression. This protective effect may provide a potential approach to restoring TJ barrier function, and AhR may be a novel therapeutic target in gut health and diseases such as IBD.













