Introduction
Cholesterol gallstone disease is one of the most common conditions in the gastrointestinal tract, which is caused by the complex interaction of multiple genetic and environmental factors that contribute to the gallstone formation (Chuang et al., 2012). Recently, in Asian countries, this biliary tract disease has been rapidly increasing due to changes in dietary habits and life style, although it is highly prevalent in people from Western countries compared to Asian countries (Chen et al., 2019). It is well known that cholesterol gallstone formation is mainly due to the imbalance of bile components, which is affected by hypersecretion and accumulation of cholesterol (Song et al., 2015). As cholesterol content in bile increases significantly, cholesterol is supersaturated, causing precipitation and aggregation of excess cholesterol in the gallbladder, and which can become gallstone (Purushortham et al., 2012). Additionally, the formation of cholesterol gallstones is caused by mucin protein hypersecretions associated with certain variants in MUC genes, as mucin proteins have the ability to bind to lipids and bile pigments due to hydrophobic binding sites, thus contributing mucus gel formation and gallbladder hypomotility (Bar Dayan et al., 2004; Chuang et al., 2012). Generally, patients with cholesterol gallstones exhibit a higher level of mucin proteins, especially gel-forming mucin, in gallbladder than control patients without cholesterol gallstones (Bar Dayan et al., 2004; Lee et al., 1979).
It is important to inhibit mucin overproduction in the gallbladder to prevent the gallstone formation (Chuang et al., 2012). Urosodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) can reduce the concentration of mucin proteins and the formation of cholesterol crystals in patients with gallstones (Castro-Torres et al., 2015). Thus, UDCA is commonly used as a pharmacological agent for treating cholesterol gallstone disease (Castro-Torres et al., 2015). However, this agent can cause cholestasis and cell membrane damage through inhibition of bile acid absorption and choleretic function (Guarino et al., 2013). In addition, it takes a long time for UDCA to take effect and it may cause gallstone recurrence after lithotripsy (Vidyashankar et al., 2010). Therefore, the search for a better treatment is needed for the cholesterol gallstone disease. It is important to not only treat the cholesterol gallstone disease, but also to prevent the occurrence and recurrence of gallstones (Song et al., 2015).
Lactobacilli are well-known probiotics that help improve human health and prevent various diseases (Lee et al., 2011). Previous studies have shown the health benefits of lactobacilli, including immune modulation, antimicrobial, and anticarcinogenic effects in the human intestine (Oelschlaeger, 2010). Additionally, some lactobacilli, including Lactobacillus acidophilus and L. fermentum, reduced not only lipid level, and but also total and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels in the serum and liver (Kim et al., 2008; Lye et al., 2012; Park et al., 2007). Due to these hypocholesterolemic properties, we reasoned that L.acidophilus and L. fermentum may affect the mucin biosynthesis and cholesterol gallstone formation. However, research on the effects of lactobacilli on cholesterol gallstone formation is limited. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the effects of L. acidophilus ATCC 43121 and L. fermentum MF27 supplementation on biochemical indices, including cholesterols, triglycerides, and phospholipids, in the serum of lithogenic diet (LD)-induced C57BL/6J mice. Additionally, this study also examined the effects of probiotic supplementation on expressions of genes related to cholesterol metabolism in the liver and mucin in the gallbladder to determine the preventive effects of lactobacilli on gallstone formation in LD-induced C57BL/6J mice.
Materials and Methods
Both L. acidophilus ATCC 43121 and L. fermentum MF27 were obtained from the Food Microbiology Laboratory at the Korea University (Seoul, Korea), and the origins of these lactobacilli were pig and human intestines, respectively. One percentage inoculum of bacterial strains was cultured under the anaerobic condition (Oxoid Anaerobic Gas Generating Kit, Oxoid, Basingstoke, UK) monitored by an anaerobic indicator (Oxoid). The microorganisms were grown in sterile de Mann, Rogosa, and Sharpe (MRS) broth (Difco, Becton, NJ, USA) at 37°C for 24 h and was diluted consecutively three times in fresh MRS broth prior to use. For long-term storage, stock cultures were maintained at −80°C in MRS broth containing 15% glycerol.
A total of forty inbred 6-week old male C57BL/6J mice were purchased from Samtako Bio Korea (Osan, Korea) and used in this study. After a conditioning period of 7 d, the animals were randomly divided into the following 5 groups (8 mice per group): control (standard diet with saline), LD containing 1.25% cholesterol, 16% fat (5.0% soy bean oil, 7.5% cocoa butter, and 3.5% coconut oil), and 0.5% sodium cholic acid (D12336, Research Diets, New Brunswick, NJ, USA), LD with UDCA (LD+UDCA; 20 mg/kg per day, Alfa Aesar, Ward Hill, MA, USA), LD with L. acidophilus ATCC 43121 (LD+P1; 109 CFU/mL in 500 μL per day), and LD with L. fermentum MF27 (LD+P2; 109 CFU/mL in 500 μL per day). Mice from each group were treated for 4 week, and body weight was measured weekly. Saline, UDCA, L. acidophilus ATCC 43121, and L. fermentum MF27 were orally administered to mice according to their respective groups. All mice were kept under the controlled condition of 12 h light/dark cycles with temperature 22°C to 25°C and relative humidity 56% to 60%, and water and food were allowed ad libitum. The animal experiments were approved by the Korea University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (KUIACUC-69). All experiments in this study were conducted in accordance with the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (National Research Council, 2010).
Blood samples were collected by cardiac puncture after administration of Anesthetics [Zoletil 50 (Vibac Laboratories, Carros, France) 60 mL/100 g and Rompun (Bayer Korea, Seoul, Korea) 40 μL/100 g]. The blood samples were placed in heparinized sterile microfuge tubes and centrifuged at 2,000×g for 15 min at 4°C. Total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, triglycerides, and phospholipids concentrations were enzymatically assessed by a Cobas C111 automatic analyzer (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) using assay kits from Roche (Mannhein, Germany). Ratio of cholesterol and phospholipid (C:P) was calculated from the total cholesterol level divided by phospholipids level.
Total RNA was extracted from the liver and gallbladder with a GeneJET™ RNA Purification Kit (Thermo Scientific, Massachusetts, MA, USA) according the manufacturers’ protocol, and cDNA was prepared by reverse transcription of 2 μg total RNA using first strand cDNA synthesis kit (LeGene Biosciences, California, CA, USA). Primers used for RT-PCR and the size of the PCR products are listed in Table 1. The mRNA levels of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase (HMG CoA R), and cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7A1), MUC1, MUC2, MUC5AC, MUC5B, and β-actin were quantified using PCR (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany). RT-PCR conditions and the expression levels of relevant genes were determined using the quantification methods as described by Liu et al. (2017) and Yong et al. (2019). Expression levels of relevant genes were normalized against the expression of β-actin as housekeeping gene.
To compare the body weight, serum biochemical indices, and expressions of various genes involved in cholesterol synthesis and gallstone formation among the five groups, association analysis by the general linear model was carried out using SAS software (SAS Institute Cary, NC, USA). Significant differences among the five treatments were determined using the probability difference (PDIFF), based on a significant value of 5%. All means were presented as least square means with standard errors.
Results
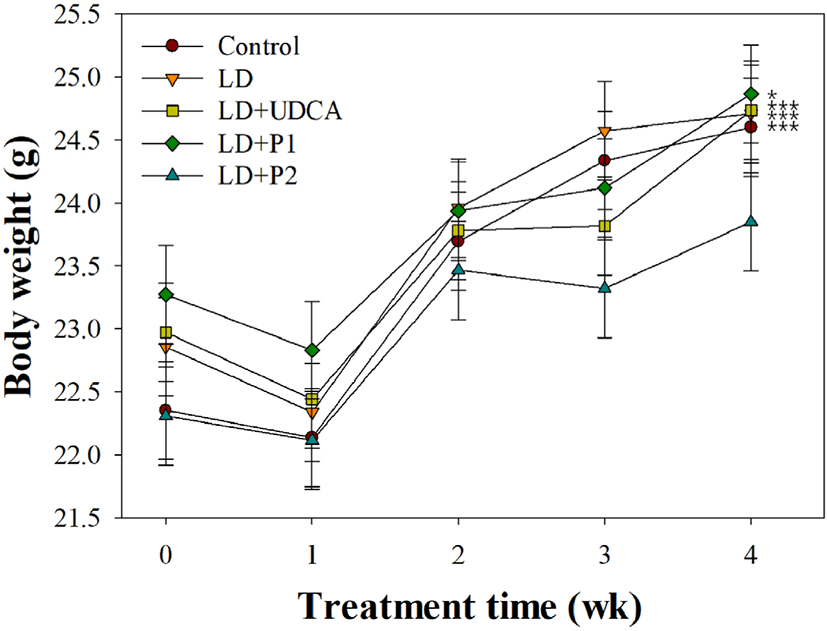
Fig. 1 presents the effects of lactobacilli on body weight in LD-induced C57BL/6J mice. No significant difference in body weight was observed between experimental groups at each period (p>0.05). By the end of 4 wk, body weight in the control and treatment groups was significantly increased compared to that at 0 wk (p<0.05). In contrast, mice group fed on LD with L. fermentum MF27 (LD+P2) showed no significant weight gain (p>0.05).
Serum biochemical indices by the end of 4 wk of the experimental period are shown in Table 2. Total cholesterol level was approximately 1.8 times greater in the LD group on high-fat and high-cholesterol diet compared to the control group (180.3 vs. 102.0 mg/dL, p<0.001). Additionally, the LD+P1 group showed a lower level of total cholesterol compared to the LD+P2 and LD+UDCA groups (155.6 vs. 184.8 and 186.0 mg/dL, p<0.001). No significant difference in total, LDL, and HDL cholesterol contents was observed between the LD and LD+UDCA groups (p>0.05). The LD+P1 and LD+P2 groups showed lower content of LDL cholesterol (34.4 and 54.0 mg/dL) compared to the LD and LD+UDCA groups (59.6 and 58.8 mg/dL, p<0.001), even though no difference was observed in the HDL cholesterol between the LD and LD+P2 groups (112.6 vs. 120.0 mg/dL, p>0.05). Higher level of triglycerides was observed in the LD group compared to the LD+P1 and LD+P2 groups (67.3 vs. 51.8 and 54.6 mg/dL, p<0.01), although no difference was observed between the LD and control (58.2 mg/dL) groups. The LD+P2 group showed a higher value of phospholipids compared to the control and LD+P1 groups (274.0 vs. 225.8 and 241.0 mg/dL, p<0.01). However, the control group displayed a lower ratio of C:P compared to the LD+UDCA and LD+P1 groups (0.45 vs. 0.75 and 0.65, p<0.001).
Expression levels of HMG CoA R and CYP7Al, two genes involved in the cholesterol and bile acid synthesis pathway in the liver, are shown in Fig. 2A. Significantly higher expression levels of HMG CoA R (1.81 vs. 1.00, p<0.05) and CYP7A1 (1.38 vs. 1.00, p<0.05) showed in the LD group compared to the control group. The LD treatment groups, including +UDCA, +P1, and +P2, had lower expression levels in HMG CoA R compared to the control group (p<0.05), although no significant difference was detected in CYP7A1 expression among the control, LD+UDCA, and LD+P1 groups (p>0.05).
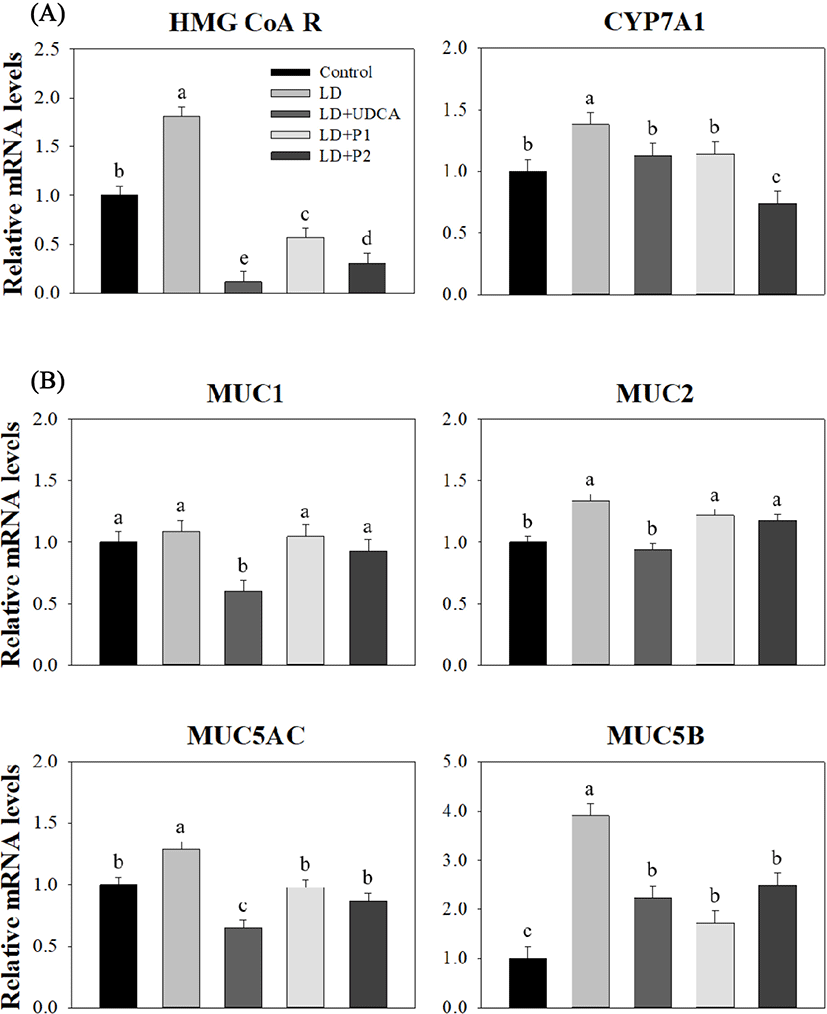
The results for expression levels of MUC genes in the gallbladder between the groups are shown in Fig. 2B. There was no significant difference in expression levels of MUC1 among the groups except the LD+UDCA group, which exhibited the lowest level compared to the other groups (0.60, p<0.05). Expression of gel-forming mucin genes (MUC2, MUC5AC, and MUC5B) in the LD+UDCA group was lower compared to the LD group (p<0.05). Lower expression levels of MUC5AC and MUC5B were detected in both the LD+P1 and LD+P2 groups compared to the LD group (p<0.05), although no difference was observed in MUC2 level among these groups (p>0.05).
Discussion
It is generally accepted that dietary habit, especially a long-term high-fat diet, is a major risk factor contributing to the formation of cholesterol gallstone among all known factors (Acalovschi, 2014; Castro-Torres et al., 2015). Additionally, such LD can induce changes in serum biochemical indices (Deng et al., 2015; Liu et al., 2017). Liu et al. (2017) reported that mice fed on a LD containing high-fat and high-cholesterol contents for 8 wk exhibited increased levels of total cholesterol and triglycerides in the serum compared to mice fed on a control diet, although no difference was observed in the levels of LDL and HDL cholesterol between the groups. On the other hand, many studies have reported the inhibitory effect of UDCA on formation of cholesterol crystals, whereas opinions among scientists on the hypocholesterolemic effect are divided (Dorvash et al., 2018; Shan et al., 2008; Song et al., 2015). Liu et al. (2017) suggested that UDCA treatment of mice fed with a LD reduced the total cholesterol level. However, Song et al. (2015) reported no significant difference in the total cholesterol level between mice fed on a LD and LD with UDCA, although a lower level of triglycerides was observed in the LD with UDCA group than the LD group. Numerous studies have demonstrated that L. acidophilus and L. fermentum could positively modulate the serum lipid profiles (De Rodas et al., 1996; Lye et al., 2012). These results were consistent with our findings that levels of total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and triglycerides were reduced in the L. acidophilus ATCC 43121 group compared to the LD group (p<0.001), although no difference was found in total cholesterol content between the L. fermentum MF27 and LD groups (p>0.05). This decrease of serum cholesterol levels was associated with reduction of C:P ratio in the lactobacilli groups compared to the LD group (p<0.001). Increased C:P ratio causes supersaturation of gallbladder bile with cholesterol (Berr et al., 1992). Therefore, our results suggested that lactobacilli, especially L. acidophilus ATCC 43121, have the cholesterol-lowering effects in LD-induced C57BL/6J mice.
It is well known that polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), especially eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), play a critical role in regulating biological functions of the human body, and could positively affect on the serum biochemical indices (Cho et al., 2015; Sugiyama et al., 2008). These cholesterol-lowering effects in the serum may occur through modulating cholesterol metabolism in the liver (Sugiyama et al., 2008), and are associated with decreased activity of HMG CoA R, which is involved in cholesterol synthesis, in the liver (Ramaprasad et al., 2006). A similar result was observed in the current study, the LD+P1 mice with a lower expression of HMG CoA R exhibited a lower total cholesterol level than the LD mice with a higher expression of HMG CoA R (p<0.05). This result suggests that the hypocholesterolemic effects of the lactobacilli treatments occurred through suppression of HMG CoA R in the liver. Additionally, higher expression of CYP7A1 led to increased conversion of cholesterol to bile salts in the body (Liu et al., 2017). In this study, suppression of CYP7A1 in the LD+P2 group could be responsible for decreased bile acid synthesis in the liver, even though no difference was observed between the LD and LD+P1 groups.
Mucins are considered the major component of gallbladder mucus that provides the specific gel properties to protect the epithelium. Mucins are secreted by the mucous and submucosal cells in the epithelium (Chuang et al., 2012). However, altered expressions of mucins in the gallbladder could promote gallstone formation by accelerating cholesterol crystal nucleation in supersaturated bile (Bar Dayan et al., 2004). Notably, the gel-forming mucins, such as MUC2, MUC5AC, and MUC5B, play an important role in enhancing the gel properties and thus affect both the nuclear formation and enlargement of gallstones (Chuang et al., 2012; Zen et al., 2002). The membrane-bound mucins, including MUC1, do not form a mucous gel, but increased expression of these proteins was also associated with increased risk of the gallstone disease in human (Chuang et al., 2012; Wang et al., 2008). Thus, overexpression of MUC1, MUC2, MUC5AC, and MUC5B can participate in the gallstone formation with different lithogenic effects (Chuang et al., 2012). UDCA as a conservative treatment has demonstrated antilithiatic effect, which is associated with expression of MUC2, MUC5AC, and MUC5B, and reduced mucin secretion, as seen in the gallbladder bile (Jüngst et al., 2012; Kim et al., 2012). Cho et al. (2015) reported that PUFAs, including DHA and EPA, have the antilithogenic effects, as they led to reduced expression of MUC2, MUC5AC, and MUC5B genes in C57BL/6J mice. In the current study, L. acidophilus ATCC 43121 and L. fermentum MF27 were found to inhibit the expression of MUC5AC and MUC5B, although no significant effect was observed on the expression of MUC1 and MUC2 compared to the LD group. Thus, mucin genes involved in the cholesterol gallstone formation were differentially expressed following probiotic treatments used in this study.
Conclusion
Both L. acidophilus ATCC 43121 and L. fermentum MF27 positively affect the biochemical indices of the serum without impairing the growth rate in LD-induced C57BL/6J mice after 4 wk of treatment. These hypocholesterolemic effects in the serum, more evidently seen from L. acidophilus ATCC 43121, were mediated by a decreased expression of HMG CoA R in the liver. Additionally, these properties may contribute to decreased expression of gel-forming mucins, including MUC5AC and MUC5B, in the gallbladder. However, no differences were detected in the expressions of mucins between two strains. Thus, both lactobacilli have the preventive effect against the formation of cholesterol gallstones in the gallbladder in LD-induced C57BL/6J mice. Therefore, a steady intake of these lactobacilli can be used clinically to prevent the formation of cholesterol gallstones.













