Introduction
Plant-based meat alternative has secured a significant market share around the world (Ismail et al., 2020; Kumari et al., 2023). However, consumers are not ready to compromise on the taste or quality parameter (McClements and Grossmann, 2021). Thus, researchers and industrialists are trying to find a way in between (Hoek et al., 2013), including replacing a portion of meat with more sustainable protein source, either plant based or cultured meat (Alam et al., 2024; Molfetta et al., 2022). These products are known as hybrid meat products (Grasso and Jaworska, 2020). Various types of hybrid meat products have been developed around the world. The production of hybrid meat is expected to solve food related problems due to the increasing population and consumer perception for balanced diets (Grasso, 2024). Products conventionally available in the market are manufactured by combining different sources with real meat such as chicken and beef (Annoh-Quarshie, 2018; He et al., 2021; Zahari et al., 2021). This combining strategy creates a flow of simple processed products such as hamburger patties and chicken nuggets. These processes require the use of a high temperature. Most of the hybrid meat products are produced using a high-temperature processing which causes loss of nutrients with deteriorating effects on cooking parameters of final products (Chandler and McSweeney, 2022; Grasso, 2024). In other words, the manufacturing process of hybrid meat has a limitation (Alam et al., 2024). To overcome problems related to high-temperature processing, a wet spinning approach can be considered.
The wet-spinning technique has been traditionally used in the textile industry. This particular technique is based on a bottom-up approach that requires complicated facilities (Dekkers et al., 2018; Kyriakopoulou et al., 2019). However, it is easier to control characteristics of fibers. In recent years, researchers have added a small amount of protein into the spinning solution to improve physicochemical properties of fibers (Cui et al., 2022). Based on this notion, a preliminary study has been conducted to utilize different protein sources including pea protein and wheat protein (WP; Kumari et al., 2024). It was found that imitation fiber from a combination of two kinds of plant protein had the potential to mimic conventional meat. Additionally, incorporating cultured meat with plant protein has not been reported yet. This creates a gap in this field of hybrid meat product. To leverage advantages of wet spinning and fulling this gap, plant protein and cultured meat tissue (CMT) were utilized in this study. Plants-based protein can control production price increases due to relatively expensive CMT. Nutrients that cannot be provided by only plant proteins could be supplemented with CMT. Therefore, in this study, differences in quality characteristics between manufactured hybrid cultured chicken breasts were examined by adding CMT at different concentrations to plant-based protein using wet-spinning.
Materials and Methods
Chicken satellite cells (CSC) were isolated from hindlimb muscles as previously published study (Kim et al., 2022; Kim et al., 2023). Isolated CSC was suspended in growth media (GM) containing 20% fetal bovine serum (FBS; S1-004, Welgene, Gyeongsan, Korea), 1% GlutaMAXTM supplement (35050061, Gibco, London, UK), 1% antibiotic-antimycotic (15240062, Gibco), and 5 ng/mL basic fibroblast growth factor (233-FB-025, R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA) in DMEM. The cells were initially cultured in 175T flasks at a density of 3,000 cells/cm2 in 41°C and 5% CO2 incubator for scale-up. When the cell confluency came over 70%, the supernatant was aspirated, and the cells were dissociated using 0.25% trypsin-EDTA (LS015-10, Welgene). The cell suspensions were centrifuged at 800×g for 5 min to harvest the cells for further 3D culture. Cytodex 1 (Cytiva, Marlborough, MA, USA) microcarriers were sterilized by autoclaving at 121°C for 20 minutes, and subsequently hydrated in GM for 1 hour prior to use. The cells were seeded into the spinner flasks with Cytodex 1 microcarriers and cultured at a density of 3,000 cells/cm2 in 41°C and 5% CO2 incubator with stirring at 50 rpm. When the cells reached 100% confluency, the GM was aspirated, the cells were rinsed three times with DPBS. The cells were then dissociated using 0.25% trypsin-EDTA for 5 mins and the cell suspensions were passed through a 100 μm sieve to remove Cytodex 1 microcarriers. The cell suspension was centrifuged at 800×g for 5 min to harvest CMT. The harvested CMT was lyophilized using freeze-dryer (OPERON OPR-FDB-5503 FREEZE DRY SYSTEM, OPERON, Gimpo, Korea) and then kept in a –70°C deep freezer until a sufficient amount of CMT was collected for the next experiments.
Pea protein isolate (PPI) and WP were purchased from an online platform. Sodium alginate (SA) with high viscosity was obtained from online market (ESfood, Gunpo, Korea). Calcium chloride was purchased from Qingdao Soda Ash Industrial Development (Qingdao, China). All materials used for experiments were of food grade.
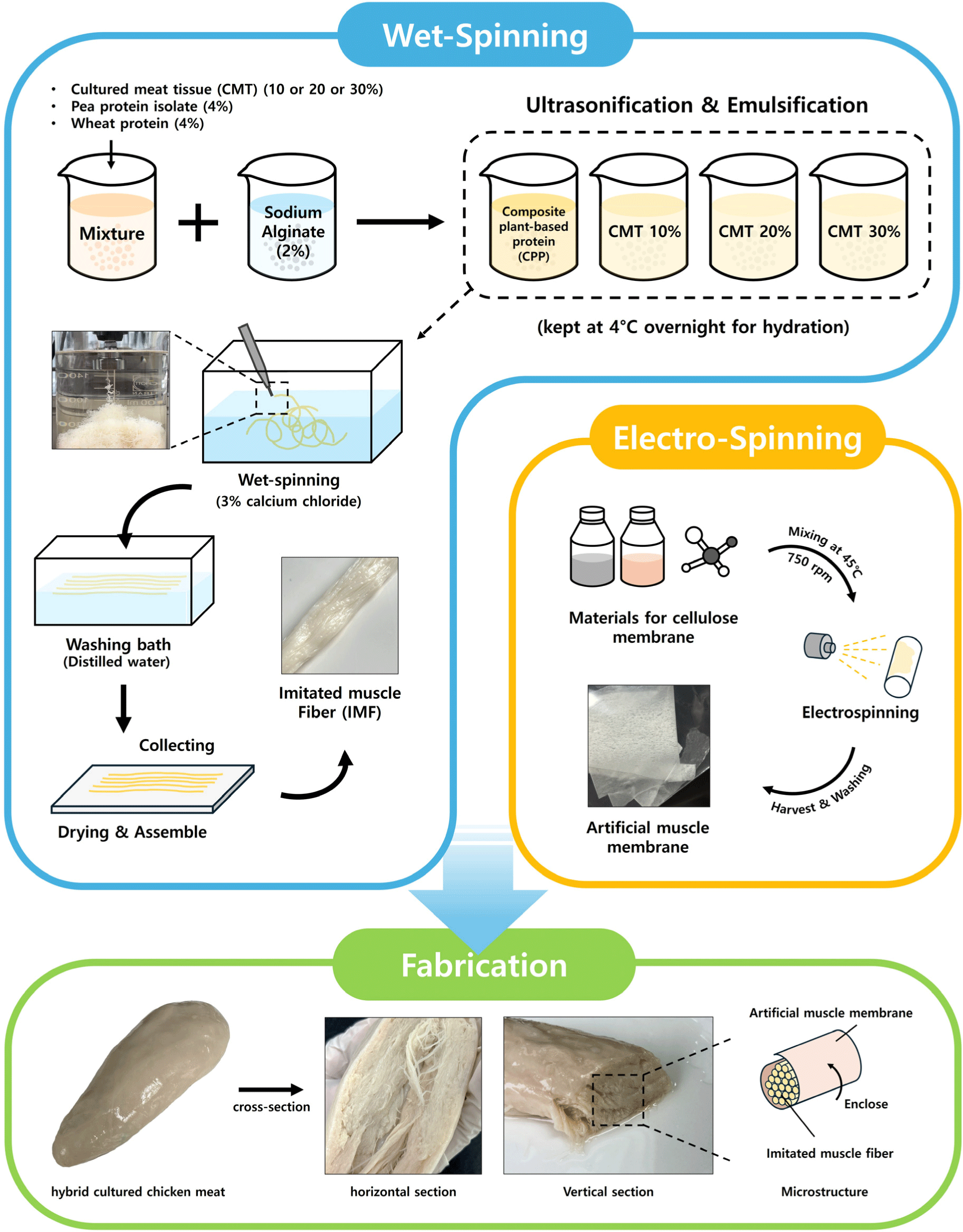
Plant protein solution was prepared by dissolving 4% (w/v) WP and PPI in distilled water (DW) respectively. SA solution was formulated by dispersing SA in DW at a concentration of 2% (w/v). All solutions were kept at 4°C overnight to achieve complete hydration and a stable state. The plant protein solution was prepared by mixing WP and PPI solutions in equal amounts. Then, for making composite plant-based protein (CPP) solution, SA solution was mixed with plant protein solution in equal ratio. Hybrid cultured chicken meat (HCCM) contains 4% PPI, 4% WP, and CMT at concentrations of 10%, 20%, and 30%, which were mixed in equal volumes. SA solution was also added to mixture for HCCM production. All the solutions were uniformly mixed for 20 min and degassed for 20 min at room temperature with at 20 kHz using ultrasonicator (VCX 750, SONICS, Newtown, CT, USA).
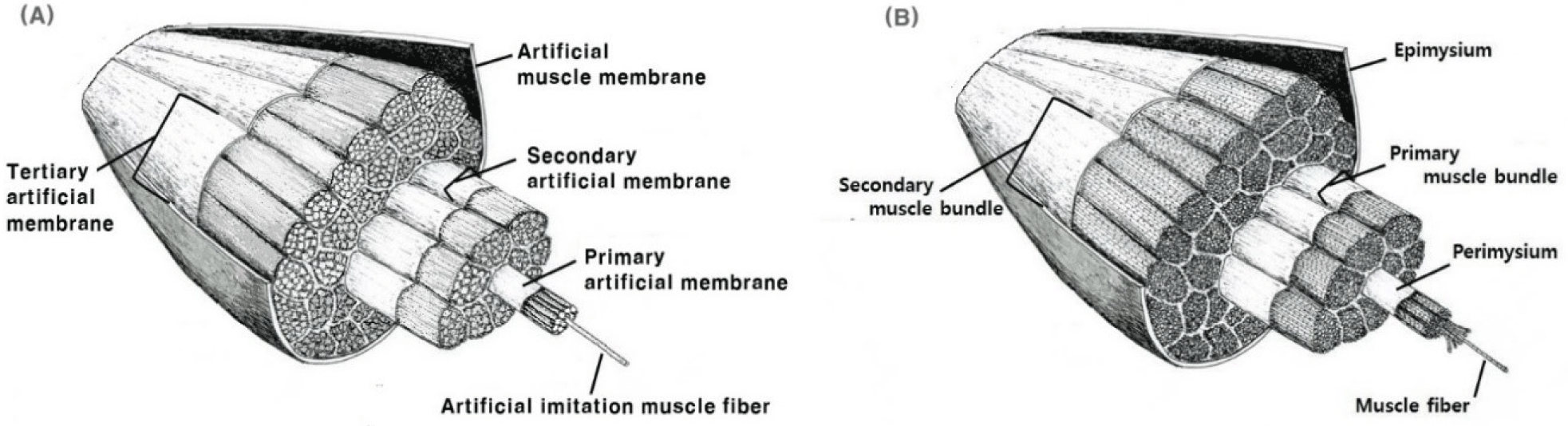
Imitated muscle fiber (IMF) was manufactured using wet-spinning according to the method of Kumari et al. (2024). In a coagulation bath, CPP solution or CPP solution containing CMT were extruded through a needle of 0.13 mm in diameter into a 3% calcium chloride (w/w) at room temperature (20°C–25°C). IMFs were washed in the washing bath containing DW to remove the excess or remaining calcium chloride from surfaces of IMFs. After collecting IMFs, a cellulose membrane produced by electrospinning technique was used for warping each IMF. The process was repeated a number of times to make several muscle bundles which were then surrounded by a secondary membrane to provide a mimicking effect like conventional meat. CPP samples added with 10%, 20%, and 30% concentrations of CMT were designated as CMT 10%, CMT 20%, and CMT 30% respectively. Fig. 1 is a diagram showing the structure of artificial imitation meat that mimics the structure of conventional meat.
Cellulose acetate (CA), glacial acetic acid (AA), and citric acid anhydrous (CAA) of food grade were purchased from an online platform. CA solution stock solution was prepared by blending into 20% (w/v) of CA dissolved in 85% (V/V) AA. The process was carried out at 45°C with continuous stirring at 750 rpm for 12 hours until the solution became fully homogenized. For crosslinking, CAA was added to the stock solution of CA (30%). This solution was mixed with a magnetic stirrer for 30 minutes at 25°C with shaking at 1,500 rpm until a homogenous solution was obtained. Prepared solutions were then loaded into a 10 mL syringe with a 23 G needle and put into an electrospinning device (Electrospinning System, Nano NC, Seoul, Korea). Based on preliminary examinations, optimized electrospinning parameters were: a voltage of 18 kV, a needle-to-collector distance of 12 cm, a flow rate of 0.4 mL/h, and a collector rotating speed of 500 rpm.
HCCM was manufactured by introducing CMT into CPP solution at different levels (10%, 20%, and 30%). Fig. 2 illustrates the manufacturing process of HCCMs. Wet-spinning and electro-spinning techniques were used to produce IMF and artificial muscle membrane, respectively. The CPP solution without CMT was designated as CPP, while HCCMs produced by adding CMT to CPP were designated as CMT 10%, CMT 20%, and CMT 30% according to CMT content. Each IMF produced through coagulation using wet-spinning was fabricated by wrapping IMF with an artificial muscle membrane in order to replicate the structure of traditional muscle.
Color values of IMFs (CPP, CMT 10%, CMT 20% and CMT 30%) were measured with a Chroma Meter (CR-300, Konica Minolta, Osaka, Japan). Color values (CIE L*, CIE a*, and CIE b*) are presented as average values obtained from five measurements for each sample. Results are expressed as mean±SD.
IMF was homogenized with DW at a ratio of 1:9. pH was measured triplicate using a digital pH meter (A211 pH Meter, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
IMF samples were cut into pieces with dimensions of 1 cm×1 cm×1 cm (length×width×height). Warner-Bratzler shear force (WBSF) was measured with a texture analyzer (AMETEK, Berwyn, PA, USA) and a V-shaped shear blade on its shear mode. The analysis was performed at a speed of 100 mm/min with a force of 50 kg. Data were processed and expressed as mean and SD of values measured five times.
Texture profile analysis (TPA) was conducted using a double compression test, involving compression of the sample under fixed conditions. TPA of IMF was performed with a texture analyzer (AMETEK). All samples were shaped into 1 cm×1 cm×1 cm cubes. Compression and decompression were conducted twice at a fixed speed of 100 mm/min and a maximum load of 180 kg on a measuring cell. TPA parameters included hardness, springiness, gumminess, chewiness, and cohesiveness of each sample. Data were processed and expressed as mean and SEM for values measured five times.
IMF (500 mg) was hydrolyzed with 6 N HCl in a dry oven at 110°C for 16 h. The hydrolysate was filtered with a Whatman filter no.1 paper and diluted with DW to a concentration of 0.1 N. Sample vials were then prepared by filter through a 0.22 μm PTFE syringe filter. Total amino acid content was analyzed using an OPA derivatization protocol provided by Agilent.
An electronic tongue system (ETS; INSERT SA402B Electric Sensing System, Insent, Tokyo, Japan) was used for measuring relative sensory characteristics of each sample with the technique exemplified by Ismail et al. (2020). The ETS can distinguish five different flavors with five different taste sensors (CA0, C00, and AAE) to analyze relative intensities of sourness, bitterness, umami, and richness, respectively. All membranes in sensors were stabilized in a standard meat taste (SMT) solution containing 0.01% lactic acid (DAEJUNG, Busan, Korea), 0.25% monosodium glutamate (DAEJUNG, Korea), and 0.0005% quinine hydrochloride (TCI, Tokyo, Japan). A solution obtained by mixing IMF with DW at 100°C was used for sensory analysis at ratio of 1:4 for 30 min. The agitated solution was centrifuged at 1,000×g for 15 min. The supernatant was collected and stored at –70°C for further analysis.
Statistical analyses were conducted using GraphPad Prism 10 software 10.0.2 (GraphPad, San Diego, CA, USA). All data are presented as mean and SD or SEM. The WBSF and TPA were measured in quintuplicate, while all other experiments were conducted in triplicate. Results were subjected to one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Principal component analysis (PCA) was conducted to assess the variation in overall qualities among the treatment groups (CPP, CMT 10%, CMT 20%, and CMT 30%). The variables used in PCA included the data of physicochemical analysis, amino acid analysis, and sensory analysis, respectively. A score plot was illustrated for the differences in distribution among groups. Statistical significance was considered when p-value was less than 0.05.
Results and Discussion
The solution pH for wet-spinning decreased significantly (p<0.05) after adding CMT to CPP (Table 1). The pH of the CPP solution (6.83) was mild neutral due to the presence of pea protein and WP along with SA. This trend could be due to increased amounts of glutamic acid and aspartic acid as total amino acid content was increased with each addition (Ferreira and Teixeira, 2003). Additionally, with increasing concentration of CMT, the buffering capacity of plant proteins may have been insufficient to neutralize additional acidic by-products from CMT, causing the overall pH to drop (Ebert et al., 2021).
This change in pH due to the addition of CMT is likely to interfere with homogeneous distribution of particles in the solution, leading to difficulties in dissolving materials. Moreover, in a previous study (Kumari et al., 2024) using wet-spinning, the highest water-holding capacity (82.66%) was observed at pH 6.44. This indicates that pH is directly related to water-holding capacity, highlighting the importance of pH control during the preparation of a solution for wet-spinning.
Results of color measurements including CIE L*, CIE a* and CIE b* are shown in Table 1. Overall color values showed a significant increase compared to CPP as the concentration of CMT in HCCM increased (p<0.05). This indicates that the addition of CMT makes the color brighter, redder, and more yellow. This color change was caused by a brighter and more yellowish color of the CMT than other plant-based protein relatively, indicating that the color of HCCM produced through wet-spinning could be greatly influenced by the color of materials used in its production (Cui et al., 2014; Fraeye et al., 2020). It has been suggested that color attributes can enhance visual attractiveness of hybrid cultured chicken breast, potentially increasing consumer acceptance by adding CMT (Lee et al., 2020). In addition, the cross-sectional view of HCCM produced using wet-spinning showed a fibrous structure more similar to that of muscle fibers in conventional meat when CMT was added (Fig. 2). This suggests that the addition of CMT during the manufacture of HCCM using wet-spinning techniques has the potential to achieve a more similar appearance to conventional meat.
Table 2 shows changes in tenderness and texture of HCCM with the addition of CMT. WBSF of CPP was significantly higher than those of CMT 20% and 30% HCCM. The WBSF decreased significantly (p<0.05) when CMT content was increased. This decrease of WBSF implies that addition of CMT can make tender HCCM. Adding CMT could have created a softer texture by interfering with the rigid cross-linking structure of plant protein with SA, resulting in a reduction in WBSF for CMT 20% and CMT 30% HCCMs. For CMT 10% containing, it was thought that plant-based proteins interacted with CMT to form strong gels with increased structural integrity of the structure, resulting in a stiffness of HCCM. In a study by Bakhsh et al. (2021) and Caine et al. (2003), the WBSF of plant-based meat analog (PBMA) patty was approximately 2.74 kgf/cm2. This value fell between values for conventional beef and pork patties. Similarly, in the present study, HCCM produced by wet-spinning had WBSF values generally ranging from 2.0 to a maximum of 3.2, close to the WBSF value of conventional meat. This result suggests that wet-spinning techniques can control tenderness more easily by adjusting the composition of IMFs than the high-temperature extrusion method for manufacturing textured vegetable protein (TVP).
On the other hand, the addition of CMT resulted in a significant change in the texture of HCCM. Similar to WBSF results, hardness values of CMT 20% and CMT 30% were significantly higher than that of CPP (p<0.05). However, CMT 10% and CPP showed no significant difference in hardness (p>0.05). This trend was observed similarly in a previous study (Kumari et al., 2024). The springiness displayed no significant difference until CMT was introduced into CPP at 20% (p>0.05). However, springiness showed a significant decline in CMT 30% (p<0.05). The decrease of springiness in hybrid meat containing 30% of CMT could be due to interactions of different protein types. These proteins might have affect cross-linking with SA during the process (Nagamine et al., 2023). Gumminess, chewiness, and cohesiveness were significantly lower in CMT 10% among HCCMs. This could be due to an antagonist effect of the plant-based protein and a low concentration of the CMT protein (Ježek et al., 2020). With increased concentration of CMT, the overall cultured meat protein content might have cross-linked with each other, creating a firm and more cohesive structure (Kumari et al., 2024; Younis et al., 2023).
Amino acid analysis was conducted to determine how much CMT should be incorporated into CPP to have an effect on amino acid compositions and contents of HCCM. Results of amino acid analysis are shown in Table 3. Essential amino acid levels were increased comprehensively except for phenylalanine, improving the nutritional quality of the HCCM. These significant changes in essential amino acid level were attributed to the incorporation of CMT into CPP which resulted in increased total amino acid content. Results of amino acid composition analysis showed a distinctive decrease in glutamic acid due to wheat gluten in CPP solution because gluten could produce glutamic acid by hydrolysis (Manning, 1950). Glutamic acid sees a large increase, reflecting a high protein content in cultured meat, making it a key contributor to the blend (Qi et al., 2017). Lysine showed a dramatic rise displaying that the addition of CMT has compensated for its lower levels in plant proteins, along with a significant increase in amounts of leucine, isoleucine, and valine due to their abundance in animal-derived proteins, highlighting the impact of cultured meat on enhancing the solution’s nutritional value. On the other hand, proline and tyrosine showed smaller increases, with significant changes emerging at higher cultured meat levels (CMT 20% and 30%). Additionally, the other amino acids such as phenylalanine, aspartic acid, and arginine also increased notably with each addition of cultured meat, further enriching the overall amino acid profile.
The increase in amino acid content with the addition of CMT could be due to its rich protein profile, which complements plant proteins in pea and wheat (Treich, 2021). Therefore, this study confirms that adding CMT could compensate for amino acids that are lower or missing in plant proteins, such as lysine, proline, and branched-chain amino acids (leucine, isoleucine, valine), leading to significant improvements in the overall nutritional quality (Wu, 2021).
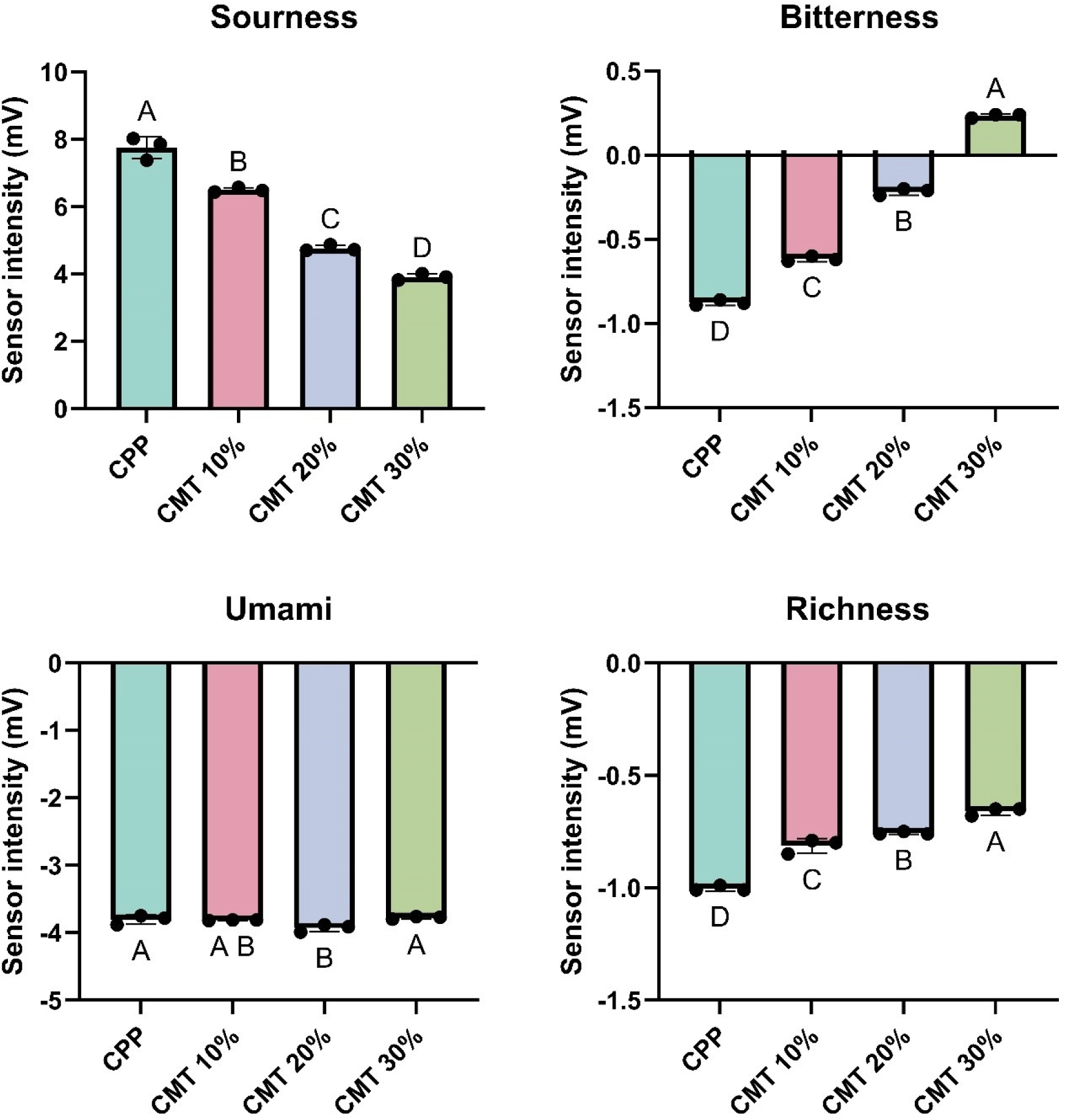
Changes in taste characteristics of HCCM evaluated by electronic tongue with addition of CMT to CPP are shown in Fig. 3. Overall, taste profiles including sourness, bitterness, and richness were significantly increased except for Umami (p<0.05). In general, considering that a decrease in the sourness of HCCM improves the overall taste, it is presumed that the addition of CMT can positively enhance the taste of HCCM. However, there was no change in umami level with an increase in the amount of CMT. The reason for the unchanged umami level can be due to the antagonist effect resulting from an increase of aspartic acid and a decrease of glutamic acid (Table 3). Although the richness of HCCM increased significantly, indicating that the overall mouthfeel may have increased due to increasing overall amino acid profile and the protein interaction (p<0.05; Paradowska et al., 2021; Xu and Falsafi, 2023). Meanwhile, the CMT addition increased the bitterness, especially in CP30 could be due to additional peptides and amino acids (e.g., histidine, arginine isoleucine, leucine; Tagliamonte et al., 2024).
PCA was conducted to analyze variations in quality among the four treatment groups (CPP, CMT 10%, CMT 20%, and CMT 30%). The first principal component (PC1) accounted for 66.19% of the total variance and the second principal component (PC2) explained an additional 12.29% of the total variance (Fig. 4). These two components explained approximately 78.48% of the total variance, providing most of the differences among treatment groups.
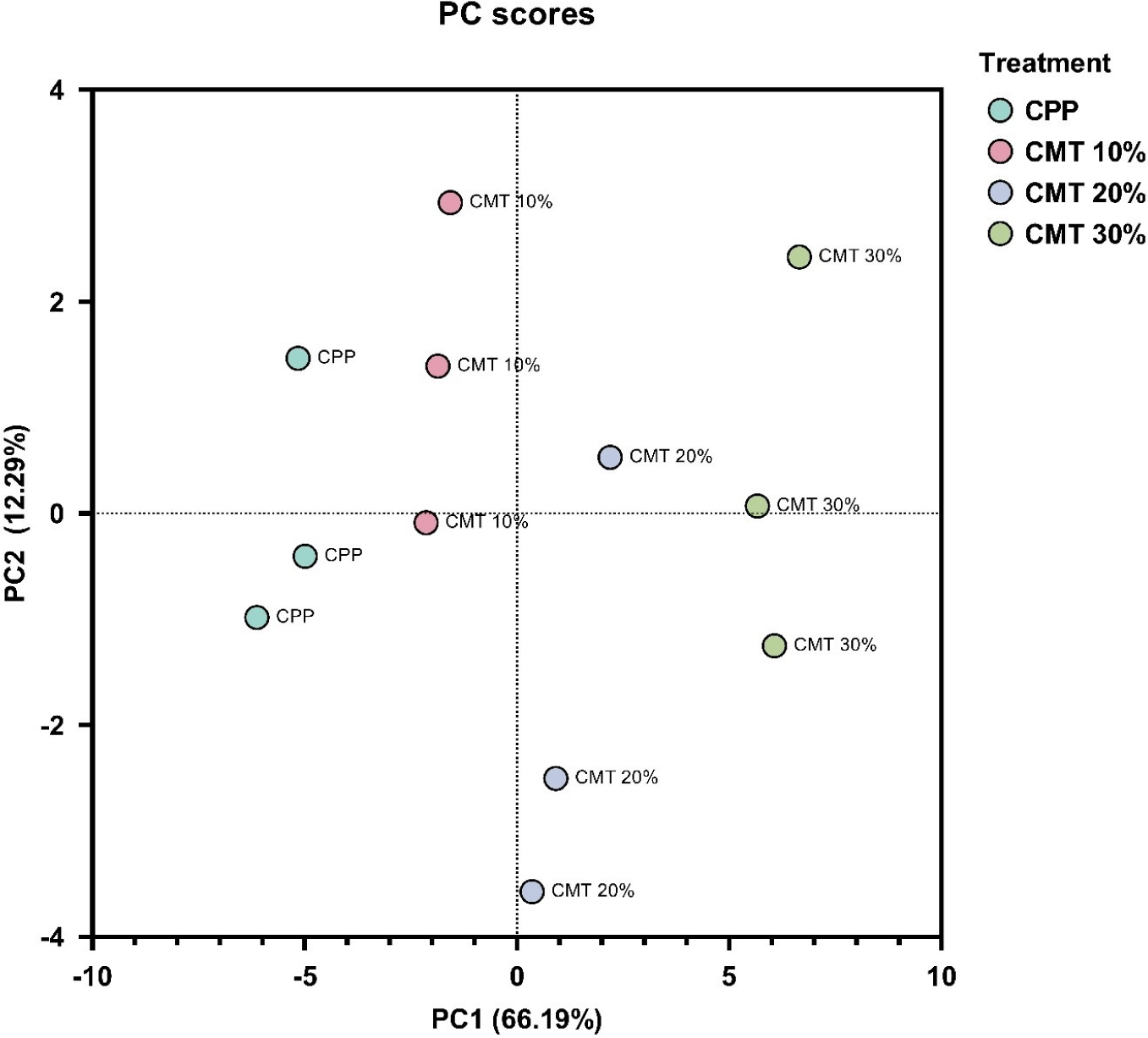
CPP and CMT 10% groups were mainly positioned on the negative side of PC1. This indicates that CPP and CMT 10% have similar characteristics. The result indicated that although CMT was added to the CMT 10% group, the effect on quality was minimal, leading to a closely clustered grouping with CPP in the PCA plot.
CMT 20% and CMT 30% groups showed positive values in PC1 compared to the other two groups. In particular, CMT 30% was located on the far right of the PC1 plot, which was clearly separated from the other three groups. When comparing CPP and CMT 30% groups, these two groups were most distinctly separated by PC1 in the PC plot, indicating significant differences in their quality. The addition of CMT to hybrid cultured chicken breast has a significant impact on the quality of HCCM, indicating that selecting the optimal combination of plant and animal proteins in hybrid meat production can considerably enhance both its nutritional value and overall quality.
Conclusion
The addition of CMT to CPP significantly improved the quality of IMF and HCCM produced via wet spinning. Specifically, CMT incorporation reduced pH and WBSF but enhanced essential amino acid levels, thus improving nutritional quality. Texture and sensory properties also improved from CMT addition, with higher content increasing the hardness, chewiness, and flavor richness. Overall, CMT can effectively compensate for deficiencies in plant proteins, enhancing both nutritional and sensory qualities of HCCM.













