Introduction
Goat meat is a rich source of protein with essential amino acids for consumers to meet their dietary requirements, and it is also an excellent source of iron because heme iron is more available than non-heme iron (Casey and Webb, 2010). Furthermore, because of its low cholesterol and fat content, it is a good source of nutritious red meat for human nutrition (Resul Ciftci and Kor, 2010). According to Ivanović et al. (2016), goat meat is high in unsaturated fatty acids (UFAs), and the presence of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) is associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease and stroke. However, frequent consumer complaints regarding goat meat are associated with an unpleasant flavor and smell. The peculiar odor, called goaty flavor, affects the acceptability of goat meat. This odor is produced during cooking by the interactions of nonvolatile precursors such as free amino acids, UFAs, and reducing sugars (Madruga et al., 2010).
Evidence suggests that the specific odor of cooked goat meat is partially caused by branched-chain fatty acids (BCFAs; Madruga et al., 2000). The peculiar odor of mature males is caused by sebaceous gland secretions that are stimulated by testosterone (Van Lancker et al., 2005). BCFAs in serum have been identified as the odor components, it is possible that the peculiar odor transfers from blood to meat (Nagamine and Sunagawa, 2017). Higher levels of BCFAs in meat can cause a peculiar odor, but lower levels of BCFAs can increase overall acceptability (Watkins et al., 2021). The combination of smell (volatiles) and taste (non-volatiles) chemicals influences meat flavor, although taste is more important for consumer perception (Grabež et al., 2019).
Small molecules of water-soluble metabolites such as free amino acids, nucleotides, peptides, sugars, thiamine, and acids are important meat flavor precursors in Malliard, Strecker, and other reactions (Mottram, 1998); and they also contribute to the development of savory, kokumi, umami and meaty flavors that consumers find appealing (Hartley et al., 2019; Kuroda and Miyamura, 2015). The reaction of amino acids and sugar is crucial in the development of desirable meaty flavors; carnosine, creatine, creatinine, and nucleotides are also involved in meat flavor characteristics (Madruga et al., 2010).
Additionally, androsterone, skatole, and indole are known to be the primary odor-causing substances in boars (Ma et al., 2021). Typically, the goat breeding season lasts from the end of summer to the start of winter (Brunet et al., 2011). Matured male goats change their behavior and emit an intense odor during the breeding season (Nagamine and Sungawa, 2017), which may cause boar taint (Claus et al., 1994). The primary cause of boar taint in goats is androsterone, a testicular steroid hormone that imparts a urine-like odor to meat (Lee et al., 2005). Another reason for the production of boar taint is indoles, especially 3-methyl indole or skatole (Robic et al., 2008). Indoles are produced by bacteria in the monogastric colon and correlate with a high concentration of gonadal hormones, emitting a faecal-like odor and bitterness (Salvatore, 2003). Skatole impairs the organoleptic quality of meat and contributes to an unpleasant odor during cooking (Deslandes et al., 2001). Therefore, castration is a possible method for reducing the peculiar odor and improving the marbling score of the meat (Nagamine and Sunagawa, 2017).
Castration is a key tool for reducing animal stress and male aggressiveness, improving animal welfare (Bretschneider, 2005), and producing carcasses with higher meat quality in comparison to intact carcasses (Solaiman et al., 2011). It improves meat tenderness and flavor by increasing intramuscular fat content (Park et al., 2018). Additionally, castration is widely used to reduce the strong and unpleasant odor in goat meat and to manage the breeding program (Kebede et al., 2008). Further, Daszkiewicz et al. (2003) reported that the aging process improved the sensory properties of meat. According to Miller et al. (1997), beef aged for 14 days as opposed to 7 days had a more intense flavor. Thus castration and aging of goat meat could reduce the goaty flavor produced by some flavor precursors.
To produce high-quality goat meat preferred by consumers, identifying the precursors of goaty flavor is crucial with an appropriate animal management system that incorporates nutrition, transportation, sex, castration, storage techniques, and aging. However, there have been few published studies on aroma precursors in goat meat (Dinh et al., 2021; Madruga et al., 2010). Furthermore, there is considerable debate about why goat meat has an intense flavor regardless of sex. Therefore, this study aimed to determine the causative agent of the goaty odor in Korean native black goat meat. Moreover, we sought to compare the physiochemical and functional components of the loin meat from different sexes of black goats.
Materials and Methods
Thirty-five Korean native black goats (Capra hircus coreanae), namely A: 12 were castrated male (CM), B: 11 were non-castrated male (NCM), and C: 12 were female (FM) were reared under the same diet and farming conditions at a goat farm, Gangjin-gun, Jeollanam-do, Korea. The goats were 16 mon of age and their average weights were 35.26±4.22 kg for CM, 40.7±3.52 kg for NCM, and 27.94±2.56 kg for FM. After slaughter, the loin meats were collected with oxygen permeability packaging at 4°C and transported to the laboratory for further analysis. The lean meat was separated by trimming off visible fat, then identifying the portions with less marbling, carefully separating them from the rest of the meat with a sharp knife, and finally ground with a meat grinder (KitchenAid – Mixer Model 5K5SS, Foodmach, La Habra, CA, USA). The samples were then stored at 4°C in a laboratory refrigerator before being analyzed on the 1st, 5th, and 8th consecutive days.
General component analysis was conducted in accordance with the AOAC (2000) method. The moisture content of the loin portions of three different black goats was determined using the oven-drying method. The fat content was determined from 5 g of the sample using a 2:1 ratio of chloroform/methanol in accordance with the method used by Folch and Lees (1951). The crude protein was determined using an automatic Kjeldahi apparatus (K-370, Buchi, Flawil, Switzerland).
A colorimeter was used to assess the color of the meat on the cut surface (CR-410, Minolta, Osaka, Japan) and calibrated with a black and white calibration plate. First, the meat was sliced and allowed to bloom for 30 min at room temperature, and CIE L*, CIE a*, and CIE b* were obtained using the average value of three repeated measurements on the surface of each sample. For the pH test, 2 g of the sample was homogenized with 18 mL of distilled water in a Polytron PT 10-35 GT (Kinematica AG, Luzern, Switzerland) at 15,000×g for 1 min before being filtered through Whatman No. 4. The filtrate of each sample was assessed at room temperature with a pH meter (Seven ExcellenceTM, Mettler-Toledo, Schwerzenbach, Switzerland). Lipid oxidation was measured by adding 5 g of sample, 15 mL of distilled water, and 50 μL of butylated hydroxytoluene (7.2% in ethanol, w/v) to a 50-mL test tube and then homogenizing the mixture (Ahn et al., 2008). The homogenate (2 mL) was shifted to a 15 mL centrifuge tube, and then 4 mL of TBA/TCA (20 mM thiobarbituric acid/15% trichloroacetic acid, w/v) solution was added. The mixture was vortexed, placed in 90°C hot water for 15 min to accelerate the color development process, and then cooled for another 15 min. The mixture was then centrifuged at 4°C and 1,100×g for 15 min, and the supernatant absorbance was estimated at 531 nm. Next, 2 mL of the TBA/TCA solution and 1 mL of distilled water were used to make the blank solution. Malonaldehyde (MDA) standard curves were created by employing 1,1,3,3-tetra-ethoxypropane. The quantity of TBARS was expressed in milligrams of malondialdehyde (MDA) per kilogram of meat sample from the standard curve.
In order to perform descriptive analyses through preliminary training, 10 sensory evaluation panels were selected. The panelists underwent eight initial sessions to become familiar with the criteria and scales. Under the same cooking conditions, the sample was sliced into a cubic form (30×50×30 mm) and heated until its core temperature reached 72°C, and a portion of the sample was provided to the panel. The sample was evaluated using a 9-point scale method based on 5 points of non-castration. Rancid odor (1 point=very weak, 9 points=very strong), off-flavor (1 point=very weak, 9 points=very strong), flavor preference (1 point=very weak, 9 points=very good), and overall preference (1 point=very weak, 9 points=very good) were assessed. Sensory evaluation was approved by the Sunchon National University Institutional Review Board (1040173-202107-HR-010-02).
The back fat samples were stored at –20°C until analysis and separated from the skin after thawing. The samples were quantified using the extraction method (Dehnhard et al., 1993). The fat sample was heated in a microwave oven at 700 W for 1 min. Only 200 μL of adipose tissue was placed in a 2 mL Eppendorf (EP) tube, and 800 μL of methanol: hexane (9:1) was added. Then, it was extracted using ultrasonic waves at 50°C for 40 min, and mixing was performed every 5 min. For fat phase separation, samples were stored at –18°C for 30 min before being centrifuged at 27,000×g for 10 min. The supernatant was transferred to a 2 mL brown autosampler vial, and the androgen, indole, and skatole contents were analyzed according to GC-MS conditions.
The fatty acid composition of black goat meat was estimated using a procedure reported by O’Fallon et al. (2007). For the separation of fatty acid methyl esters, 0.7 mL of 10 N potassium hydroxide (KOH) and 6.3 mL of methanol was mixed with each sample (1 g). This mixture was then added to a water bath that was kept at a constant temperature of 55°C. The samples were heated for 1.5 h, with vigorous shaking every 30 min. Subsequently, 0.58 mL of 24 N H2SO4 was added to the compound after being cooled for 1–2 min in ice-cool water. The mixture was then heated again at the same constant temperature using the same process. Centrifugation was carried out at 1,100×g for 5 min (HANL Combi-514R, Hanil Scientific, Inchon, Korea) after adding 3 mL of hexane and placing it in a vial using a Pasteur pipette. This assay was conducted under the following conditions using a gas chromatography-flame ionization detector (Agilent 7890 series, Agilent, Wilmington, DE, USA): The injector was in split mode with a split ratio of 25:1 at a temperature of 250°C, and the detector was flame ionization. High-purity air, H2, and He were used as the carrier gas, and the flow rate was 40 mL/min for H2 and 400 mL/min for air. The column for analysis was HP-88 (60 m×250 μm×0.2 mm). A relative percentage of all evaluated fatty acids was used to represent each fatty acid.
Sample extraction and NMR analysis were conducted following the procedure described by Kim et al. (2019a). Each treatment sample (5 g) was extracted using 20 mL of 0.6 M perchloric acid. The sample was homogenized, and the homogenate was centrifuged (Continent 512R, Hanil, Daejeon, Korea) at 3,500×g for 20 min. Then, the pH was adjusted to 7.0 using KOH solution, and the supernatant was centrifuged once again under the same conditions. Each supernatant was filtered (Whatman No. 1) and lyophilized (Lyoph-Pride, LP03; Ilshin BioBase, Dongducheon, Korea). Additionally, before NMR analysis, 20 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) was used with D2O containing 1 mM 3-(trimethylsilyl) propionic-2,2,3,3-d4 acid (TSP) to dilute the lyophilized sample. NMR analysis was performed using a Bruker 850 MHz cryo-NMR spectrometer (Bruker Biospin, Rheinstetten, Germany). Next, spectral analysis was conducted using Topspin 4.0.8 (Bruker Biospin), and quantitative analysis was performed using TSP as an internal standard.
The general linear model procedure of the SAS program (Version 9.3, SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA) was used for the calculation of experimental data. A significant test between the mean values was performed using the Student-Newman-Keuls multiple-test method when significant differences were found after a one-way ANOVA with a confidence level of p<0.05. Notably, Tukey’s multiple range test was used to analyze water-soluble metabolites. Results were expressed as the mean value and the SEM, which is the SE of the treatment interval.
Principal component analysis (PCA) and partial least squares-discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) were performed using MetaboAnalyst 5.0 (http://www.metaboanalyst.ca).
Results and Discussion
Table 1 shows a comparison of the meat compositions of NCM, CM, and FM. FM had significantly lower moisture content than NCM and CM, but there was no significant difference in goat meat between NCM and CM. Meat products with high moisture content are more prone to spoilage and microbial growth, whereas meat products with low moisture content are dry and tough (Rawat, 2015). These results are consistent with those of Kumar et al. (1983), who found no significant difference between CM and NCM. However, Kim et al. (2020b) reported that moisture content was not significantly different between male and FM native black goats. In the current result, the moisture content of FMs decreased which could be attributed to the lower pH. When the pH falls, myofibrillar proteins are denatured and finally water molecules come out from the lattice that can contribute to lower water holding capacity (WHC) and moisture content. Watanabe et al. (2018) also mentioned that WHC can be positively correlated with the pH of meat.
| Sex | Moisture | Protein | Fat | Ash |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-castration | 75.80a | 21.97c | 3.56a | 1.04a |
| Castration | 75.33a | 22.62b | 2.57b | 0.98b |
| Female | 74.34b | 24.31a | 3.45a | 1.04a |
| SEM | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.21 | 0.01 |
Kim et al. (2019b) reported a crude protein content of 21.30%–21.60% in black goat meat. Furthermore, the protein content of both CM and NCM goats was 18.69% to 23.39% (Madruga et al., 2000). The protein content was within the previously reported range (21.97%–24.31%) in our study (Table 1) and was significantly different between NCM, CM, and FM (p<0.05), where the FM recorded the highest value, followed by CM and NCM. In an earlier study, Kim et al. (2020b) described that the crude protein was not significantly different between FM and male black goats (18.02% and 19.54%, respectively). Kansal et al. (1982) found that the protein content of meat from intact male goats was marginally higher than that from CM goats. However, Hoffman et al. (2008) reported that M. longissimus dorsi of FM mountain reedbuck observed higher protein content in FM than male. It is possible due to the hormonal difference that may contribute to higher protein content in FM. The results of the present study revealed that sex and castration status had a significant impact on the protein content of black goats.
There was no difference in fat and ash contents between NCM and FM, but the CM was lower than the NCM and FM (p<0.05, Table 1). Generally, CM goat meat has a higher fat content than NCM meat because of the regulation and different concentrations of growth hormones and metabolites (Galbraith et al., 1978). However, castration does not affect fat accretion in goats (Tahir et al., 1994). Additionally, castration had no discernible impact on the amount of fat in goat meat (Kumar et al., 1983; Madruga et al., 1999). Choi et al. (2010) reported that the fat composition and content in meat change according to the castration time; earlier castration had higher fat content and vice versa. Castration performed too late may lead to incomplete fat deposition during slaughter, affecting the fat content of the meat.
Consumers focus on the color of meat because it indicates the freshness and quality of the product (Kimball, 1986). Table 2 compares the quality characteristics of black goat meat based on sex during the storage period. On the 1st day, the CIE L* was higher in NCM than in CM and FM, whereas CM had the lowest CIE L* (p<0.05). Higher CIE L* is caused by a low concentration of myoglobin, which is a meat pigment (Ali et al., 2021). In addition, Fiems et al. (2000) mentioned that higher fat content can contribute to the higher CIE L* of meat. Furthermore, the lower CIE L* of meat is a result of higher antemortem glycolysis rates and a slower pH decline (Mach et al., 2009). After 5 days of storage, the CIE L* increased in all groups, especially in CM, which had the highest CIE L* (p<0.05). Protein structures changed with ageing as a result of proteolysis, which can affect CIE L* (Renerre, 1982). After 8 days of storage, the CIE L* of CM decreased while the of NCM increased, and FM had a stable CIE L* throughout the storage period.
In terms of the CIE a*, there is no noticeable difference between treatment groups on the 1st day. On day 5, the CIE a* of CM and FM increased significantly, whereas NCM did not. The CIE a* of the meat was probably altered by the presence of oxygen. Fresh meat has a distinctive bright red color due to the red myoglobin, which is produced as a result of oxygen binding (Suman and Joseph, 2013). However, it decreased significantly again in CM and FM on day 8. Meat loses its CIE a* as metmyoglobin builds up, and it may take on a brownish or greyish color (MacDougall, 1982). In addition, this is associated with the decreased reduction in myoglobin during the storage period (Karamucki et al., 2013), which occurs because myoglobin probably loses its oxygen, thereby reducing the CIE a* of the meat (Bekhit et al., 2019). However, there was no significant change in the CIE a* of NCM throughout the storage periods.
The CIE b* increased significantly with increasing storage for 5 days in all treatment groups. CIE b* alter depending on how rapidly myoglobin is exposed to oxygen (Lindahl et al., 2001). According to Saucier et al. (2000), these increases are associated with the progression of meat spoilage processes, with an emphasis on oxidative processes. After 8 days of storage, the CIE b* decreased significantly in CM and FM whereas NCM increased continuously.
The pH values of different sex groups of black goat meat are listed in Table 2. The results showed that on day 1, the pH of FM was significantly lower than other treatments (p<0.05), while CM and NCM were almost the same (6.03 and 6.01, respectively). After 5 days, the pH of all meat was lower and significantly differ among treatment groups (p<0.05). However, after 8 days of aging, the values continued to increase regardless of the treatment group (p<0.05). Jones (2004) mentioned that the pH of meat tended to decrease during storage, and this is associated with both a rise in the LAB population and a rise in the concentration of acetic acid. However, after some days of aging, the pH can stabilize and increase again. This could be attributed to proteolysis, i.e., the breakdown of proteins into smaller peptides and amino acids; this procedure can aid in the release of alkaline substances into meat, thereby neutralising some of the acidity and increasing pH levels (Addy et al., 2004).
The initial TBARS level was higher in NCM than in CM and FM; however, the TBARS levels increased significantly with time in all treatment groups. Among them, the MDA level of NCM increased significantly compared to the other treatment groups (p<0.05). One of the main factors contributing to the degeneration of meat is lipid oxidation, which is influenced by the intramuscular fatty acid content, especially PUFAs (Wood et al., 2004). In the current investigation, the PUFA concentration is significantly higher in NCM than in CM and FM.
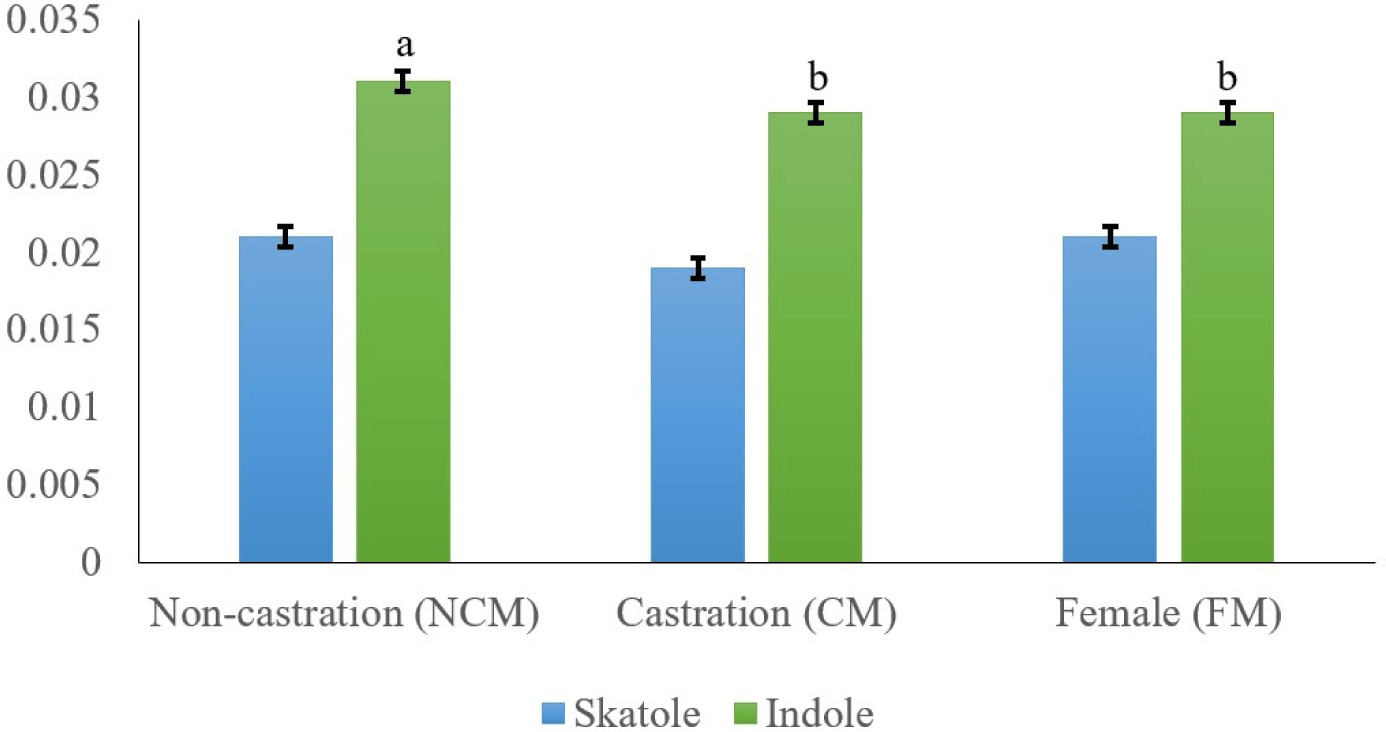
The main compounds that cause boar odor (skatole and indole) were examined in relation to the sex of black goats (Fig. 1). Skatole production depends on the availability of tryptophan, which originates mainly from gut mucosa cell debris (Claus et al., 1994; Zamaratskaia et al., 2008). Skatole causes an unpleasant odor in meat, and many consumers mistake this odor for feces odor (Bonneau, 1998). The off-odor in meat may also be caused by other substances like androstenol and indole (Garcia Regueiro and Rius, 1998). Indole is also synthesized in the large intestine from tryptophan, similar to how skatole is produced. Our results showed that CM had the lowest skatole content, but there was no significant difference between NCM, CM, and FM (0.021, 0.019, and 0.021 mg/kg, respectively). Intact goat meat had a significantly higher indole content than CM and FM goat fat (p<0.05). In several species (e.g., pork meat), Weiler et al. (2013) found that intact males had higher skatole content than immuno-CMs and FMs. Furthermore, Young et al. (2006) reported that both skatole and indole contents were significantly higher in ram than in CMs. Therefore, castration has positive effects on the reduction of hormones responsible for goaty flavor.
The fatty acid metabolism pathway is crucial in the production of meat aromas (de Araújo Cordeiro et al., 2020). Table 3 describes how sex affects the fatty acid composition of black goat meat. There was a slight difference in fatty acid concentration between CM and NCM, whereas the differences between FM were significant. Among them, oleic acid (C18:1) is the most abundant fatty acid in black goat meat, with concentrations ranging from 43.85% to 47.22%. The saturated fatty acid (SFA) content was higher in FM than in NCM and CM (p<0.05). According to Kim et al. (2020b), although myristic acid (C14:0) and palmitic acid (C16:0) were significantly higher in FMs, the overall SFA ratio did not show significant differences between sexes in the fatty acid composition of Korean native black goats. Furthermore, our results indicated that the content of UFAs and PUFAs was significantly higher in NCM and CM than in FM (p<0.05). The higher UFAs can increase unpleasant flavors in meat because the unsaturation of phospholipids plays a major role of oxidative rancidity (Legako et al., 2015). In addition, Dinh et al. (2021) found that the autoxidation of UFAs causes unpleasant odors. According to Nute et al. (2007), PUFA content and composition can significantly affect the sensory characteristics of lamb meat. The unpleasant odors can obscure the aromas of the typical species and affect the meat aroma profile, especially if the n-3 PUFA level is high (Elmore et al., 2002). Notably, although eicosapentaenoic acid (C20:5) and docosahexaenoic acid (C22:6) levels did not differ significantly between all treatments groups, linolenic acid (C18:3) and eicosatrienoic acid (C20:3) were significantly higher in NCM and CM (0.44% and 0.45%, 0.33% and 0.23%, respectively). These results also indicated that linolenic acid (C18:3) has been associated with a negative sensory attribute (Wood et al., 2004). Furthermore, arachidonic (C20:4) and linoleic acid (C18:2) oxidation produce n-nonrenal,2,4-decadienal, and other carbonyl compounds, which are perceived as “rancid” or “meaty” in sensory test (Elmore and Mottram, 2006). In the present results, these two fatty acids were significantly higher in NCM and CM (p<0.05). Therefore, n-3 PUFAs may be related to the peculiar flavor of black goat meat. Additionally, the different compositions of fatty acids between sexes may also affect the goaty flavor.
In contrast, short-chain fatty acids (less than 10 carbons) with retention times of 5.258 and 5.809 were noticeably higher in NCM and CM than in FM (p<0.05). In a study identifying and predicting hydrolytic rancidity in milk, González-Córdova and Vallejo-Cordoba (2003) reported that rancid flavor was strongly correlated with short-chain fatty acids. Furthermore, muscle and adipose tissues often contain low levels of unsaturated short-chain branched fatty acids, which is closely related to their contribution to lamb and goat flavors (Brand et al., 2018).
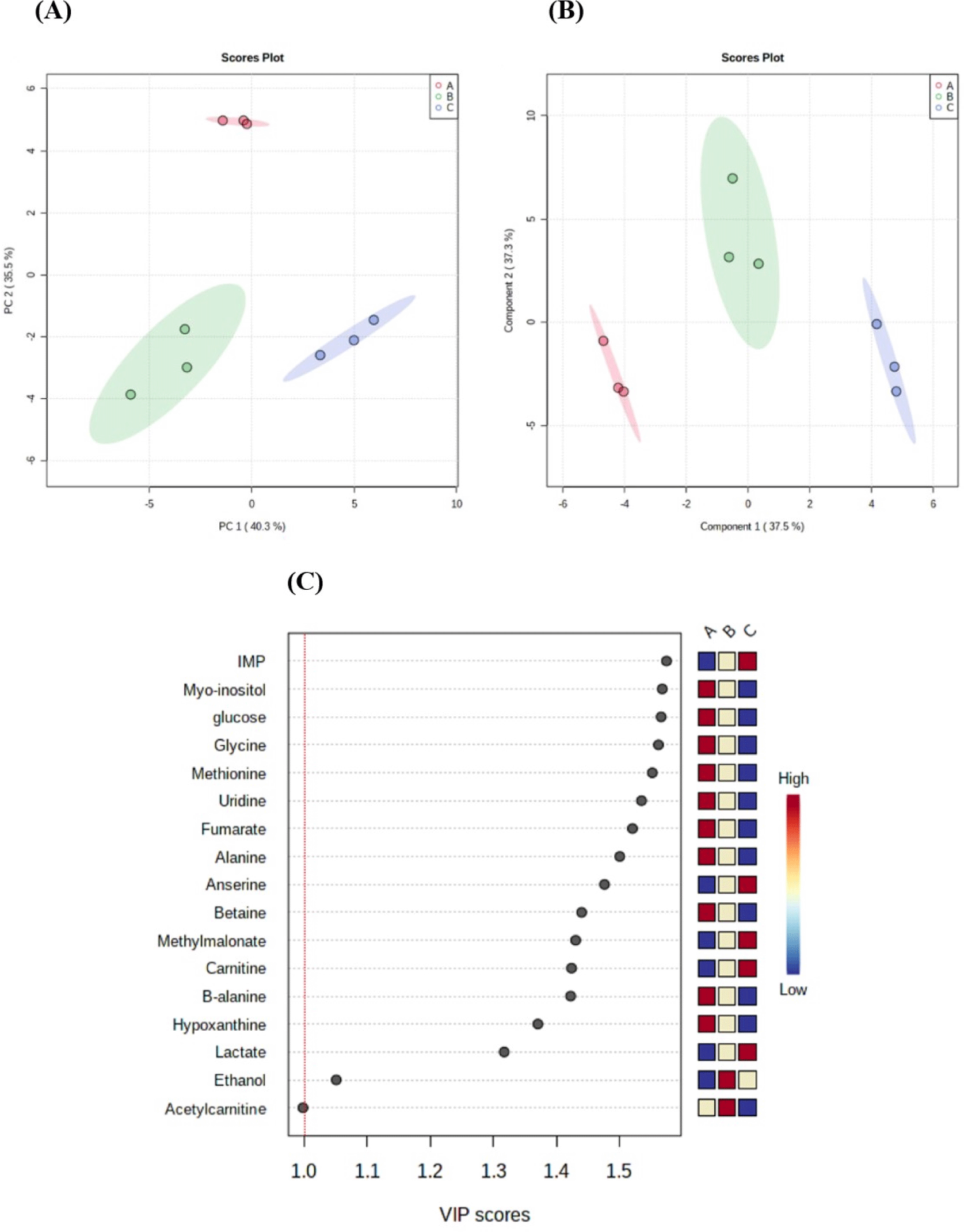
Based on NMR analysis, metabolites, such as amino acids, bioactive compounds, energy metabolism-related products, nucleotide-related products, and other products were identified in black goat meat (Table 4). The water-soluble metabolites of three different sex groups were then compared using a PCA analysis to check if there were any overall differences. PCA and PLS-DA of black goat samples (A: NCM, B: CM, and C: FM) confirmed that each group was separated by a significant distance, with PC1 accounting for 40.3% and Component 1 accounting for 37.5% of the total variance (Figs. 2A and B). These findings show that sex can influence metabolic changes. Furthermore, the variable importance in projection score showed the 16 water-soluble metabolite compounds (alanine, anserine, betaine, carnitine, ethanol, fumarate, glucose, glycine, hypoxanthine, IMP, lactate, methionine, methylmalonate, Myo-inositol, uridine, β-alanine) in meat that exceeds 1 mg/100 g (Fig. 2C). As a result, it reflects the importance of the variables in PLS-DA for group discrimination.
The term “proteolysis” refers to the breakdown of proteins in muscles to release peptides and amino acids that contribute to flavor and taste (Koutsidis et al., 2008a). The results indicated that the free amino acids such as alanine and betaine were significantly higher in NCM and CM than in FM whereas glycine, methionine, and β-alanine acids were significantly higher in NCM than in CM and FM. Testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, can influence protein metabolism (Griggs, 1989), which potentially affects alanine, betaine, and glycine levels. Glycine plays a role in two metabolic processes: protein synthesis and collagen formation (Satyanarayana et al., 2021). Methionine, a sulfur-containing amino acid, contributes to the characteristic of goaty flavor during decomposition (Li et al., 2020). Higher amounts of testosterone in intact male goats than in CMs and FMs could explain higher levels of β-alanine levels. Artioli et al. (2010) reported that testosterone administration in rats increased the expression of the enzyme responsible for β-alanine synthesis in skeletal muscle. β-alanine is a component of carnosine and anserine dipeptides, which have anti-oxidant, chelating, and free radicals scavenging activities (Chan et al., 1994).
Furthermore, the umami or savoury flavor is contributed by aspartate and glutamate acids, both of which were considerably higher in CM than in NCM in our study (p<0.05). Aspartate and glutamate acids can add to the overall flavor perception of goat meat because umami is recognised to increase the taste and palatability of food (Rangan and Barceloux, 2009). Additionally, our findings revealed that CM is a good source of valine, isoleucine, phenylalanine, histidine, and leucine acids (p<0.05). The levels of amino acids can be influenced by hormonal regulation and metabolic processes (Hoberman, 1950). Castration, which inhibits the synthesis of sex hormones like testosterone, can have an effect on the control of many metabolic processes, including amino acid metabolism. Valine is associated with a bitter taste, however, phenylalanine, leucine, tyrosine, and histidine are associated with a sweet taste (Kato et al., 1989). Furthermore, phenylacetaldehyde and benzaldehyde are produced via a thermal reaction of leucine and phenylalanine (Wei et al., 2020). These results indicated that proline and tyrosine levels are also significantly higher in CM than in NCM and FM (p<0.05). Proline, a crucial component of protein molecules, aids in protein stability and structure (Yaron et al., 1993) and contributes to a sweet flavor (Quelen et al., 1995). Our results revealed that the sex of the animal affects the amino acid deposition in the muscle of black goat meat, and the amino acid composition was different between NCM, CM, and FM. In particular, castration can affect how muscle enzymes cause protein denaturation and have a positive effect on flavor preference and overall acceptability.
Similarly, most of the bioactive substances (acetylcarnitine, carnosine, taurine) were abundantly present in CM, and anserine and carnitine were the most abundant in FM (p<0.05). Wu et al. (2003) demonstrated that carnosine and anserine are imidazole dipeptides, which have a high antioxidant power in systems containing linoleic acid. Therefore, it may reduce the formation of unpleasant flavors by inhibiting fatty acid autoxidation (Koutsidis et al., 2008b). Lana et al. (2015) also reported carnosine’s positive effect on organoleptic quality due to its association with the umami flavor. In addition, anserine is also related to umami flavor (Dashdorj et al., 2015). As a result, castration can provide a mechanism for suppressing the development of unpleasant flavors by inhibiting autoxidation.
Among the substances related to energy metabolism, fumarate and glucose had the highest content in NCM; succinate had the highest content in CM; and lactate had the highest content in both CM and FM (p<0.05). Fumarate has been shown to have a favorable relationship with meat pH, which has a significant impact on the flavor, tenderness, and juiciness of the meat (Meng et al., 2023). According to Young et al. (2006), increased glucose levels in lambs were a sign of flavor quality deterioration. Furthermore, succinate and lactate potentially minimize lipid oxidation and improve the color intensity of meat by reducing the metmyoglobin activity (Puntel et al., 2007; Ramanathan et al., 2011). Thus, it can be inferred during the storage period, lactate and succinate were responsible for the difference in TBARS levels between the sexes. Therefore, it is believed that this may lessen the development of unpleasant flavors. Furthermore, high lactate caused variations in quality properties, such as lower pH in FM (Table 2). Therefore, castration has a positive impact on flavor by inhibiting lipid oxidation.
Nucleotide-related products demonstrated that goat meat had quantitatively greater levels of IMP and inosine but comparatively low quantities of guanosine, hypoxanthine, UMP, and uridine. Furthermore, these results indicated that hypoxanthine and inosine levels were significantly higher in both NCM and CM than in FM (p<0.05) and uridine levels were noticeably higher in NCM (p<0.05). In the present study, IMP levels were the highest in FM (93.53 mg/100 g) followed by those in CM (72.27 mg/100 g) and NCM (61.24 mg/100 g). In postmortem muscle cells, adenosine triphosphate is broken down into adenosine diphosphate and then into adenosine monophosphate, which can be converted further to IMP (Ingwall, 2002). IMP is primarily responsible for the “umami” flavor and impacts the flavor of the meat (Kim et al., 2020a). Hypoxanthine and inosine are precursors of IMP, which may contribute to the bitter taste of meat (Dashdorj et al., 2015). According to Yamaguchi (1967), a specific proportion of IMP and glutamic acids has a potent synergistic effect on the umami flavor. Therefore, IMP and the umami amino acids represented by glutamic and aspartic were umami substances in CM and FM and interacted with each other to produce a more delectable flavor.
Furthermore, acetate levels were high in CM, and 3-hydroxybutyrate levels were high in both CM and NCM. Methylmalonate was the most abundant in CM and FM, and Myo-inositol was the most abundant in NCM (p<0.05). Myo-inositol is a product of phospholipid cleavage and an important component of phospholipids. Grabež et al. (2019) suggested that sugars such as mannose-6-phosphate, glucose, and Myo-inositol play critical roles in suppressing unpleasant flavors in lamb and sheep meat.
The water-soluble metabolite study reveals that there is a substantial difference in metabolite compounds by sex, which provides details of the characteristics of the meat quality of black goat meat. CMs and FMs have favorable effects on their metabolite profiles, which can contribute to suppressing unpleasant and goaty flavors. Therefore, it may be related to the overall acceptability of sensory evaluation as well as flavor preference.
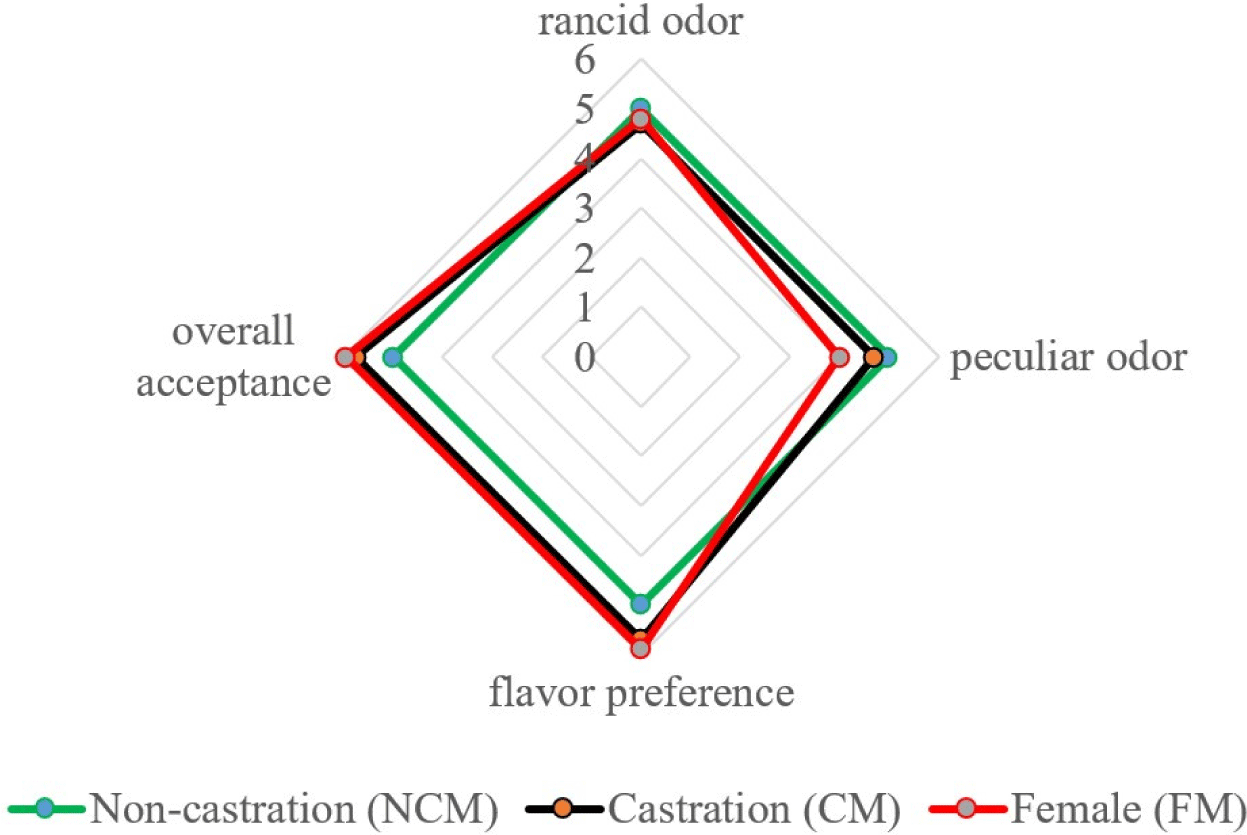
The species-specific meat aromas and flavor depend on lipid properties (Young et al., 1994), which is also true for goat meat. According to Resconi et al. (2009), the lipids in meat produce fat-soluble volatile compounds that are responsible for a specific flavor. In addition, they can interact with other volatile compounds and serve as a precursor to some unpleasant odors produced by lipid oxidation (Mottram, 1998). Fig. 3 depicts a sex-specific sensory analysis of black goats. The scores were assigned to each of the four attributes, namely rancid odor, peculiar odor, flavor preference, and overall acceptance. We found that the rancid odor of NCM was the strongest, with no significant difference between NCM, CM, and FM (5.00, 4.70, 4.80). Additionally, the highest goaty flavor score was observed in NCM, in contrast, FM had a lower intensity of goaty flavor (p<0.05). Madruga et al. (2000) reported no distinct difference in the “goaty” aroma between intact and CM goats. Furthermore, Kim et al. (2020b) discovered that the aroma of Korean native black goats differed between NCMs and FMs, which is similar to the present findings. However, our results indicated that flavor preference and overall preference are better in CM and FM than in NCM. These findings are similar to those of Gravador et al. (2018), who found that sex and castration status had a significant effect on consumers’ overall preference for lamb meat. Furthermore, the overall preference for CM goats was significantly higher than that of intact goats (Zamiri et al., 2012). Gravador et al. (2018) mentioned that skatole and indole degrade meat organoleptic quality and reduces the overall acceptance by contributing to an unpleasant odor. In the current data, the lower indole was observed in CM and FM which is responsible for unpleasant odor and smell. Therefore, CM and FM observed the highest overall acceptance. In addition, Werdi Pratiwi et al. (2004) noted that the slaughter weight correlated with the overall acceptance and that the meat from CM and light-weight slaughtered animals had a higher sensory quality. In the present study, the FM and CM had higher overall acceptance than intact goat meat.
Conclusion
Analysis of the quality traits, flavor compounds, and metabolite profile of Korean native black goats by sex showed considerable differences. The moisture content was lowest in FM, whereas the protein content was highest in FM. The fat and ash content of NCM and FM showed similarly but were the lowest in CM. In color attributes, sex didn’t affect the CIE a* and CIE b*. Castration has positive effects on meat quality characteristics, such as controlling lipid oxidation and increasing the pH of meat. In addition, castration can suppress the development of boar taint by reducing indole level. Furthermore, the composition of the fatty acids in NCM and CM showed minimal differences, however, FM showed distinct differences in SFA, UFA, PUFA, and n-6/n-3 levels. Both CM and FM had higher concentrations of umami-producing amino acids, such as aspirate and glutamate, as well as lactate and succinate, that affected lipid oxidation. According to sensory evaluation, CM and FM showed higher flavor preference and overall acceptance scores, whereas NCM indicated the highest score in goaty odor and rancid odor. Therefore, castration can provide the opportunity to produce high-quality goat meat based on consumer preferences. In conclusion, each causative agent of goaty odor is considered a sex discriminant, and the different sexes have different effects on the physiochemical and functional components in Korean native black goat meat.













