Introduction
Muscle fiber type distribution, relative composition, fiber size, total number, and fiber density have been considered as the major criteria for assessing meat quality, growth performance, and carcass characteristics of livestock animals (Bee et al., 2007; Chang et al., 2003; Choi and Kim, 2009; Hwang et al., 2010; Joo et al., 2013; Lebret et al., 1999; Lefaucheur et al., 2002; Ozawa et al., 2000; Ryu and Kim, 2006). These muscle fiber characteristics are assessed based on the muscle functions in the body, thereby resulting in different physiological and morphological properties of each muscle (Maclntosh et al., 2006; McDonald et al., 1997). Individual muscles have their own muscle fiber architecture and are classified into several types, such as fusiform, pennate, and parallel muscles (Narici, 1999; Nigg and Herzog, 1994). Among the skeletal muscles, present in the mammalian body, M. longissimus thoracis et lumborum (LTL) is located on the vertebrae and supports and regulates the body movements. Accordingly, the LTL muscle is pennate type and its pennation angle ranges from 31.36° to 83.33° regardless of the species (Derington et al., 2011; Kim et al., 2018). Owing to the diverse muscle fiber architecture, muscle fibers of inconsistent faces are exposed to the muscle surface while cutting meat pieces or chops. In pork loin chops, an oval shape is predicted due to the leaned muscle fibers in the LTL muscle. Moreover, a changeable shape is expected due to the angle degree of muscle fiber pennation while considering the pennation angle ranges from 48.00° to 83.33° in porcine LTL muscle (Kim et al., 2018).
Previous studies on muscle fiber characteristics have mainly focused on their relationships with carcass traits and meat quality (Chang et al., 2003; Choi and Kim, 2009; Hwang et al., 2010; Joo et al., 2013; Kim et al., 2010; Kim et al., 2013a, 2013b; Ozawa et al., 2000; Ryu and Kim, 2006); however, skeletal muscle morphology and muscle fiber architecture have not been fully addressed from the meat science point of view. In addition, loin steak is normally prepared by cutting vertically to the muscle length. Consequently, meat quality characteristics, such as color, water-holding capacity, and tenderness may be affected by the chop surface condition, especially the characteristics of the muscle fibers on the chop surface, as it has been demonstrated in beef striploin influenced by the muscle fiber angle (Derington et al., 2011). Therefore, in the present study, the degree of pennation angle was evaluated to understand the morphological characteristics (muscle fiber architecture) of porcine LTL muscle and its influence on the muscle fiber characteristics of the pork loin chop surface. Furthermore, their relationships with meat quality in pork loin chop was assessed.
Materials and Methods
Pig carcasses (n=20, crossbred of Landrace×Yorkshire×Duroc, 82.5±3.8 kg of carcass weight) were randomly selected at 24 h postmortem at a commercial slaughterhouse. Whole loin muscle (M. longissimus thoracis et lumborum, LTL) was removed from the left side of each carcass. Loins were cut vertically to a muscle length of 15 cm. Three chops of the medial region of each loin were selected and randomly allocated to three groups: 1) chops prepared by cutting vertical to the length of LTL (M-Vertical), 2) chops prepared by cutting vertical to the muscle fiber orientation (F-Vertical), and 3) chops for measuring the loin-eye area and pennation angle of muscle fiber. For the F-Vertical and M-Vertical groups, each piece of LTL muscle was divided into 3.0-cm-thickness chops. The LTL chop of the F-Vertical group was used to analyze muscle fiber characteristics, whereas that of the M-Vertical group was used to assess muscle fiber characteristics and meat quality.
Loin-eye area was measured by tracing the surface of the LTL chop using acetate paper. The tracings were measured using an Image Pro Plus Program (Media Cybernetics, Rockville, MD, USA) after scanning by a high-resolution scanner (11000XL, EPSON, Nagano, Japan). To measure the muscle fiber pennation angle (Fig. 1A), we applied the Kim et al. (2018) method with some modifications. Briefly, the LTL chop was prepared by cutting it 2.0 cm in thickness and again parallel to the muscle length. The muscle fiber lean degree to the LTL muscle fascial membrane was calculated using a protractor.
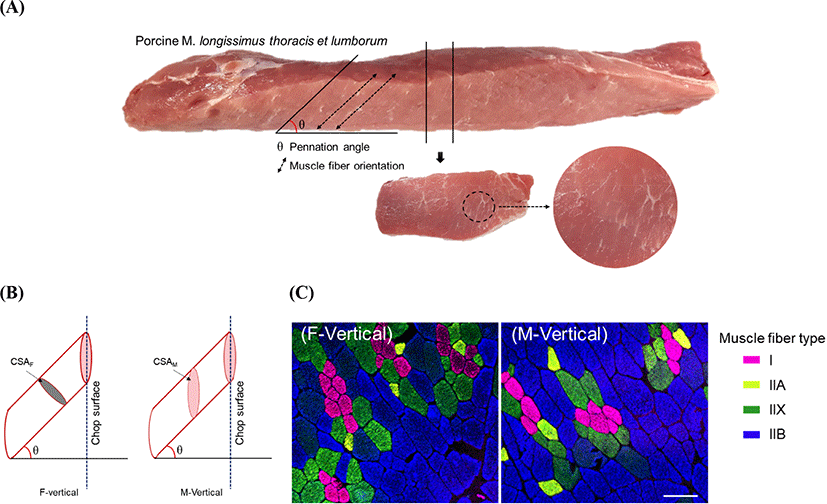
Muscle pieces (1.0×1.0×1.5 cm) were cut from each chop of M-Vertical and F-Vertical groups and immediately frozen in 2-methybutane chilled with liquefied nitrogen. 10-μm-thickness sections were obtained by making parallel cuts to the chop surface of M-Vertical group and by making vertical cuts to the muscle fiber orientation of F-Vertical group, respectively, using a cryostat microtome (CM1520, Leica Biosystem, Wtezlar, Germany). The method by Song et al. (2020) with some modifications was used to stain the cross-sections and muscle fiber typing. Briefly, each section was incubated with monoclonal anti-myosin heavy chain (MHC) antibodies purchased from DSHB (Iowa, IA, USA), such as BA-F8 (anti-MHC slow/I), SC-71 (anti-MHCs 2a and 2x), BF-35 (anti-MHCs slow/I and 2a), and BF-F3 (anti-MHC 2b). Secondary antibodies (anti-mouse IgG2b, anti-mouse IgG1, and anti-mouse IgM) conjugated with fluorescent dyes (Alexa Fluor 350, 488, 594, and 647; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) were used. Primary and secondary antibodies were applied to the sections for 1 h at room temperature in a dark container. Images were captured using a confocal scanning laser microscope (TCS SP8 STED, Leica Biosystems). Three images obtained from the different regions of each section were analyzed using Image-Pro Plus 5.1 (Media Cybernetic, Rockville, MD, USA). Based on the specificities of anti-MHC antibodies to MHCs, the muscle fibers were classified as I (MHC I/slow), IIA (MHC 2a), IIX (MHC 2x), and IIB (MHC 2b). Hybrid fibers comprising two or more isoforms of MHC were excluded from this study due to their low frequencies. Approximately 500 fibers per sample were typed and their relative fiber compositions (number or area to the total number or area of fibers, respectively, %), cross-sectional area (CSA, μm2), and total number of fibers (TNF) distributed on the loin-eye (chop surface) were analyzed.
The pH of LTL chop was directly measured via a portable pH meter (Seven2Go, Mettler-Toledo, Greifensee, Switzerland), with triplication into different regions. Meat color on the chop surface was assessed after oxygenation of myoglobin via exposure to air for 30 min using a colorimeter (CR-400, Minolta, Tokyo, Japan). Prior to measuring meat color, the colorimeter was calibrated with a white plate (Y=93.5, x=0.3132, y=0.3198). The color values were expressed by a Commission Internationale de l’Eclairage (CIE, 1978) system, such as lightness (CIE L*), redness (CIE a*), and yellowness (CIE b*). Drip loss was analyzed by suspending the LTL chops in a plastic bag for 24 h at 4°C according to the method of Honikel (1987), with certain modifications. After suspension, the LTL chops were weighed and drip loss was presented as a percentage of the initial weight. Cooking loss was measured by cooking the LTL chops in a water bath at 75°C after packing them in a plastic bag. When the internal temperature reached 70°C, the chops were removed from the water bath and cooled to room temperature. Cooking loss was presented as a percentage of the initial weight of the LTL chop. After measuring cooking loss, the chops were used for Warner-Bratzler shear force (WBSF) measurements. Three cores (1.3 cm in diameter) were obtained from each chop by making parallel cuts to the chop surface. The cores were cut vertically using a texture analyzer TA1 (Ametek, Largo, FL, USA) with a V-shaped blade, and the WBSF values (N/cm2) were presented as the average of the three cores.
Experimental data obtained from each pork chop are presented as standard error of means (SE). Data was statistically analyzed using SAS 9.4 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA). To compare the relative CSA and fiber area composition between the F-Vertical and M-Vertical groups and among the muscle fiber types, t-tests were performed within the same fiber type or within the same group. Correlation coefficients between pennation angle, loin-eye area, muscle fiber characteristics, and meat quality traits were analyzed using the CORR procedure. Values of p<0.05, p<0.01, and p<0.0001 were considered as statistically significant.
Results
Porcine LTL is unipennate type muscle, as illustrated in Fig. 1. Due to the leaned muscle fibers, the surface of the loin chop cut vertically to the length of the muscle had ellipse-shaped muscle fibers regardless of the fiber type. Muscle fiber characteristics (relative number, relative area, CSA, and TNFs) were evaluated using the cross-section prepared by making a vertical cut to the muscle fiber orientation (F-Vertical) as well as by using the section cut vertically to the muscle length (M-Vertical) (Fig. 1B). Their basic data, loin-eye area, and pennation angle degree are listed in Table 1. The loin-eye area was 52.90 cm2. Muscle fibers were leaned at 51.33° to 69.00° from the pennation angle. For the F-Vertical muscle fiber characteristics, the relative number and area of muscle fiber varied according to the fiber type, and relatively higher compositions were found in type IIB (65.97% relative number and 75.10% relative area). Types I and IIA presented numerically lower compositions of both fiber number and area than those observed in type IIX or IIB. The CSA of types IIB and IIX was larger than that of type II or IIA. Moreover, the CSA of F-Vertical (CSAF) was higher in types IIX or IIB than that in type I or IIA. A similar result was observed for fiber composition (relative fiber number and area) in M-Vertical when compared to that in F-Vertical; however, CSA in M-Vertical (CSAM) was larger than that in F-Vertical, with approximately twice the size, regardless of the fiber type (Table 1 and Fig. 2). For meat quality characteristics, a pH range of 5.40–5.62 was observed in pork loin chop. The CIE L*, CIE a*, and CIE b* on the chop surface were 51.06, 5.51, and 5.62, respectively. Drip loss was 2.62% with 0.65% of SD, whereas cooking loss was 22.16% with 2.78% of SD. The WBSF values ranged from 27.58 N/cm2 to 47.34 N/cm2, as listed in Table 1.
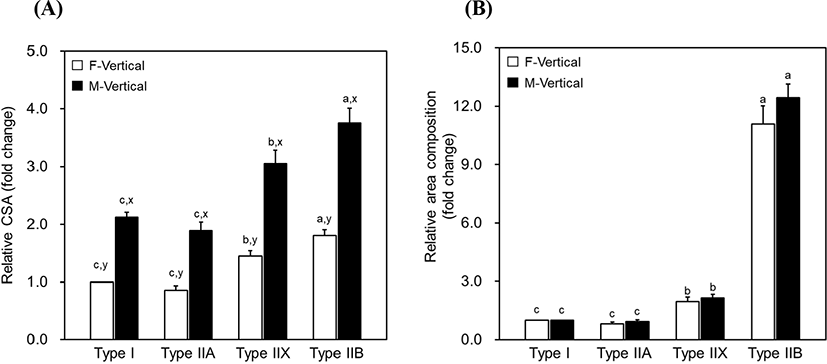
Table 2 presents the results of correlation coefficients between the loin-eye area, pennation angle, and muscle fiber characteristics. Loin-eye area was correlated only with the relative area of type IIB regardless of the cross-section type (r=0.39, p<0.05 for F-Vertical; r=0.42, p<0.05 for M-Vertical). Pennation angle revealed negative correlations with CSAM of all fiber types (p<0.05), whereas the other traits of muscle fiber characteristics and loin-eye area were not significantly correlated with the pennation angle (p>0.05). TNF was negatively correlated with the pennation angle (r=−0.45, p<0.05). The relative number of type I was positively correlated with TNF (p<0.05), whereas that of type IIB presented negative correlation with TNF (p<0.01) regardless of the cross-section type. Nevertheless, no significant correlation was found in all compositions of the fiber area in F-Vertical as well as M-Vertical (p>0.05). CSAM of all fiber types exhibited negative correlations with TNF (p<0.01), whereas no significant correlations were observed in any type of muscle fiber in F-Vertical between TNF - and CSAF (p>0.05).
Among the meat quality traits, pH, CIE L*, and WBSF were significantly correlated with the pennation angle or muscle fiber characteristics (p<0.05), whereas other meat quality traits such as CIE a*, CIE b*, drip loss, and cooking loss did not indicate significant correlations with the pennation angle or muscle fiber characteristics (p>0.05; Table 3). Moreover, the loin-eye area did not reveal significant correlations with any meat quality traits (p>0.05). pH was negatively correlated with TNF (r=−0.45, p<0.05) but positively correlated with CSAM of type IIX (r=0.36, p<0.05) and IIB (r=0.39, p<0.05) fibers. CIE L* was positively correlated with type IIX in the relative fiber number or relative area (p<0.05). WBSF was positively correlated with the pennation angle (r=0.53, p<0.01), relative fiber area (r=0.55, p<0.01), and CSAM (r=0.41, p<0.05) of type IIX; whereas it was negatively correlated with the relative fiber area of type IIB (r=−0.55, p<0.01).
Discussion
Muscle fibers were leaned at 51.33° to 69.00° in the porcine LTL muscle, which is within the range of previous observations in porcine LTL (48.00° to 83.33°) or bovine longissimus lumborum (31.36° to 53.90°) muscles (Derington et al., 2011; Kim et al., 2018). Pennation angle was not significantly correlated with the loin-eye area but was considerably correlated with the total number and fiber size on the loin-eye (chop) surface (Table 2). As illustrated in Fig. 1B, CSA is dependent on the pennation degree (θ) of muscle fiber, that is, LTL with a smaller θ has smaller CSAM but LTL comprising muscle fiber with bigger θ has larger CSAM regardless of the original CSA (transverse to the muscle fiber orientation) of the fibers. Consequently, TNF on the loin-eye is negatively correlated with both the pennation angle and CSAM of muscle fibers regardless of the fiber type. Furthermore, a negative correlation between TNF and muscle fiber size was previously demonstrated, and these parameters are considered for muscle development and muscle mass, which are influenced by various factors (species, breed, gender, hormones, genotype, and growth promoters) (Rehfeldt and Ender, 1993; Rehfeldt et al., 2000; Ryu et al., 2004; Ullman and Oldfors, 1989). Both are positively correlated with muscle mass, whereas the results observed in this study were not correlated with the loin-eye area. Whether these inconsistent results seem to be a result of the muscle fiber architecture (unipennate type of LTL muscle) and pennation degree remains unclear. Further studies on the relationships between TNF, CSA, and muscle mass in LTL muscle by considering the muscle fiber architecture are warranted to understand the muscle development of livestock animals in detail.
Muscle fibers exposed to the surface of the loin chop look elliptical and their size is considerably larger than that of the transverse section (Fig. 2A); however, muscle fiber composition (relative area) did not differ between the F-Vertical and M-Vertical. The size and composition relationships in glycolytic fibers (IIX and IIB) with pH and tenderness observed in the present study are in accordance with the findings in previous studies that demonstrated their positive or negative correlations with pH or tenderness, respectively, regardless of the animal species, breed, gender, age, and muscle type (Choi and Kim, 2009; Joo et al., 2013; Karlsson et al., 1993; Kim et al., 2013a; Kim et al., 2018; Larzul et al., 1997; Ryu et al., 2008). The CIE L* and CIE a* in meat color are highly affected by the fiber size and composition (Hwang et al., 2010; Kim et al., 2010; Kim et al., 2013a; Ozawa et al., 2000), that is, oxidative fibers are positively correlated with CIE a*, whereas glycolytic fibers are negatively correlated with CIE a* but positively correlated with CIE L* due to their diverse reliance on oxygen and consequent demands of myoglobin for energy metabolism of different muscle fiber types (Cassens and Cooper, 1971; Kim et al., 2010; Ozawa et al., 2000; Whipple et al., 1992). In this study, type IIX, one of the glycolytic fibers, revealed positive correlations in its relative area and CSA with CIE L*; however, except for these results, we did not find any relationship between the muscle fiber characteristics and color traits. These results are observed due to the difference in shape and size of the muscle fiber cross-section between F-Vertical and M-Vertical. F-Vertical is a general type of muscle fiber cross-section, whereas M-Vertical is considerably larger and elliptical in shape, as aforementioned. Moreover, the converse relationships of WBSF were observed in relative fiber areas of type IIX (positive) and IIB (negative). The fiber area composition and size of IIX revealed a similar relationship to tenderness when compared to the previous observations in beef and pork (Karlsson et al., 1993; Renand et al., 2001). The positive correlation between the pennation angle and WBSF indicates that the shear force increased because the muscle fiber cross-section came closer to the longitudinally cut shape as the muscle fibers gradually leaned with the increase in the pennation angle.
Conclusion
Pennation angle degree determines the muscle fiber shape, size, and TNFs on loin eye (chop surface). In particular, muscle fiber size is highly affected by the pennation angle regardless of the fiber type. Consequently, muscle fiber size and composition of glycolytic fibers (IIX and IIB) are closely related to the pH, CIE L*, and tenderness of loin chop. A high degree of pennation angle and large size of IIX fiber negatively affected the tenderness of the loin chop. In conclusion, these observations help to understand the porcine LTL muscle architecture and the influence of muscle fiber characteristics of the chop surface on the meat quality of pork loin.













