Introduction
Oxya chinensis sinuosa (OC) is a well-known edible insect (Bahuguna et al., 2022; Kim et al., 2020). OC is an incomplete metamorphic insect of the genus Orthoptera of the order Orthoptera, with a body length of 21–35 mm. It appears from August to October and has been used as food for a long time worldwide (Jeong et al., 2023; Kim et al., 2020). Furthermore, OC has long been used in Korea as a treatment for seizures, paralysis, whooping cough, asthma, and bronchitis (Im et al., 2019; Kim et al., 2020). OC is studied for its properties, such as antibacterial activity, immunomodulatory functions, and ability to correct metabolic diseases (Anusha and Negi, 2022; Ki et al., 2014; Yoon et al., 2014). However, the effects of OC extracts on eye health, particularly the protective roles on the oxidative damage of retinal pigment epithelial cells, have not been fully investigated. Therefore, in this study, human retinal pigment epithelial cells were treated with OC extracted in different solvents to investigate the eye health effects of OC.
The macula, tasked with detecting light within the eye and playing a pivotal role in vision as the site where images of objects are formed, can result in impaired vision when deformed due to various causes (Handa, 2012). In particular, age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is caused by excessive production and accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) due to oxidative stress leading to mitochondrial damage and severe damage to retinal pigment epithelial (PER) cells (Du et al., 2017; Williams, 2008). The dysfunction of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) in AMD can result in the loss of photoreceptors, ultimately leading to blindness. AMD is mainly linked to visible clinical pigmentary changes in retinal disorders predominantly occur in the RPE rather than in the retina or choroidal melanosomes (Kauppinen et al., 2012). Oxidative damage of retinal epithelial cells leads to excessive accumulation of ROS, which causes the denaturation of intracellular proteins and DNA leading to impaired cell function, and eventually apoptosis (Tokarz et al., 2016; Zhu et al., 2017). Therefore, regulating the stress caused by oxidation of retinal pigment epithelial cells can help prevent and treat AMD.
ROS, such as H2O2 and superoxide anion, are representative chemicals that induce oxidative stress in cells (Lushchak, 2014). It is known that H2O2-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis are caused by the phosphorylation and expression of intracellular proteins, such as mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB; Del Rio and Velez-Pardo, 2006; Song et al., 2008; Zhang et al., 2020). Changes in the environment (dust and UV radiation) and life style (use of mobile phones and computers) have contributed to an increased oxidative stress in the eye and accordingly, the aging rate of the eyes is rapidly increasing (Balci et al., 2009; Ozguner et al., 2006; Varma et al., 2011; Williams, 2008; Yoon et al., 2018). While the prevalence of AMD is rapidly increasing, research on eye health functional foods is currently limited to materials, such as β-carotene, zeaxanthin, and lutein. Therefore, research on various eye health foods is urgently needed (Johra et al., 2020). Therefore, the aim of this study was to identify the mechanism underlying the protective effects of OC extracts against H2O2-induced oxidative stress and the retinal pigment epithelial cell death.
Materials and Methods
Dried OC was ground to a powder using a commercially available blender. The OC powder was resuspended in distilled water, 70% ethanol, or 70% methanol at a ratio 1:10 (w/v), respectively. The water extract samples were extracted at 60°C hot water for 24 h in shaking water bath, while the 70% ethanol and methanol extract samples were homogenized using an ultrasonicator (VCX500, Sonics & Materials, Newtown, CT, USA) at 35% amp for 10 s on the ice. The supernatants were filtered through a 0.45 μm PVDF membrane (GE Healthcare, Little Chalfont, UK), dried using a vacuum evaporator (CVE-3100; EYELA, Tokyo, Japan) and OC stored at –80°C until use. Accordingly, we designated the hot water extract of OC as OCH, the 70% ethanol extract as OCE, and the 70% methanol extract as OCM, and utilized them in the experiments.
ARPE-19 (human derived retinal pigment epithelial cell line) was purchased from ATCC (Manassas, VA, USA), was cultured in DMEM/F12 (Gibco, Carlsdad, CA, USA) media with 10% FBS (Gibco, Burlington, ON, Canada) and 1% penicillin–streptomycin (Gibco, Waltham, MA, USA). The cells were incubated at 37°C and 5% CO2 in a humidified CO2 incubator.
ARPE-19 cells were cultured at a density of 1×104 cells/well for 24 h. After 24 h, the media replaced with DMEM/F12 (phenol red-free; Gibco, Carlsdad, CA, USA) with 10% FBS and 1% penicillin–streptomycin. The cells were treated with varying concentrations of H2O2 ranging from 300 μM to 700 μM for 24 h, and 10 μL/well MTS solution (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) was added and further incubated in the CO2 incubator for 4 h. The cell viability was estimated by measuring the absorbance at 490 nm using a microplate reader (Varioskan LUX, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Approximately 60% of the cells were viable at 300 mM H2O2 compared to the control group. This concentration was used in all subsequent experiments.
ARPE-19 cells were cultured on a 96-well plate (1×104 cells/well) and incubated for 24 h. The cells were pre-treated with three OC extracts (hot water, ethanol, and methanol) at various concentrations for 1 h and stimulated with 300 μM H2O2 for 24 h. Then, the culture medium was added MTS solution (10 μL/well), incubated for 4 h in the CO2 incubator, and the OD was determined using a microplate reader at 490 nm. The cell viability (%) was calculated according to the following Eq. (1):
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release is traditionally used an indicator for the loss of cell membrane integrity (Li et al., 2015). Therefore, to evaluate the efficacy of OC extracts in inhibiting membrane damage, LDH release was analyzed using an LDH assay kit (Biomax, Seoul, Korea). First, ARPE-19 cells were cultured on a 96-well plate (1×104 cells/well) and incubated for 24 h. Then the cells were pre-treated with three OC extracts (hot water, ethanol, and methanol) at various concentrations for 1 h and stimulated with 300 μM of H2O2 for 24 h. The culture supernatant was mixed with LDH solution, and incubated for 30 min. Finally, stop solution (10 μL/well) was added, and OD was determined using a microplate reader at 490 nm.
To confirm the antioxidant efficacy of three OC extracts on the generation of intracellular ROS due to oxidative stress, intracellular ROS was measured using the Intracellular ROS assay kit (Cell Biolabs, San Diego, CA, USA) according to the proposed method. Briefly, ARPE-19 cells were plated on a 96-well plate (1×104 cells/well) and incubated for 24 h in the CO2 incubator. The cells were pre-treated with 2 mg/mL OC extracts (hot water, ethanol, and methanol) for 1 h and stimulated with 300 μM H2O2 for 24 h. The cells were then treated with DCF-DA (100 μM) and incubate for 1 h. The culture medium was completely removed, washed twice with 1× PBS, and 100 μL of serum/phenol red-free DMEM/F12 medium and 100 μL of cell lysis buffer (2×) were added and incubated for 5 min. Finally, 150 μL of cell lysates were transferred to a black plate and measured at 485 nm and 530 nm wavelengths using a microplate reader.
ARPE-19 cells were cultured in a six-well plate (1 105 cells/well) and incubated for 24 h. The cells were pre-treated with 2 mg/mL three OC extracts (hot water, ethanol, and methanol) for 1 h and stimulated with 300 μM H2O2 for 30 min or 24 h. After stimulation, the cells were washed with 1× PBS and lysed with M-PERTM protein extraction reagent containing HaltTM protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The protein concentration was estimated using a PierceTM BCA protein assay kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Proteins were separated using BoltTM 4%–12% Bis-Tris Plus gel (Invitrogen, San Diego, CA, USA) and electro-transferred onto PVDF membranes (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA). The membranes were blocked with 5% skim milk for 1 h and incubated with primary antibodies against MAP kinases (ERK, JNK, and p38), phosphorylated MAP kinases (P-ERK, P-JNK, and P-p38), IκBα, and antioxidant proteins (SOD1, NQO, and HO-1, and HO-2) (Cell Signaling Technology, Beverly, MA, USA) at 8°C for 20 h. After washing thrice with tris-buffered saline with tween 20 (TBST; Thermo Fisher Scientific) buffer, membranes were incubated with secondary antibodies (Cell Signaling Technology) at RT for 1 h. The membranes were washed thrice with TBST, and immunoreactive bands were developed using enhanced chemiluminescence reagent (ECL; Thermo Fisher Scientific) and the image was acquired using a chemiluminescence imaging equipment (Alliance Q9 advanced, Uvitec, Cambridge, UK).
All experiments were performed in triplicates and presented as the means. The results are expressed as the means±SDs. Differences between the control and OC extract groups were evaluated using Student’s t-test. SPSS version 18.0K (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA) was used for the statistical analysis.
Results and Discussion
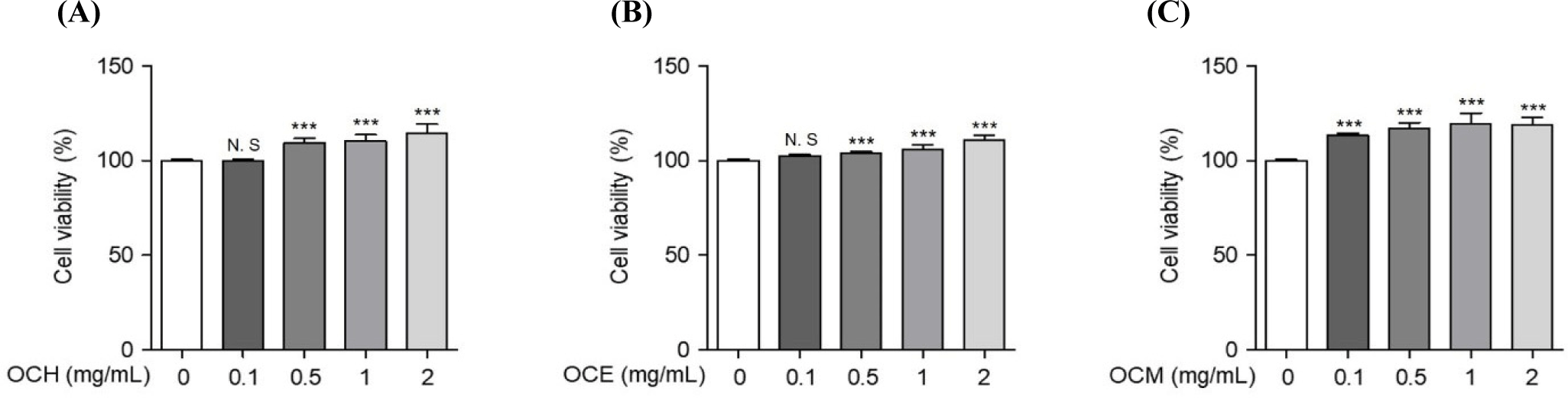
To compare the efficacy of OC extracted in different solvents, three OC extracts were prepared in various solvents, such as hot water, ethanol, and methanol. Human retinal epithelial cells were treated with various concentrations of the extracts to confirm their cell death-protective effects. To optimize the concentration required to induce oxidative stress, the cells were treated with various concentrations of H2O2 for 24 h, and the concentration inducing oxidative stress was set at 300 μM, which showed a survival rate of approximately 60% of ARPE-19 cells (data not shown). To confirm the optimal treatment concentration, ARPE-19 cells were treated with various concentrations of the extracts, and the optimum concentration was set to a maximum of 2 mg/mL, a concentration that does not cause cytotoxicity (Fig. 1). As shown in Fig. 2, the inhibition of cell death was confirmed using a MTS assay on ARPE-19 cells exposed to 300 μM H2O2 for 24 h after pre-treatment with various concentrations of the OC extracts for 1 h. OC extracts inhibited cytotoxicity in a dose-dependent manner, suggesting that OC extracts can prevent AMD by inhibiting cell death caused by oxidative stress.
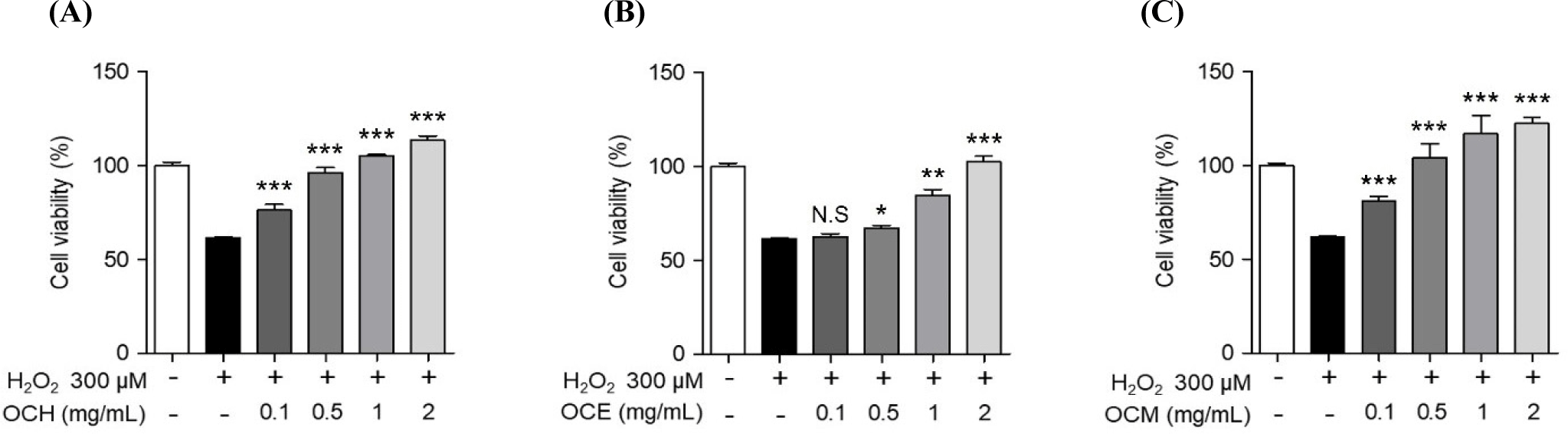
Eating insects has been used to treat a variety of illnesses as a natural remedy (Bukkens, 1997). However, there is a scarcity of research on eye health. Therefore, we confirmed the cell membrane protection effect of OC extract using retinal pigment epithelial cells. ARPE-19 cells were pretreated with OC extracts at various concentrations (0.1, 0.5, 1, and 2 mg/mL) for 1 h, then stimulated with 300 μM H2O2 for 24 h, and the protective effect of three OC extracts against cell membrane damage was confirmed using an LDH release assay. In the experimental group treated with 300 μM H2O2 for 24 h, LDH release from the cell membrane increased due to membrane damage. The treatment with OC extracts substantially reduced the LDH release in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 3). In particular, in the group treated with three OC extracts at 2 mg/mL, the LDH increase due to treatment with H2O2 was suppressed by approximately 50%, demonstrating excellent cell membrane protection efficacy. Accordingly, it is believed that OC extracts can prevent retinal disease by protecting the cell membrane of ARPE-19 cells from damage caused by H2O2.
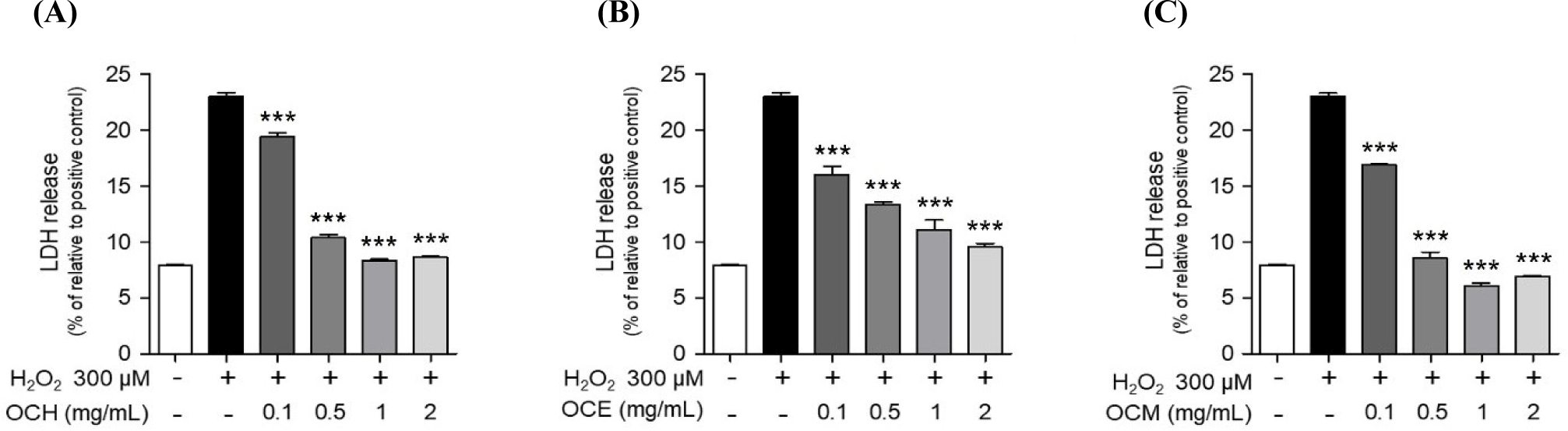
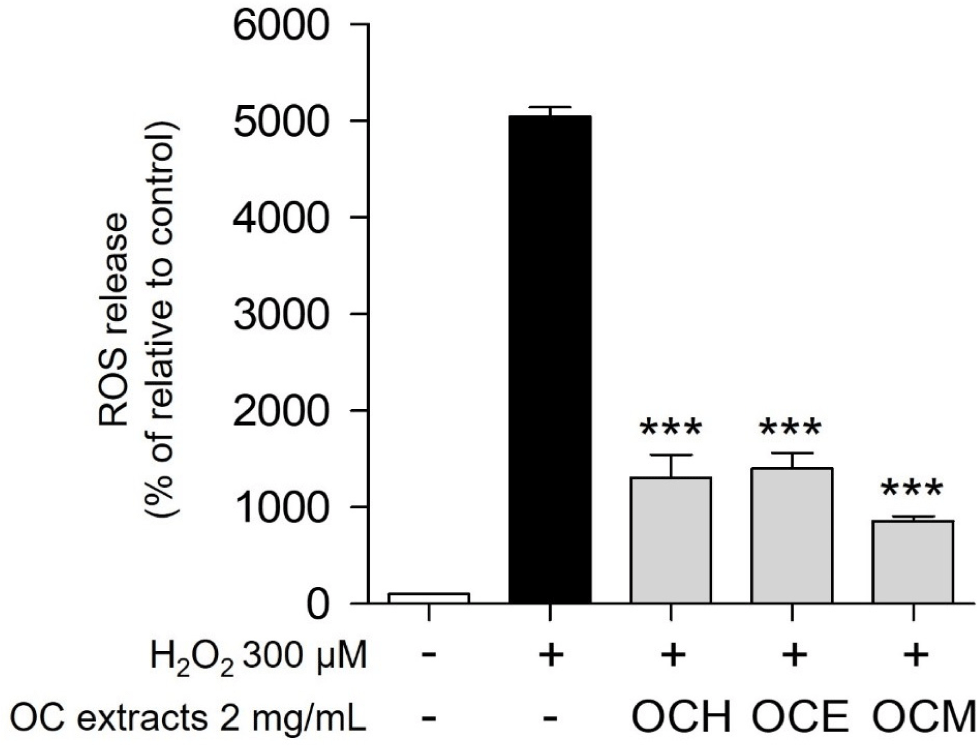
ROS, such as H2O2 and superoxide anions, which accumulate within the cells, are representative chemicals that cause cell death (Gechev et al., 2006). It is well known that one of the most representative antioxidant effects occurs through a pathway that prevents the accumulation of ROS in cells (Weng et al., 2017). Therefore, the antioxidant efficacy and apoptosis inhibition efficacy of the three OC extracts were evaluated by confirming whether they could regulate ROS generated by H2O2 in ARPE-19 cells. As a result, when treated with 300 μM H2O2, the intracellular ROS level increased approximately 50-fold compared to the control group (Fig. 4). Upon treatment with 2 mg/mL of three OC extracts, the ROS production was reduced by approximately five-fold compared to treatment with H2O2 alone. These results suggest that the OC extracts inhibit oxidative stress by controlling excessive ROS accumulation in cells, a representative trigger of oxidative stress.
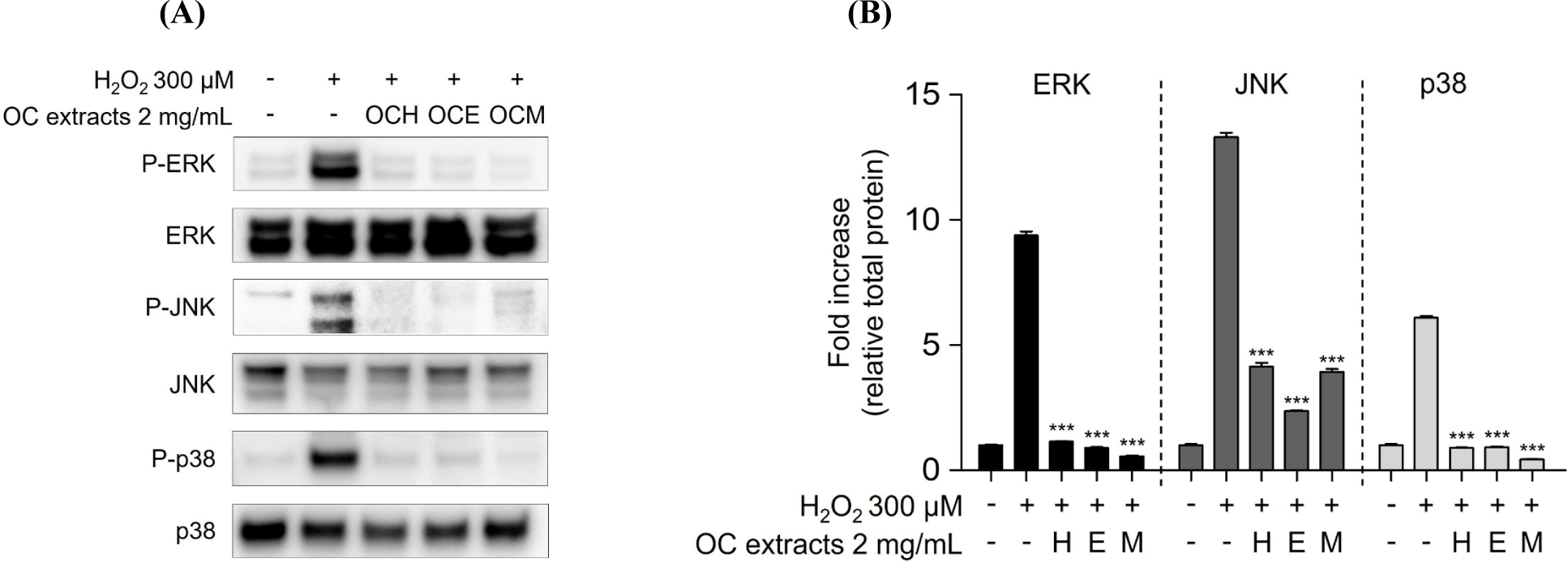
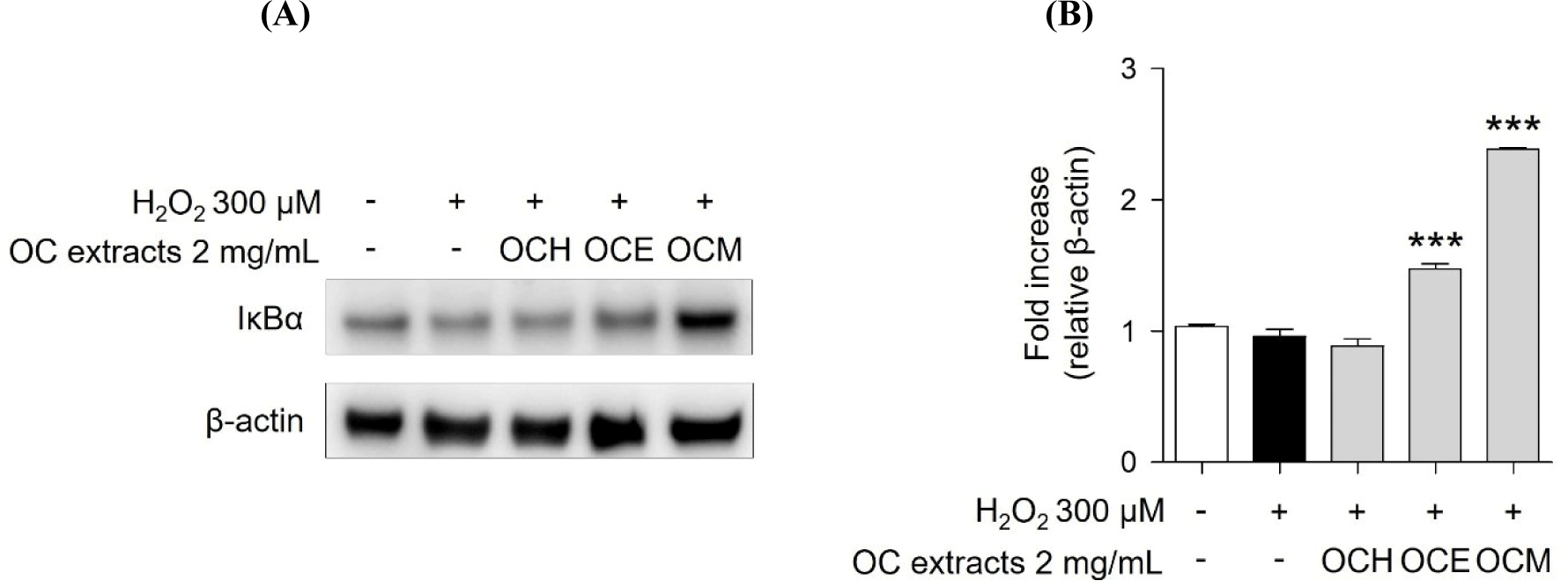
MAPKs subtypes p38, ERK, and JNK are well-known as intracellular signaling proteins involved in cell proliferation, differentiation, inflammation, and cell death (Osaki and Gama, 2013; Ren et al., 2002; Thalhamer et al., 2008). MAPKs are known to be affected by factors inside or outside the cell, and the cell signaling pathway is activated through the phosphorylation of the proteins, eventually resulting in the transcriptional activation of the respective genes in the nucleus (Cowan and Storey, 2003; Huang et al., 2020). Through the results of the H2O2 treatment experiment, it was confirmed that the phosphorylation of MAPKs occurred actively in the H2O2 30 min stimulation experiment group. However, it was confirmed that 2 mg/mL of three OC extracts significantly reduced the phosphorylation of MAPKs increased by H2O2 in the 1 h pre-treatment experiment group (Fig. 5). These results suggest that the OC extracts regulate cell survival and apoptosis by regulating the phosphorylation of MAPKs. In addition, inhibitor of NF-κB, such as IκBα, are related with the downregulation of NF-κB (Kanarek and Ben-Neriah, 2012). H2O2 enhanced IκBα degradation, suggesting that cell death was increased by NF-κB activation. However, pre-treatment of ARPE-19 cells with three OC extracts (Fig. 6) inhibited IκBα degradation, indicating that the three OC extracts diminished NF-κB activation, which was related with H2O2-induced cell death responses. The OCM has been confirmed to be most effective, and this is attributed to the differences in the components extracted depending on the polarity of the solvents used. It is believed that the extract from the most polar solvent among the extracts exhibits the highest efficacy against AMD.
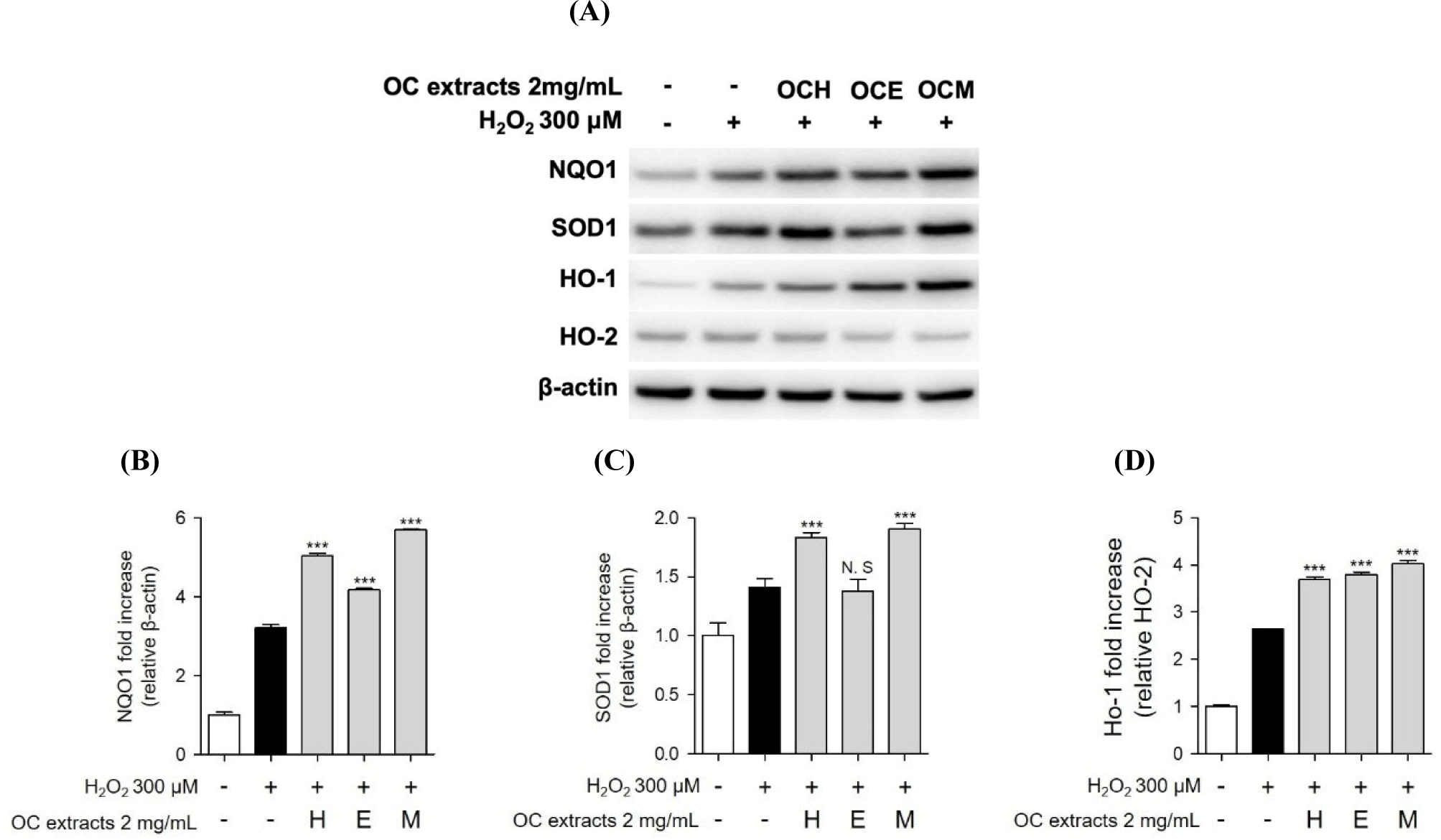
Furthermore, we conducted western blot analysis to confirm the expression of SOD, NQO, and HO-1/HO-2 proteins, recognized indicators of the antioxidant mechanism. When ARPE-19 cells were treated with three OC extracts and H2O2, an increase in antioxidant-related protein expression was observed (Fig. 7). Additionally, similar to previous studies, some expression of antioxidant proteins was also observed as a result of H2O2 treatment alone (Huang et al., 2019). However, in the co-treatment with three OC extracts, we observed a higher expression of antioxidant proteins compared to the results of H2O2 treatment alone. Consequently, we propose that the antioxidant mechanism of three OC extracts involves increasing intracellular antioxidant proteins to regulate oxidative stress induced by H2O2.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we demonstrated the inhibitory effects of three OC extracts on H2O2-induced oxidative stress response. This study extracted OC extracts using various solvents and confirmed the protection and mechanism of ARPE-19 cells against oxidative stress. First, three OC extracts were extracted with various extracts. Afterwards, we performed MTS assay to verify the cytoprotective effect against oxidative stress-induced ARPE-19 cell death. The cell membrane protection effects of the three OC extracts was confirmed through LDH release analysis. Furthermore, we evaluated the efficacy of regulating increased oxidative stress within surviving cells by examining ROS levels. Additionally, we explored the regulatory mechanism of cell death through the MAPKs signaling mechanism, which are important for cell proliferation, differentiation, and death. To confirm the anti-inflammatory effect of OC extracts, the presence of IκBα in the cytoplasm was verified to assess its impact on NF-κB activation, with the expectation that an increase in IκBα in the cytoplasm would influence the activity of NF-κB. In addition, it was shown that the three OC extracts possess antioxidant effects by up-regulating the intracellular expression of key antioxidant proteins, such as SOD, NQO, and HO-1. According to the results, the efficacy of OC extract in suppressing macular degeneration caused by oxidative stress may be suggested. However, based on the results of this study, future research on its applicability as an actual macular degeneration control agent is considered necessary.













