Introduction
Cholesterol, an essential substrate used in cell membranes and for the production of certain hormones, is obtained through food or produced in the liver. However, an excessive amount of cholesterol causes hypercholesterolemia, a known risk factor for coronary artery disease (Akalin et al., 1997; Anderson and Gilliland, 1999; Lin and Chen, 2000). For this reason, the World Health Organization (WHO) and the American Heart Association recommend that consumers limit their intake of saturated fatty acids and cholesterol to reduce the risk of coronary artery disease (Hansel et al., 2007). However, animal foods such as eggs, meat, and shrimp, in addition to milk and dairy products, which are consumed on a daily basis, contain high levels of cholesterol.
In general, dairy products are considered healthy. However, products such as butter, cream, and certain types of cheese, which contain high amounts of fat, are not necessarily healthy. In particular, butter is used in various ways in the dairy industry. It serves as a basic material for other dairy products and is provided directly to consumers due to its unique flavor and sensuality. Nevertheless, cholesterol content in butter is approximately 210 mg/100 g in general, which is higher than that in cream cheese (110 mg/100 g) and condensed milk (35 mg/100 g). Therefore, it is essential to manage cholesterol intake from butter.
Various processing methods that remove cholesterol from butter have been studied. These include new processes, such as ultrasound, nano-filtration, accelerated solvent extraction, and solid-phase extraction, as well as methods involving β-cyclodextrin and lactic acid bacteria (LAB) (Allègre et al., 2006; Jia et al., 2020; Lye et al., 2012; Richter et al., 1996). In particular, there have been many studies attempting to reduce cholesterol in butter using the chemical mechanisms of β-cyclodextrin; however, this process is costly, resulting in relatively expensive butter products. As such, this process reduces the flavor components of butter, and these products often fail to be selected by consumers for both sensory and economic reasons (Aloğlu and Öner, 2006; Kim et al., 2006).
Meanwhile, there are currently several efforts underway to apply biological methods using microbes, which incur no extra costs and are thought to have beneficial effects on sensory properties, taste, and texture. In particular, studies have focused on LAB and yeast, which have demonstrated not only reductions in serum cholesterol after intake into the body, but also assimilation of cholesterol during the fermentation process. Aloğlu et al. (2016) found that cholesterol in butter could be assimilated by probiotic LAB and yeast (Aloğlu and Öner, 2006; Aloğlu et al., 2015). Additionally, Gilliland et al. (1985) and Pan et al. (2011) reported, respectively, that Lactobacillus acidophilus and Lactobacillus fermentum SM-7 assimilate cholesterol in vitro.
In this study, we examined the effects of cholesterol-assimilating LAB on butter production. To this end, we isolated LAB from a traditional fermented food of Korea, kimchi, and acquired strains that exhibited cholesterol-assimilating abilities when grown in a medium containing cholesterol as the only carbon source. Further, to investigate the effects of bile on cholesterol assimilation, various types and concentrations of bile were tested. The ultimate goal of this study was to produce butter with a reduced amount of cholesterol using bile and isolated LAB to provide butter, which otherwise is high in cholesterol despite its excellent flavor and nutritional value, as a healthy food.
Materials and Methods
To isolate bacterial strains, approximately 200 kimchi samples were collected from a traditional market in Korea and diluted in sterile distilled water before being homogenized with a mill homogenizer. Depending on the degree of fermentation, there were 66, 95, and 45 kinds of kimchi less than 3-days old, less than 4-weeks old, and more than 1-month old, respectively. After serial dilution of the homogenized solution, the appropriate concentration of solution was spread on de Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe (MRS) agar containing 0.002% bromo-cresol purple and cultured for 48 h, following which, colonies showing a yellow hue were selected. To isolate the selected strains that showed cholesterol-assimilating ability, cholesterol-MRS agar was prepared based on the method of Gilliland et al. (1985), where the only carbon source was cholesterol. The specific composition of the agar medium was as follows: cholesterol 0.2 g/L, proteose peptone 10 g/L, ammonium citrate 2 g/L, sodium acetate 5 g/L, MgSO4·7H2O 0.1 g/L, MnSO4 0.05 g/L, K2HPO4 2 g/L, and agar 15 g/L. After placing sterilized 8-mm paper discs (Paperdisc, Advantec, Ehime, Japan) onto the agar medium, 10 μL of each seed culture broth from the purified strains was added, and the agar was incubated for 48 h at 37°C. Subsequently, the areas surrounding the paper discs were examined for the growth of bacterial colonies, and strains that used cholesterol as a nutrient were selected. As a positive control for cholesterol assimilation, 10 μL of the cholesterol-oxidizing enzyme peroxidase solution (peroxidase from horseradish, 1,000 U/mL, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) was used, and as a negative control, 10 μL of cholesterol-MRS broth without bacteria inoculation was used.
The primarily selected strains were inoculated into 15-mL tubes containing 10 mL of MRS broth, and after 48 h of incubation at 37°C, the tubes were centrifuged (10,000×g, 10 min), the supernatant was removed, and the pellet was washed with 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH 6.8). After repeating this process three times, 5 mL of 0.1 M phosphate buffer was added to the pellet to obtain a bacterial suspension and complete the production of the seed culture. After inoculating 1% of the seed culture in MRS broth with cholesterol as the only carbon source, the broth was incubated for 48 h at 37°C. Thereafter, 10 mL of isopropyl alcohol was added, the mixture was vortexed for 5 min and centrifuged at 5,600×g for 5 min, followed by collection of 4 mL of the supernatant. To the supernatant, 100 μL of 4 M KOH, 1.5 g of NaCl, and 4 mL of distilled water were added, the mixture was centrifuged (5,600×g, 5 min), the supernatant was collected, and the cholesterol concentration was measured using a gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometer system (GC-MS/MS 5977A, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Medium without bacterial inoculation was used as the negative control, and L. acidophilus ATCC43121, the most studied strain regarding serum cholesterol-lowering effects in vivo, was obtained from a U.S. bioresource center (ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA) and used as a comparison group.
The API 50 CHL kit (Biomerieux, Rue des Aqueducs, France) was used as a simple way of identifying the isolated bacterial strains by measuring sugar utilization. Colonies cultured in MRS broth were inoculated into the API 50 CHL kit and incubated at 37°C. After 24 h and 48 h, the change in color (yellow) was measured according to the type of sugar. The measurements were used for simple identification of the bacteria via the Biomerieux DB (https://apiweb.biomerieux.com).
In addition, 16S rDNA was analyzed for genetic identification. Specifically, after extracting genomic DNA using a genomic DNA preparation kit (Promega, Madison, WI, USA), a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) reaction was run using the universal primer pair 27F (5′-AGA GTT TGA TCC TGG CTC AG-3′) and 1492R (5′-TAC GGY TAC CTT GTT ACG ACT T-3′) to amplify the 16S rDNA (Buck and Gilliland, 1994). The PCR products were purified using a QIA quick PCR kit (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany) and sequencing was outsourced to Macrogen (Seoul, Korea). The base sequences were then compared with the NCBI GenBank DB using BLAST analysis (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi).
After activation and seed culturing of the isolated bacterial strains into MRS agar and broth, the seed culture was inoculated into cholesterol-MRS broth containing different types of bile. After adding 0.1% (w/v) of either bile extract, oxgall powder, bile acid, or bile salt (Sigma-Aldrich), 1 M NaOH was used to adjust the pH to 6.8±0.2. Following incubation, the bile that produced the greatest decrease in cholesterol concentration was selected as optimal. The selected bile was added to cholesterol-MRS broth at concentrations of 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, and 0.5% (w/v), after which 1% (v/v) of the seed culture of the isolated strains was also inoculated, and the broth was cultured. As stated previously herein, the bile concentration that resulted in the greatest decrease in cholesterol was selected as the optimal concentration.
LRCC5307 LAB was cultured, centrifuged, and washed. The supernatant was removed, and cells were diluted in PBS (pH 6.8±0.2) to prepare seed cultures. In a 1-L beaker immersed in a 90°C water bath, 500 g of commercially available unsalted butter was completely dissolved. While stirring the butter in a paste form at 150 rpm using a magnetic mixer (digital stirring hot plates, Corning®, Corning, NY, USA) maintained at 40°C or higher, 1 g of bile salts and 2.5 g of seed culture were added for 1 h to increase dispersibility. The beaker was sealed, placed on a magnetic mixer, and put in an incubator for fermentation for 72 h at 42°C to prevent the butter from hardening. After incubation, viable cells, pH, and cholesterol concentrations were assessed and compared to those before incubation.
All data are presented as means (±SDs) of at least three independent experiments; each experiment had three replicates of each sample. Data were analyzed statistically using IBM SPSS Statistics software version 25.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). The statistical differences between the mean values of test groups were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance and a paired sample t-test. Statistical significance was defined as p<0.05. Multiple comparisons between different groups were assessed using Duncan’s test.
Results and Discussion
Approximately 300 strains of bacteria were isolated from traditional kimchi. Fig. 1 shows the patterns of the colonies that formed after the incubation of each of these strains on cholesterol-MRS agar. As shown in Fig. 1, when peroxidase was applied as a positive control, there was a clearly visible brown halo around the paper disc; however, when only the cholesterol-MRS broth was applied as a negative control, there was no significant change on the paper disc. When the isolated strains were added to the medium, although there were differences in size, the results could be divided into two major patterns: those that formed a clear halo (strains A and D) and those that did not (strains B, C, E, and F).
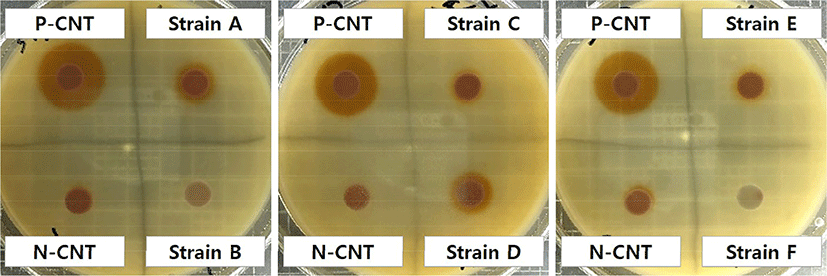
Several bacteria and their enzymes have been reported to have the ability to degrade cholesterol and 7-ketocholesterol. The degradation of these compounds is initiated by mechanisms like cholesterol oxidation (Ghosh and Khare, 2016). These bacteria have been reported to be involved in the biodegradation of cholesterol via cholesterol oxidase. Cholesterol oxidase is a FAD-dependent (flavin adenine dinucleotide) enzyme that catalyzes the oxidation and isomerization of sterols to sterones, typically cholesterol (5-cholesten-3-β-ol) to 4-cholesten-3-one (cholestenone) (Lashgarian et al., 2016; Pan et al., 2011; Sakodinskaya and Ryabov, 2000). Studies have shown that cholestenone, which is produced as a metabolite, is safe and can be used to control obesity, treat liver disease, and prevent keratinization of the skin (Elia et al., 2019). Wali et al. (2019) isolated Bacillus pumilus W1 and Serratia marcescens W8 from soil contaminated with oil and reported that these strains degrade cholesterol and produce red colonies in M9 medium containing 0.1% cholesterol as the only carbon source.
Thus, of the 300 isolated bacterial strains, 54 formed red halos and halo sizes were measured to determine their cholesterol-assimilation ability. There were 33, 12, and nine strains with a halo diameter of 10–12 mm, 12–14 mm, and 15 mm and above, respectively. We aimed to determine the cholesterol assimilating ability of these strains quantitatively.
The 54 bacterial strains isolated from traditional kimchi were inoculated into cholesterol-MRS broth, and the cholesterol concentration in the medium was measured after cultivation. The five strains that produced a decrease in the cholesterol concentration are shown in Table 1. The initial mean cholesterol concentration in the medium was 206.25±1.68 mg/L, and after 48 h of incubation with the comparison strain L. acidophilus ATCC43121, there was a 23.0% decrease in cholesterol to 158.83±3.39 mg/L. The strain that showed the highest decrease in cholesterol was P. acidilactici LRCC5307, which produced a 30.5% reduction to 143.38±2.48 mg/L, and this was closely followed by P. acidilactici PA5296, which produced a 28.0% reduction to 148.43±1.84 mg/L. Other strains showed a cholesterol concentration of ≥170 mg/L after cultivation, representing a decrease of <20%. Thus, the LRCC5307 strain was selected as the strain with the highest cholesterol-assimilation ability.
Blank, the initial media without cultivation. L. acidophilus ATCC43121 was used as reference strains.
Pereira and Gibson (2002) assessed the in vitro cholesterol-assimilation effects of LAB and bifidobacteria isolated from the human gut, cholesterol were decreased by 47% in the medium containing 100 mg/L and 0.4% of oxgall.
Considering that the initial amount of cholesterol administered in this study was approximately 200 mg/L and that LRCC5307 decreased cholesterol levels by 30%, an excellent cholesterol-assimilation activity of approximately 17% was observed. Moreover, Anila et al. (2016) demonstrated that culturing L. casei and L. brevis in medium containing 100 μg/mL of cholesterol resulted in assimilation of 18.18–47.70 μg/mL, which suggests that 17% more cholesterol was reduced compared to that with LRCC5307. As both studies showed excellent cholesterol-assimilation activity when oxgall or oxbile was added to the culture medium, we also decided to assess the effects of bile.
Table 2 shows the results from the analysis with API 50 CHL to investigate the sugar utilization of the isolated strain LRCC5307. LRCC5307 utilized galactose, glucose, fructose, mannose, cellobiose, lactose, trehalose, and esculin, but not mannitol, sorbitol, salicin, and inulin. When the sugar utilization results were compared with the API website (https://apiweb.biomerieux.com), they were similar to those of P. acidilactici standard strain (99.9% ID, T index 0.91), and the utilization of rhamnose and salicin were each 75% different. The next closest identified species was Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis standard strain 1; however, this showed very low similarity (0.1% ID, T index 0.44) and various contrasting characteristics.
1) The results were compared against the database from bioMerieux at https://apiweb.biomerieux.com.
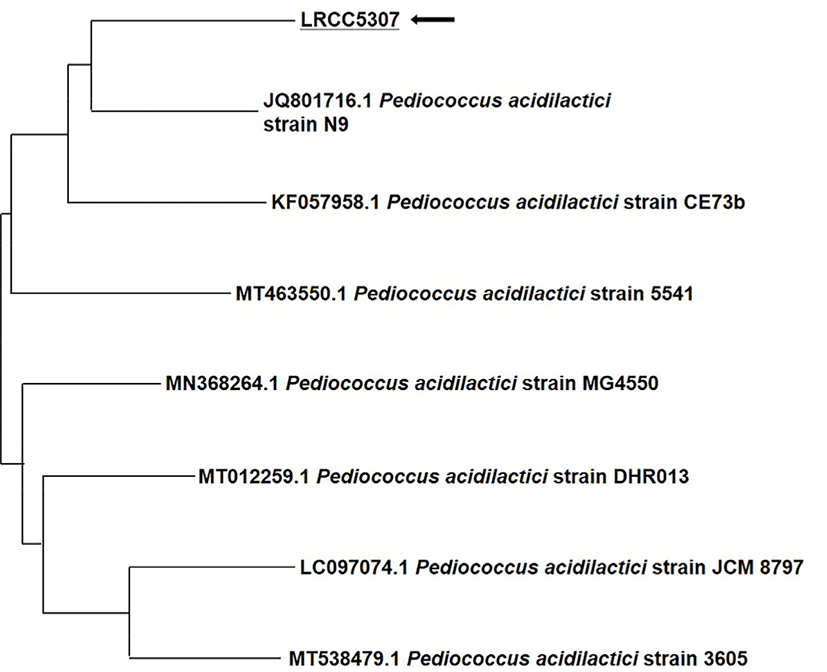
After amplifying the 16S rDNA of the LRCC5307 strain through PCR, sequencing of the 1,440 bp (base-pair) was outsourced to Macrogen, and a homology search was conducted using the NCBI BLASTN program (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov). After comparing this sequence with the GenBank database and performing a homology search with the BLASTN program, a phylogenetic tree was constructed using the neighbor joining method as shown in Fig. 2. Based on the results, the strain was identified as P. acidilactici, and the species closest in similarity was P. acidilactici strain N9. Moreover, the strain was similar to P. acidilactici strain CE73b and P. acidilactici strain 5541. Therefore, the isolated strain LRCC5307 was named P. acidilactici LRCC5307 (Lotte R&D Culture Collection).
Genetic identification, performed by analyzing 16S rDNA of approximately 300 types of LAB isolated from kimchi, showed 57, 35, 13, 71, 10, 78, and 31 species of Leuconostoc mesenteroides, L. brevis, Lactobacillus pentosus, Lactobacillus plantarum, L. casei, Lactobacillus sakei, and P. acidilactici, respectively. Moreover, a total of 308 species were observed, including four, three, and six species of Leuconostoc citreum, Lactobacillus curvatus, and Weissella cibaria, respectively. According to Jeong et al. (2009), 58.9%, 10.7%, and 7.1% of LAB species isolated from commercially available kimchi were L. plantarum, L. casei, and Lactobacillus coryniformis, respectively, whereas 5% each of L. mesenteroides and L. sakei were also observed. In a study by Song et al. (2015), various LAB species were isolated from kimchi, including P. acidilactici, in addition to various Lactobacillus sp. Moreover, Kim et al. (2019) reported that P. acidilactici K10, isolated from kimchi, inhibited the adhesion of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli O157:H7, which are enteropathogenic bacteria, to HT-29 cells. Therefore, although P. acidilactici is not a major species among many LAB that are present in kimchi, it is thought that it can be isolated and has various functions. Additionally, we deposited LRCC5307, isolated in this study, into the Korean Culture Center of Microorganisms (Daejeon, Korea) as KCCM11734P, and as of June 13, 2017, it was registered as a Korean patent strain.
Fig. 3 shows the cholesterol-assimilation ability measured when different types of bile were added to a P. acidilactici LRCC5307 cultivation. The cholesterol concentration in the medium in the absence of LRCC5307 was 201.73±1.44 mg/L, which decreased to 146.06±2.01 mg/L in the medium inoculated with LRCC5307 in the absence of bile. When the culture was incubated under the same conditions but with the addition of different types of bile, the cholesterol concentration significantly decreased compared to that after cultivation without bile and produced a 68% decrease in cholesterol to 64.27±2.84 mg/L.
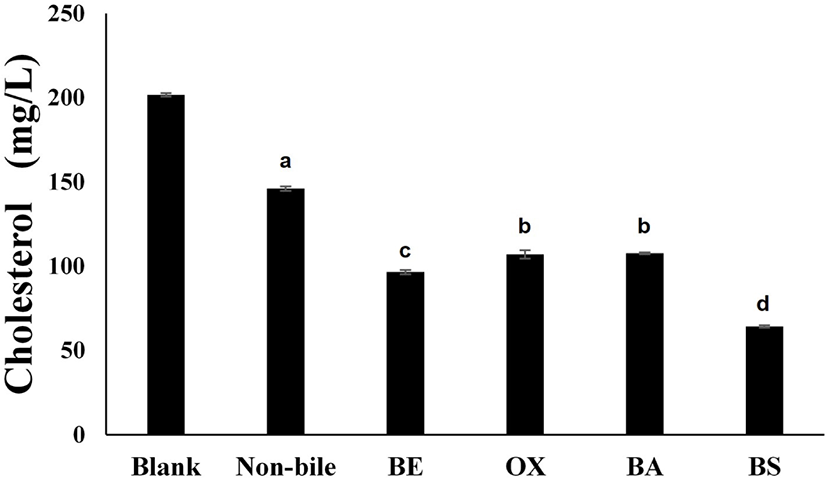
Fig. 4 shows the results of culturing P. acidilactici LRCC5307 treated with different concentrations of bile salts. The cholesterol concentration decreased to 65.64±1.76 mg/L when 0.1% bile salts were added and 51.54±1.65 mg/L when 0.2% bile salts were added. The addition of 0.3% and 0.5% bile salts resulted in cholesterol concentrations of 54.38±2.10 mg/L and 54.29±1.78 mg/L, respectively, which were no better than those obtained with the addition of 0.2% bile salts.
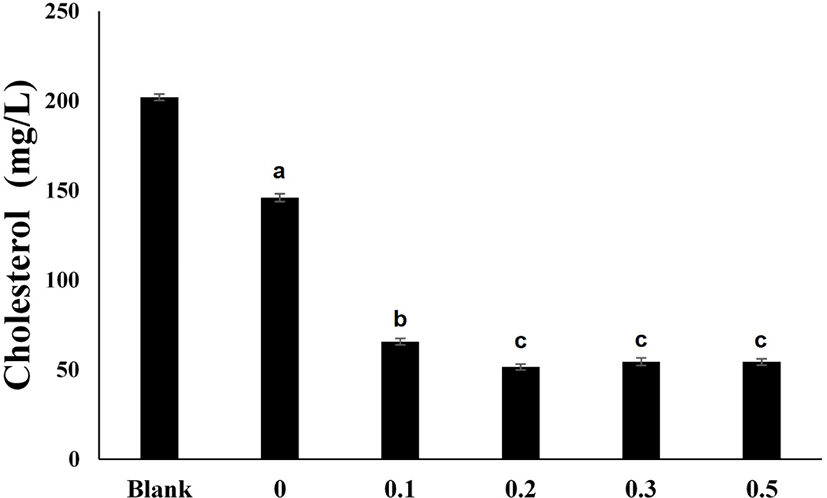
Microbial assimilation of cholesterol is related to the presence of bile, and cholesterol-assimilation ability has been surmised to increase when there is an appropriate concentration of bile in the medium. Many in vitro studies have reported much higher rates of cholesterol assimilation in the presence of bile (Anila et al., 2016; Tok and Aslim, 2010). Gilliland et al. (1985) reported a 70% decrease in cholesterol when L. acidophilus was cultured in medium containing ≥0.4% oxgall. Pereira and Gibson (2002) reported a significant increase in the cholesterol-reducing ability of L. casei Shirota in medium containing 0.4% oxgall. However, the effects are believed to differ depending on the species of microbe used for cholesterol assimilation, and the optimal bile type and concentration differ between microbes. Therefore, to achieve effective cholesterol assimilation, it is important to examine the optimal bile type and concentration for each microbe. In this study, a reduction in cholesterol levels by LRCC5307 occurred when the optimal bile type was bile salts and the optimal concentration was 0.2%.
Commercially available unsalted butter was fermented for 48 h with LRCC5307, and the viable cells, pH, and cholesterol were measured before and after fermentation (Table 3). The viable cells increased from 7.49±0.10 Log CFU/g before fermentation to 8.74±0.06 Log CFU/g after fermentation, and the pH decreased by approximately 1.2, from 6.62±0.00 before fermentation to 5.43±0.01 after fermentation. The cholesterol concentration decreased by approximately 230 mg/L, or 11% of the initial concentration, from 2,105.21±27.99 mg/kg before fermentation to 1,873.16±15.20 mg/kg after fermentation. Compared to that with cultivation in MRS medium, the pH was approximately 1.0 units higher and the viable cells were approximately 1 Log CFU/g lower; this was thought to be due to the lack of nutrients and a suitable environment for growth in butter (excessive fat content, etc.) compared to those in a medium that is optimized for LAB growth. Moreover, cell viability, pH, and cholesterol showed statistically significant differences compared to those with cultivation in butter without fermentation.
In butter fermented without bile salts, the number of viable cells and pH were similar to those of butter fermented with bile salt, and there was no statistically significant difference. However, cholesterol was 2017.37±14.73 mg/kg, which was reduced by approximately 4.2% compared to that in butter before fermentation. Therefore, similar results to the increased cholesterol assimilation after the addition of bile salts to MRS medium containing cholesterol were also observed in butter.
To reduce the risk of heart disease, the WHO, the American Heart Association, and others recommend reducing one’s fatty acid and cholesterol intake and suggest a maximum daily cholesterol intake of 300 mg/d. Although it varies depending on the region and diet, daily butter intake ranges 1–10 g/d, and as a result, cholesterol intake ranges from 2–20 mg/d. In this study, cholesterol in butter was reduced by 10% with LRCC5307. If this effect can be enhanced to produce butter without a risk of cholesterol, it would broaden options for consumers and greatly contribute to the growth of the butter industry.
Aloğlu and Öner (2006) reported research using 10 strains of LAB to degrade cholesterol in cream and butter. In that study, Lactobacillus maltaromicus AC3-16 and L. casei ssp. casei AB16-65 were reported to degrade 0.1%–25% of the cholesterol in butter, although the cholesterol-assimilation ability was assumed to differ depending on the growth of the strain. Meanwhile, Albano et al. (2018) measured the cholesterol-assimilation ability when cheese was produced and matured with seven strains of LAB and reported cholesterol-assimilation rates of 21% for L. plantarum VS513 and 18% for Lactobacillus paracasei VC213. Using cholesterol-degrading LAB to ferment actual dairy products, such as cream, cheese, and butter, is known to greatly reduce cholesterol-assimilation ability compared to that with fermentation in broth. This is thought to be because, compared to that in broth, the dairy products present a suboptimal environment for LAB growth, and butter is believed to be especially poor for LRCC5307 growth due to its high fat content and low water content. Therefore, in future research it will be important to establish the optimal conditions for butter fermentation using LRCC5307 to improve the cholesterol assimilation effect without negatively impacting the sensory properties of butter.
Conclusion
As excessive amounts of cholesterol can lead to hypercholesterolemia, the WHO and The American Heart Association recommend restricted intake of food with high levels of saturated fatty acids and cholesterol. Although butter has high calorie and fat contents for its high nutritional value and excellent flavor, it contains more than 2,000 mg/kg of cholesterol.
In this study, methods using fermentation and LAB were studied to reduce cholesterol amounts in butter. The cholesterol-assimilating ability of P. acidilactici LRCC5307 isolated from kimchi was evaluated, and the optimal conditions for cholesterol assimilation by this strain in the presence of different types and concentrations of bile in the cultures were determined. When cholesterol was added to general MRS broth as the only carbon source, there was a 30% reduction in cholesterol, but when 0.2% bile salt was added, the cholesterol concentration decreased by 74.5%. When actual butter was fermented, the cholesterol concentration decreased by approximately 11%, showing potential for this strain to produce lower-cholesterol butter. Therefore, if the cholesterol assimilation rate could be further improved by optimizing the LRCC5307 fermentation conditions for butter, we anticipate that it would enable the production of healthier butter. However, due to properties of the LAB, as fermentation conditions improve, the unique sour taste imparted by LAB would also increase, thus making it important to ensure that this does not drastically alter the particular flavor of butter.
Therefore, in future studies, finding the optimal fermentation condition that does not affect the inherent flavor of butter while reducing cholesterol would be crucial, and this would allow for the manufacturing of healthy butter with consumer acceptance.













