Introduction
One of the 20th century’s greatest discoveries was the discovery of antibiotics, which made it possible to treat various diseases more easily. Antibiotics have several uses beyond the prevention and treatment of disease, including improving the health and well-being of animals used for human consumption (Durso and Cook, 2014). However, with the excessive use of antibiotics, other threats emerged that included antibiotic resistance in human and animal feed (Ma et al., 2021). Consumers should be aware that meat and meat products may contain residues that could be harmful to their health and even more dangerous to humans, as it is not physiologically apathetic even at low concentrations and over extended periods of time (Zamojska et al., 2021). According to the literature, postbiotics are “non-viable bacterial products or metabolic products obtained from microorganisms with biological activity in the host” or “the crude cell extracts that benefit the human or animal consumer when administered orally or topically in sufficient amounts” (Homayouni Rad et al., 2021; Patel and Denning, 2013; Thanh et al., 2009; Zendeboodi et al., 2020). Postbiotics are considered better than probiotics because postbiotics contain microorganisms that are incapable of replicating; they are less likely to cause bacteremia or fungemia than probiotics (Yelin et al., 2019). Furthermore, postbiotics offer several intriguing characteristics, such as different molecular structures, long shelf lives, and safety doses (Shigwedha, 2014). Postbiotics have good metabolism, absorption, distribution, and excretion, which could affect many host organs and tissues and perform many biological tasks (Shenderov, 2013). Therefore, promising antibiotic alternatives are required. The search for other options for improving growth and health practices has become the leading research endeavor. Poultry producers face the challenge of feeding the world while adhering to the regulatory mandates of their local jurisdictions. Bird growth and health can be enhanced with dietary manipulation of feed additives such as prebiotics, postbiotics, probiotics and herbal products (Arain et al., 2018; Arain et al., 2022a; Klemashevich et al., 2014; Nabi et al., 2020a). In animal production, probiotics are referred to as direct-fed microbials because they reside in the gut of animals and preferably serve a useful purpose. Prebiotics are composed of constituents the body cannot digest and are specially designed to promote the development of good bacteria in the gut. Finally, postbiotics are generally produced by beneficial bacteria of the gut products that must be fed and apply a beneficial effect on the host’s health. Compared to the host, the intestinal microbiota contains more biochemical reactions and genomes, which significantly affect the host’s development, health, metabolism, behavior, and immunity. At the same time, the disease caused by microbial imbalance is known as dysbiosis (Yeoman et al., 2012). Metabolizing host-indigestible feed ingredients is a crucial function of the gut microbiota. Consequently, the host can utilize feed more efficiently because of the microbiome’s energy utilization ability. Additionally, the microbiota and metabolites they produce influence signal transduction in the host and regulate their response (Blacher et al., 2017; Loh et al., 2014).
Since most products have a long shelf life, postbiotics will remain stable during storage and production, but probiotics will die off. Probiotic strains die at different rates depending on their physiological traits and storage conditions (oxygen levels, temperature, water activity, duration, etc.). Thus, probiotic product dead cell counts in the last portion of their shelf life are difficult to generalize (Huber et al., 2005). Postbiotics are considered better than probiotics because postbiotics contain microorganisms that are incapable of replicating; they are less likely to cause bacteremia or fungemia than probiotics (albeitextremely rare; Yelin et al., 2019). Today, commercial poultry is regarded as the most available animal protein source (Arain et al., 2022b; Zuidhof et al., 2014). As the world’s population grows and people shift to diets richer in animal protein, food animals must be produced safely and efficiently to feed this growing population (Nabi et al., 2020b; Wu et al., 2014).
In contrast to challenged non-treated chickens, Abd El-Ghany et al. (2022) reported postbiotic treatment improved disease picture, growth performance, immune system stimulation, bursa/body weight ratio, and intestinal coliform counts compared to challenged non-treated chickens. Postbiotic compounds—dry or aqueous—improve broiler chicken performance, health, and immunity against colisepticaemia. Chang et al. (2022) found that L. plantarum postbiotic could replace antibiotic growth promoters (AGP) by improving gut health, beneficial bacteria colonization, mucin production, tight junction permeability, and immunity. Taken together, despite published literature on postbiotics being uncertain and lacking some imperative practical factors, new research has emerged regarding the possible health benefits of inactivated microbe.
Concepts of Postbiotics
The word “postbiotic” originates from Greek for the word “post”, relating to “after”, and “bios”, relating to “life”. There are many ‘biotic’ families that revolve around microbes (or their substrates), including prebiotics, probiotics, synbiotics, and postbiotics (Vinderola et al., 2022). Live microbes called probiotics are beneficial to the health of the host if administered at the proper level (Hill et al., 2014). The term postbiotic refers to cell fragments, non-viable or intact microbes, which may or may not contain metabolites and offer promising health benefits to the body (Vinderola et al., 2022). Through the metabolic process of bacteria and probiotics, soluble non-viable metabolites are considered postbiotics (Klemashevich et al., 2014; Tsilingiri et al., 2012). Postbiotics share a similar mechanism of action with probiotics, but as they are non-living organisms, they are different (Thanh et al., 2009). At the same time, purified metabolites are not considered postbiotics. International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) presented the postbiotic’s definition in mid-2021, stating that a postbiotic is “inanimate microorganisms or their component’s preparation which exert health benefits on the host.” ISAPP panel also considered other definitions focusing on microbes produced metabolites or other factors before deciding the final purpose of postbiotic (Salminen et al., 2021). In the different meanings of postbiotics, some stipulations also proved problematic. In addition, forlive microbes, well-known health benefits do not necessarily expect that the advantage in an inactivated form will also be achieved. It would also hinder innovation from using such a definition since a probiotic should be established first, or the starting microbe should be limited to those already found as probiotics before meeting the criteria for a postbiotic when it is sufficient. There was some confusion regarding whether postbiotics were given to the target host or were formed in situ by resident microorganisms or administered microorganisms. The path to transformation into food, feed, and other final products is unclear if definitions do not distinguish between distributed and in-situ products. It turned out that different purposes required postbiotics to be applied to the gut lumen only (Tsilingiri and Rescigno, 2013), thus eliminating the opportunity of applying postbiotics to other surfaces. Efficient postbiotics include various Lactobacilli species present in cytoplasmic extracts and cell wall components that include Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus fermentum, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Lactobacillus paracasei, Lactobacillus delbrueckil subsp. Bulgaricus, Lactobacillus gasseri, Lactobacillus helveticus, Lactobacillus reuteri and Lactobacillus Johnsonni (Choi et al., 2006; Cicenia et al., 2016; Johnson et al., 2019; Kim et al., 2011; Matsuguchi et al., 2003; Tiptiri-Kourpeti et al., 2016; Vidal et al., 2002). The postbiotic phase includes soluble factors (products or metabolic byproducts), which are produced either as bacterial secretions or released after lysis, e.g., enzymes, peptidoglycan-derived muropeptides, teichoic acids, peptides, polysaccharides, cell surface proteins, and organic acids (Aguilar-Toalá et al., 2018).
Interaction of Postbiotics with Their Hosts
Various populations and even individuals have different gut microbiota compositions. A person’s metabolic and functional phenotype is affected by the composition of microbiota present in the gut. It may result in individual differences in health effects from these biotics (Collado et al., 2009). Different ‘-biotics’ or different individuals may exert diverse effects on the gut microbiota, as well as can also affect the composition over time. Consequently, adding probiotics, prebiotics, or synbiotics and many proposed health effects depend on the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and other substances such as extracellular polysaccharides, functional proteins, microbial fractions, cell lysates, secreted polysaccharides, teichoic acid, pili type structures and muropeptides derived from peptidoglycans (Konstantinov et al., 2013; Markowiak and Śliżewska, 2017; O’Grady et al., 2019; Sánchez et al., 2017; Slavin, 2013; Wegh et al., 2017). Fermented matrix produces microbial metabolites, e.g., carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, vitamins, components of the cell wall, organic acids, or other complex structures, which affect postbiotic efficacy (Aguilar-Toalá et al., 2018; Konstantinov et al., 2013). The postbiotic composition may also be affected by food processing methods such as high pressure, irradiation, heat, and sonication (de Almada et al., 2016). So, postbiotic product composition and their host response are determined by the complete food production process (Taverniti and Guglielmetti, 2011). Postbiotic effects appear mediated by interactions between microbial products and the host. Thus, the host immune system can be activated, triggering, e.g., anti-inflammatory responses (Gosálbez and Ramón, 2015). Also, postbiotic compounds from Lactobacilli spp. may apply immunomodulatory action by reducing Th2-associated cytokines and increasing Th1-related cytokine levels (de Almada et al., 2016). The pili are structures of cell surfaces known to be part of the cause of the contact between the immune system and bacteria. Pili loss, for example, has been associated with reduced cell proliferation stimulation and better production of pro-inflammatory markers like IL-8 as well as a reduced ability of Caco-2 cells to resist radiologically induced bowel injury (Lebeer et al., 2012). Extracellular vesicles and exopolysaccharides (EPS) are two other products of fermentation associatedwith health-related benefits (Ahmadi Badi et al., 2017; Korcz et al., 2018). It has been indicated that EPS provides several health benefits, including cardioprotection, antiulcer properties, antioxidant properties, and the reduction of cholesterol levels (Das et al., 2014; Hongpattarakere et al., 2012). As well, EPS from Lactobacillus plantarum 70810 restricted BGC-823, hepG-2, and HT-29 tumor cell proliferation in vitro and were used as antitumor agents (Wang et al., 2014). Similar to probiotics, postbiotics promote broiler growth performance by increasing gene expression of nutrient transporter (galactose transporter, glucose transporter dependent on Na+ and long-chain of acyl CoA dehydrogenase genes; Faseleh Jahromi et al., 2016). Among antimicrobial metabolites of postbiotics, organic acids, and bacteriocins exhibit the ability to reduce the pH and pathogens’ proliferation in the gut (Aguilar-Toalá et al., 2018).
Immunological Response of Postbiotics
According to several investigations, postbiotics have been found to exert immunomodulatory effects similar to those of probiotics. The cell-free supernatant derived from L. reuteri DSM 17938 exhibited an upregulation in the synthesis of IL-10, which is a postbiotic cytokine known for its anti-inflammatory properties. IL-10 plays a crucial role in modulating the immune system by influencing the function of retinoic acid-driven mucosa-like dendritic cells. This upregulation of IL-10 production resulted in subsequent positive effects on T regulatory cells (Haileselassie et al., 2016). Postbiotics have been linked to immunomodulatory activities because they support the innate and adaptive immune systems, protect the intestinal mucosal barrier, and inhibit the growth of pathogens with antimicrobial compounds (De Marco et al., 2018). Lactobacilli postbiotics, comprising pili and protein p40/p75, have been shown to protect the intestinal barrier, stimulate the production of aggregation factor, bacteriocins, and S-layer proteins, and aid in the killing of pathogens (Teame et al., 2020). Different amounts of lipoteichoic acid (LTA) and peptidoglycan, components of bacterial cell walls, may influence their immunostimulant activity. It’s possible that these bacteria immunomodulate by upregulating Th1 cytokines and downregulating Th2 cytokines (Ou et al., 2011). Postbiotics produced from Streptococcus thermophilus may protect the stomach mucosa and boost the body’s natural anti-inflammatory response by influencing IL-8 production (Marcial et al., 2017). The research findings revealed that postbiotics, generated after the inactivation of probiotics, exhibited a significantly greater immunomodulatory effect compared to probiotics (de Almada et al., 2016). Abd El-Ghany et al. (2022) results showed that feed and water treatments with the postbiotic compound significantly (p<0.05) improved disease prognosis, growth performance, immune response, bursa of Fabricius/body weight ratio, and intestinal coliform count in challenged chickens. Finally, the postbiotic substance in a dry or liquid form improves the health, performance, and immunity of colisepticaemic broiler chickens. Postbiotics and para-probiotics containing a 0.2% active culture of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum were developed for use in broiler starter and finisher diets. The level of IgA in the colon mucosa was considerably changed by dietary treatments. Significant fluctuations in plasma IgM levels were seen during the finishing phase. Growth hormone receptor (GHR) and insulin like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) were increased with the use of postbiotics and para-probiotics (Danladi et al., 2022).
A postbiotic product known as Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermentation–based postbiotic (SCFP) is made up of functional metabolites that are created using an exclusive S. cerevisiae fermentation method. In commercial poultry, it has been reported that this product improves gut health and immune function. This is accomplished by lowering corticosterone levels, heterophil: lymphocyte ratios, and physical asymmetry during stressful events; reducing intestinal lesions and improving immune function during Eimeria maxima and Eimeria tenella infections; increasing feed conversion, growth rate, meat yield, and egg production; and possibly reducing colonization by foodborne pathogens (Gingerich et al., 2021). Postbiotics have been seen to exert an influence on immunomodulation; nevertheless, further investigation is necessary in order to comprehensively elucidate the mechanisms behind the immunomodulatory qualities exhibited by postbiotics, which represent a notable attribute of these substances. The immunomodulatory effects of postbiotics may be attributed to the presence of several components in their cell walls, including small molecules such as SCFAs, LTA, peptides/proteins, or a combination thereof (Sun et al., 2018; Vinolo et al., 2011).
Mechanism of Action
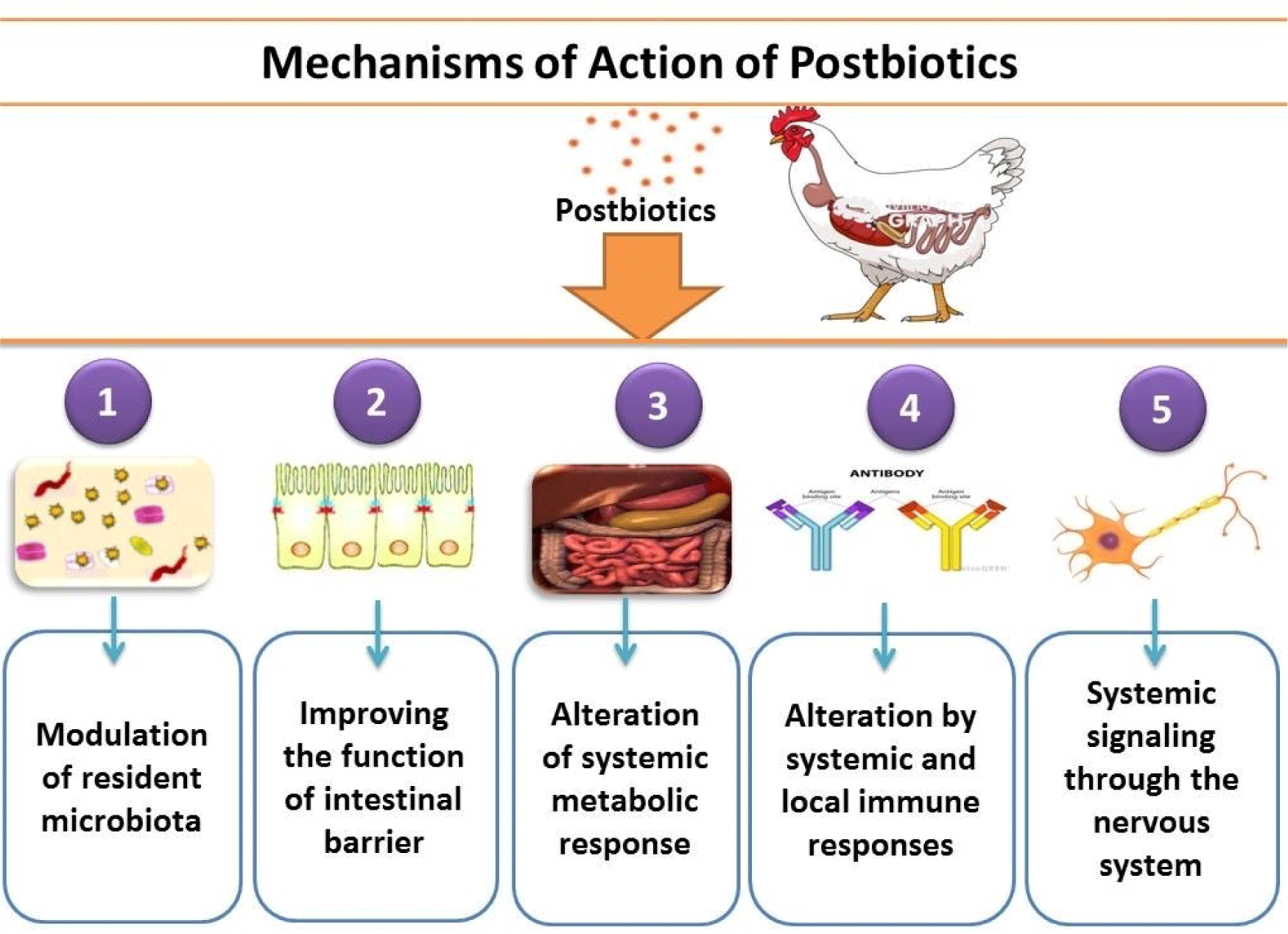
Postbiotics can act in five different ways (Salminen et al., 2021): (1) Indirectly, postbiotics may transform the microbiota such as by quorum quenchingor by carrying quorum sensing molecules (Grandclément et al., 2016) or by having lactic acid, which is used by some microorganisms to produce butyrate and SCFAs, which are helpful in the microbiota (Laverde Gomez et al., 2019). The presence of postbiotic adhesions [e.g., fimbriae (Tytgat et al., 2016) and lectins (Petrova et al., 2016)] can also compete for adhesion sites with resident microbes. (2) Improvement in the function of the intestinal barrier; If sufficient amounts of SCFAs are present in a postbiotic preparation, they may protect against disruptions caused by lipopolysaccharide and alter the functions of epithelial barriers (Feng et al., 2018). (3) Alteration by systemic and local immune responses; At systemic and local levels, immune-modulating activities are typically triggered through molecular patterns associated with microorganisms that interact with certain PRRs of immune cells. These receptors, for example, receptors of nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain, C-type lectins, and Toll-like receptors, are responsible for regulating cytokines and immune responses (Lebeer et al., 2010). (4) Alteration of systemic metabolic response: Enzymes and metabolites on and inside inactivated microorganisms’ surface in postbiotics may directly affect systemic metabolic responses. In addition to modulating the microbiota community structure and interacting with many receptors of the host, bile acids have a variety of downstream effects on metabolic processes in the host, such as lipids, xenobiotics, glucose, and energy metabolism (Long et al., 2017). (5) Systemic signaling through the nervous system; When sufficient amounts of metabolites of microbes such as SCFAs are available in preparation for postbiotic, they release serotonin by stimulating enterochromaffin cells, which then enter the bloodstream (Iwasaki et al., 2019). The Postbiotic’s mechanism of action is given below in Fig. 1. A non-exhaustive list represents some examples of microbial effector molecules mediating these systems. By maintaining postbiotics cellular structure, e.g., by an enhanced affinity for interacting with receptors of the immune system or by improving the time of residence of active molecules within the host, effector molecules’ activity could be better continued. Within the host, the cell wall protects against rapid degradation with the help of digestive enzymes and immune attacks. This condition is similar to the vaccine situation when most pathogenicand toxic parts are deleted or inactivated, but the cellular structure should be preserved.
Another Beneficial Potential
Disturbing gut microbiota, such as pathogen colonization and proliferation of native pathobionts, led to different diseases and gut health issues. From a healing point of view, components of postbiotics inhibit pathogens in the gut by competing for sticking to epithelium and mucosa (Mantziari et al., 2020). Bacteriocin is a tiny antimicrobial peptide that shows inhibitory action against pathogenic organisms. It may prove a valuable candidate as an antimicrobial agent in food and other pharmaceutical applications (Simons et al., 2020; Yang et al., 2014). Postbiotic as a growth promoter lead to improve the host’s health as well as exhibit antimicrobial, antioxidant, immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, antiproliferative hypocholesterolemic, and hepatoprotective activity (Aguilar-Toalá et al., 2018). Either alone or in combination, strains of L. plantarum are familiar postbiotic producers (Thanh et al., 2009). L. plantarum strains exhibited effectiveness in pigs (Loh et al., 2013), rats (Loh et al., 2009), broiler chickens (Faseleh Jahromi et al., 2016; Kareem et al., 2016, Kareem et al., 2017; Loh et al., 2010; Petrof et al., 2004; Thanh et al., 2009). According to Choi et al. (2006), L. casei, L. rhamnosus, Lactobacillus brevis, and L. acidophilus with soluble intracellular polysaccharide fraction can be used as anticancer material because of their selection for cancer cells of human, and exert an antioxidative effect in the food industry.
Efficacy of Postbiotics with Another Biotic Family
Among some of the excellent antibiotic alternatives, there are some biotic feed additives, including prebiotics, probiotics, postbiotics, and synbiotics. In addition to improving production and intestinal health and controlling enteric pathogens, they have also been used to relieve problems caused by antibiotics (Faseleh Jahromi et al., 2016).
To heat and oxygen, many probiotic organisms are sensitive; thus, maintaining their stability is a technological challenge, but inanimate microorganisms can be stored for an extended period. During storage and industrial processes, postbiotics possess natural strength, which is their main feature. In geographical regions without reliable cold chains or high ambient temperatures, postbiotics may be more suitable than probiotics for preserving live microorganisms. During the storage of most products with extended shelf life, probiotics mostly die. At the end of their shelf life, it is hard to idealize about dead cells level present in the effects of probiotics, as the rate of death varies depending on storage conditions (oxygen levels, the activity of water, time and temperature, etc.) and physiological characteristics of strain (Huber et al., 2005).
Promising Effects on Other Animals
Izuddin et al. (2019) concluded that postbiotic supplementation improved the weight gain of lamb, feed consumption, nutrient digestibility, and consumption. However, ruminal ammonia-N and butyrate concentrations were enhanced, whereas total VFA and pH were unaffected. Glucose, urea nitrogen, and complete protein in blood were higher in lambs fed postbiotics. The levels of triglycerides and cholesterol in the blood did not differ. Rumen protozoa and methanogens decreased after postbiotic treatment, but fiber-degrading bacteria improved. Expression of mRNA for hepatic IGF-1 and ruminal MCT-1 was also increased by using postbiotics (Izuddin et al., 2019).
Additionally, dietary postbiotics reduced serum lipid peroxidation, enhanced serum and ruminal fluid antioxidant actions, and enzyme production of hepatic antioxidants in postweaning lambs (Izuddin et al., 2020). Moreover, Loh et al. (2009) demonstrated in rats, growth performance and fecal LAB count were increased, while fecal enterobacteria count was decreased when LAB metabolites were administered in drinking water (Loh et al., 2009). But Foo et al. concluded that water consumption may be reduced due to unwanted taste of these metabolites (Foo et al., 2003). Therefore, it was suggested that to remove the undesirable taste of these metabolites, they should be used in powder form (Loh et al., 2009). In mice, inhibitory and anti-proliferative activity in carcinoma cells of the colon and cell lines, programmed cell death was demonstrated when the sonicated L. casei cell suspensions were administered (Tiptiri-Kourpeti et al., 2016). However, in post-weaning piglets, Lactobacillus plantarum could enhance growth performance, an environment of gut health, and digestibility of proteins when 0.5% metabolite combinations are administered in feed. He also revealed that in piglets, along with increasing parameters of growth performance, such as overall and average weight gain per day and birth weight, L. plantarum liquid metabolites also reduced the production of diarrhea (Loh et al., 2013).
Promising Advantages in the Poultry Industry
As feed additives, postbiotics can be used to improve the performance of growth and health in broilers (Kareem et al., 2017) and in layers (Choe et al., 2012; Loh et al., 2014). In poultry under heat stress, postbiotics containing L. plantarum exhibit antioxidative activities (Humam et al., 2019). Additionally, these metabolites improved the quality of the egg and reduced cholesterol levels of yolk and plasma in layers (Loh et al., 2014). Adding prebiotics and postbiotics containing inulin to broiler chicken rations improved the feed efficiency and total body weight of the birds and sustained growth factor1, mRNA expression of GHRs, and intestinal mucosal structure (Kareem et al., 2016). Even under heat stress conditions, postbiotics produced by L. plantarum in the feed of broiler chickens showed better maintenance of gut microbiota, the performance of growth, and intestinal morphology (Humam et al., 2019). Postbiotics and insulin together increased IL-6 mRNA expression in broiler chickens and reduced IFN expression and α-gene expression in tumor necrosis factor-induced by lipopolysaccharide in broiler chickens (Kareem et al., 2017). Abd El-Ghany et al. (2022) illustrated the effects on immunity, health, growth performance, and broilers’ gut status facing colisepticaemia when feeding stabilized non-viable Lactobacilli postbiotic. Postbiotic compounds significantly improved the disease picture, enhanced the performance of growth, boosted immune response, improved bursa to body weight ratio, and reduced the count of coliform in the intestine of challenged chickens compared to non-treated chickens (Abd El-Ghany et al., 2022). Compared to challenged groups, Johnson’s experiment revealed significant weight gain and reduced lesion scores in postbiotic-treated broilers (Johnson et al., 2019). The results of Kalavathy’s experiment demonstrated that supplementing broiler chickens with a mixture of 12 strains of Lactobacillus had a positive impact. By reducing the total cholesterol of serum, LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, and abdominal fat, it improved FCR and growth performance (Kalavathy et al., 2003). Comparing control birds to those treated with postbiotics and inulin, Kareem predicted a decrease in drip loss and increased the CIE L* of breast muscle. Most carcass attributes, shear force, and cooking loss did not differ between treatments (Kareem et al., 2015).
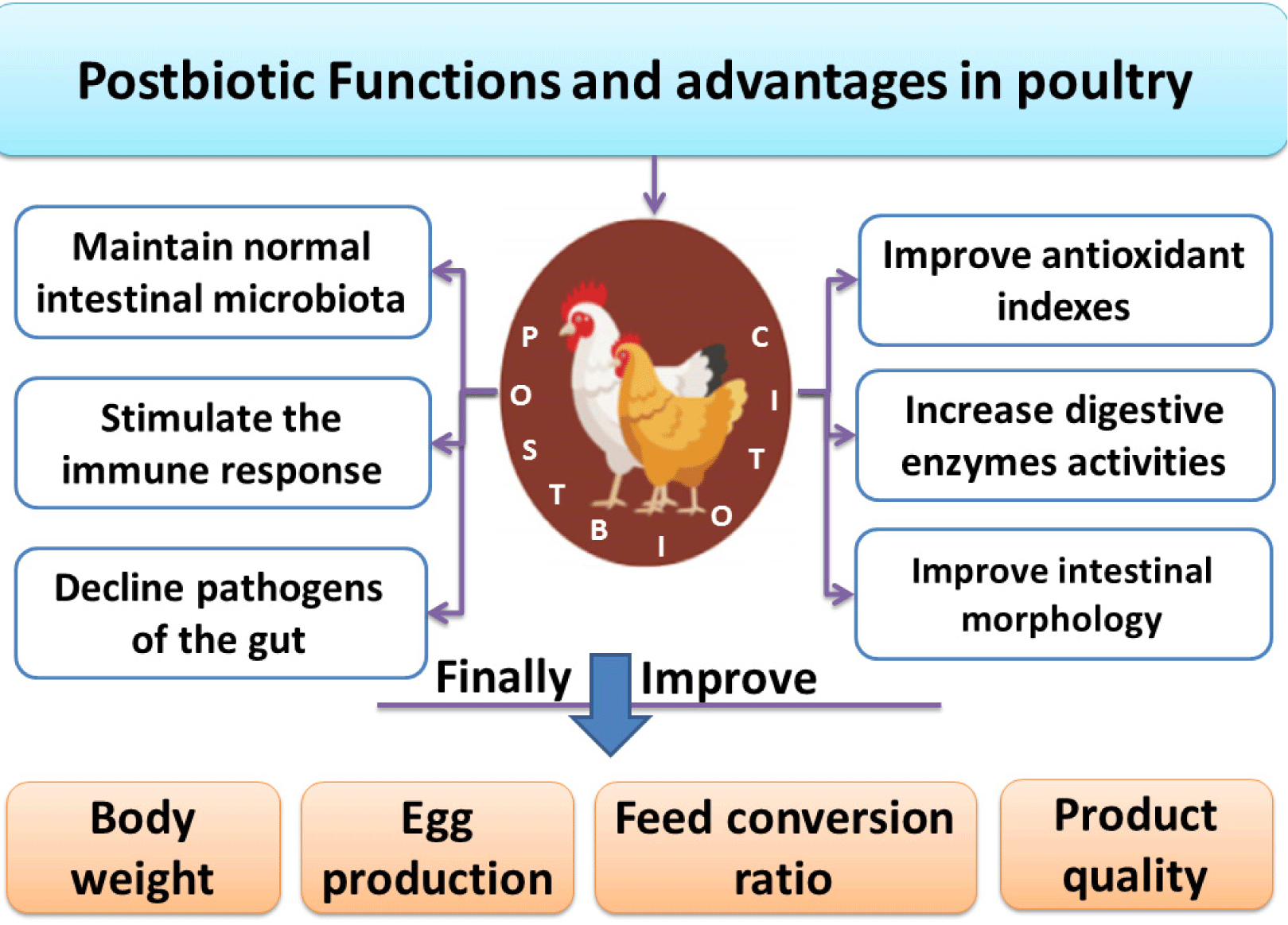
As a new feed additive in quail feed, postbiotics can be considered the most effective replacer for AGPs. By modulating the gut microbiota, Lactobacillus animalis derived from postbiotics can improve performance and promote quail health. It is possible to balance the gut microbiota of quails by feeding them postbiotic liquid instead of antibiotics (Kareem, 2020). Within the caeca of commercial layers, Salmonella Enteritidis can be reduced by the addition of probiotics derived from S. cerevisiae fermentation in feed, which could serve as preharvest food safety barriers. The addition of SCFP in layer’s feed can help in the decline of Salmonella Enteritidis within commercial laying hens ceca. It can also serve as an additional preharvest barrier for the safety of food (Gingerich et al., 2021). Thus, Humam et al. (2019) concluded that in broilers, compared to control groups, postbiotics substantially increased total Lactobacilli counts and other beneficial bacteria but reduced E. coli, Salmonella, and Enterobacteriaceae counts. Probiotics, prebiotics, and postbiotics supplementation improve enzyme activity and nitrogen utilization in poultry, which reduces ammonia output. Postbiotics enhance feed efficiency and reduce bird sickness and mortality, reducing the environmental impact of chicken production (Zhang and Kim, 2014). Prebiotics and postbiotics can lessen the ecological implications of chicken production by improving feed efficiency and reducing dung output. Feed is the biggest energy user and emitter in poultry production. Broilers supplemented with probiotics have reduced ammonia emissions, an unpleasant pollutant that poses environmental risks (Jeong and Kim, 2014; Zhang and Kim, 2014). Postbiotics reported many functions and advantages in poultry, as shown in Fig. 2. Different authors performed experiments by using different inclusion levels of postbiotics, as given below in Table 1.
| S. No. | Postbiotic strain and dose | Species/age | Results | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Postbiotic Culbac® (fermentation product produced by Lactobacillus acidophilus species) Starter diet: 1 kg/ton, grower and finisher diet: 0.5 kg/ton in dry form and in the aqueous form, 4 mL/L drinking water |
Broiler chicks 5 wk |
- Postbiotic compound either in a dry and/or an aqueous form improved the health, performance, and immunity of colisepticaemic broiler chickens | Abd El-Ghany et al. (2022) |
| 2 | 0.2% postbiotic and 0.2% paraprobiotic | Broiler chicks 5 wk |
- Paraprobiotics and postbiotics revealed a positive influence on the microbiota by supporting the decrease of harmful microbes like the Proteobacteria while increasing beneficial microbes like the Firmicutes. - Paraprobiotics or postbiotics can positively affect the colon mucosa microbiota. |
Danladi et al. (2022) |
| 3 | 0.1% Lactiplantibacillus plantarum postbiotics | Broiler chicks 6 wk |
- L. plantarum postbiotic increased growth performance and mucin production, postbiotic ameliorated immune status and tight junction permeability - It improved beneficial bacteria colonization and gut health |
Chang et al. (2022) |
| 4 | 1.0% inulin+different levels of postbiotic (0.15%, 0.30%, 0.45%, 0.60%) | Broiler chicks 6 wk |
- The level of 1.0% inulin+0.15% postbiotic had the optimal level - Combinations of inulin and postbiotic increased body weight and immune response |
|
| 5 | 0.2%, 0.4%, and 0.6% postbiotic derived from Lactobacillus animalis | Quails 5 wk |
- Postbiotic 0.4% increased body weight and body weight gain - Postbiotic promoted the health of quails by modulating gut microbiota |
Kareem (2020) |
| 6 | Postbiotic product (1 ounce/gallon of fresh water) | Broiler chicks 3 wk |
- Postbiotic administration boosts immunomodulatory responses in the gut. - Postbiotic reduces disease pathogenesis following challenge. |
Johnson et al. (2019) |
| 7 | 0.2%, 0.4%, 0.6%, and 0.8% cell-free supernatant (postbiotic: L. plantarum RI11) | Broiler chicks 6 wk |
- Postbiotic RI11 augmented plasma glutathione, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase, and boosted zonula occludens-1, mucin 2, IL-10, and mRNA expression. - Postbiotic RI11 declined heat shock protein 70 mRNA expression and plasma tumor necrosis factor alpha, IL-8, alpha-1-acid glycoprotein. |
Humam et al. (2019) |
| 8 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermentation based postbiotic (SCFP) at 1.5 kg/ton (0–21 d) and 1.0 kg/ton (22–32 d) | Layer pullets | - SCFP decreased Salmonella Enteritidis in the Layer Pullet’s Ceca. - SCFP decreased the proportion of ceca with enumerable S. Enteritidis. |
Gingerich et al. (2021) |
| 9 | L. plantarum RG14 and RI11 strains/cell free supernatant | Broilers | - Positively enhanced immune response - Reduced the proinflammatory responses, - Reduced (p<0.05) Enterobacteriaceae count. |
Kareem et al. (2016) |
| 10 | L. plantarum RI11, RG14, and RG11 strains/cell free supernatant (postbiotic component) | Laying hens | - Reduced plasma and yolk cholesterol concentrations | Choe et al. (2012) |
| 11 | L. plantarum strains/cell free supernatant (postbiotic component) | Laying hen and broilers | - Reduced faecal Enterobacteriaceae | |
| 12 | L. plantarum strains/cell free supernatant (postbiotic component) | Broilers | - Higher growth hormone receptor (GHR) messenger RNA (mRNA) | Thanh et al. (2009) |
Beneficial Effects of Postbiotic on Meat and Egg Quality
Because of the use of postbiotics, it is now possible to raise animals, including poultry, without the use of antibiotics, which has resulted in the production of chicken products such as meat and eggs that are both safe and of high quality all over the world. Poultry is raised specifically for the purpose of producing meat all over the world because it is tender, low in fat content, and has a relatively quick production cycle (Haque et al., 2020). Results from Choe et al. (2012) which showed that the plasma cholesterol concentration decreased in eggs that were administered postbiotics. Postbiotics, specifically RI11, have the potential to be used as a substitute for antibiotics and natural sources of antioxidants in heat-stressed broilers. Postbiotics have also been shown to raise breast meat pH, while simultaneously decreasing shear force and CIE L* (Humam et al., 2019). With the addition of postbiotics to their diets, broiler chickens showed both an improvement in the quality of the meat they produced and a decrease in their plasma cholesterol levels (Choe et al., 2012; Loh et al., 2013).When compared to antibiotics, the effects that postbiotics and inulin had on the quality of the meat were beneficial (Kareem et al., 2015). Poultry replaces vital food animals worldwide, boosting food security, protein supply, and employment (Reuben et al., 2021). This study showed that laying hens benefit from postbiotic metabolite combinations from Lactobacillus plantarum strains. All metabolite combinations increased hen-day egg output (Loh et al., 2014). As the world’s population grows, so does the demand for meat and eggs. Probiotics/postbiotics may improve their quality. Poultry farming focuses on safe and healthy products. Probiotics improve animal productivity and quality (Hussein et al., 2020).
Conclusion
It is evident from this article that due to the beneficial microbial influence of postbiotics on health, they can be used in food, therapeutic approach, and as AGP replacers when administered in adequate amounts in poultry. Poultry postbiotics improve health, nutrition, and production. They may replace poultry antibiotic growth boosters and other synthetic chemicals. Their gut microbiome, immune system modulation, and pathogen inhibition will ensure safer meat, egg, and eco-friendly production, as well as enormous illness treatment cost reduction and bird loss prevention. Sustainable poultry production with postbiotics will guarantee global food security and safety. There is a need for further research to prevent antibiotic use for disease prevention and to limit the presence of resistant effects among pathogenic bacteria by using postbiotics. Future research on prebiotic-postbiotic interaction may improve quality of the meat and performance or uncover new benefits.